Surface Chemistry - Classifications of Colloidal solution | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Surface Chemistry
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 10 : Surface Chemistry
Classifications of Colloidal solution
Classifications of Colloidal solution
Probably the most important colloidal systems have dispersed phase as
solid and the dispersion medium as liquid.
If the dispersion medium considered is water, then the colloids are
referred as hydrosols or aquasols.
If the dispersion medium is an alcohol, the colloid is termed as
alcosol, and if benzene is the dispersion medium, it is called as benzosol.
One more type of classification is based on the forces acting between
the dispersal phase and dispersion medium.
In lyophillic colloids definite attractive force or affinity exists
between dispersion medium and dispersed phase. Examples: sols of protein and
starch. They are more stable and will not get precipitated easily. They can be
brought back to colloidal solution even after the precipitation by addition of
the dispersion medium.
In a lyophobic colloids, no attractive force exists between the
dispersed phase and dispersion medium. They are less stable and precipitated
readily, but can not be produced again by just adding the dispersion medium.
They themselves undergo coagulation after a span of characteristic life time.
They are called irreversible sols
examples: sols of gold, silver, platinum and copper.
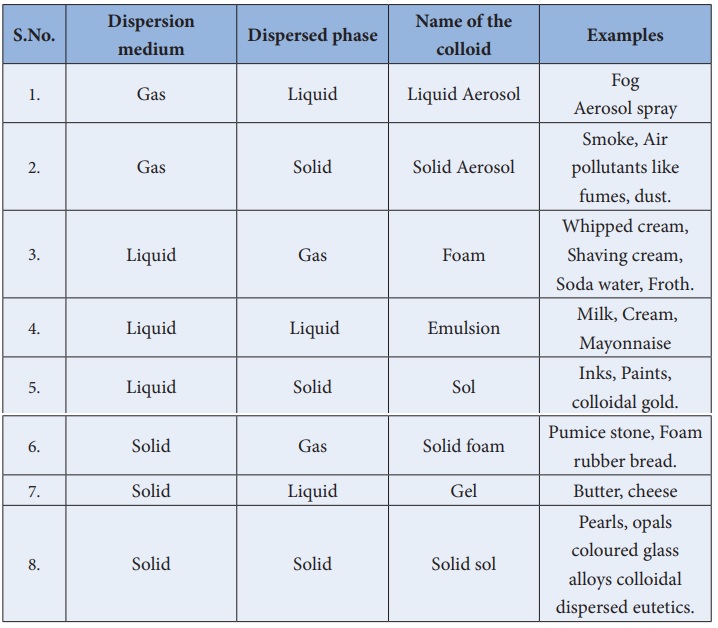
The following table lists the types of colloids based on the physical
states of dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
Classification of colloids based on the physical state of
dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
Related Topics