Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Classification, Factors affecting of adsorption of gases on solids
ADSORPTION
Adsorption
is a surface phenomenon. It is observed at the surface of the solution.
Adsorption is a phenomenon of concentration of substance on the surface of a
liquid or solid.
'The
condition in which concentration of a substance in the interfacial layers
between two phases is greater than in the bulk of either phase, then the
substance is said to be adsorbed at the interface and the phenomenon is known
as adsorption'.
The
process of adsorption of gases by solids is a common phenomenon. The charcoal
specially coconut charcoal has a great capacity of the adsorption of gases.
Silica gel is also utilised for the adsorption of number of gases. The solid
that takes up gas or vapour or solute from a given solution is called adsorbent and the solute or gas which
is held to surface of solid is known as
adsorbate.
Classification of adsorption of gases on solids
The
adsorption of gases on solids has been divided in to two types based on the
nature of forces holding the gas molecules to the solids.
i.
Physical adsorption (or) Vander waal's
adsorption
ii.
Chemical adsorption (or) chemisorption.
1. Physical
adsorption
This
adsorption is due to the operation of forces between solid surface and the
adsorbate molecules that are similar to vander waal's forces between molecules.
These forces are generally undirected and relatively non specific. Physical
adsorption can also be defined as that type of adsorption where physical forces
hold the gas molecules to the solids.
2. Chemical adsorption
Chemical
adsorption is defined as a type of adsorption in which chemical bonds serve the
function of holding gas molecules to the surface. It occurs due to the stronger
binding forces, comparable with those leading to formation of chemical
compounds. It is generally an irreversible process.
The
main differences can be summarised as follows:-
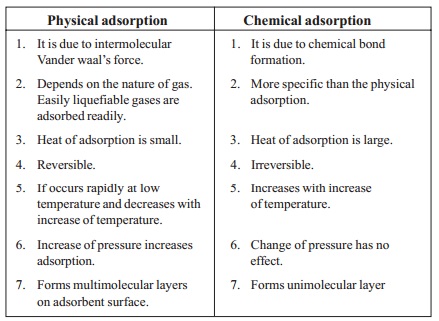
Physical
adsorption
1. It
is due to intermolecular Vander waal's force.
2. Depends
on the nature of gas. Easily liquefiable gases are adsorbed readily.
3. Heat
of adsorption is small.
4. Reversible.
5. If
occurs rapidly at low temperature and decreases with increase of temperature.
6. Increase
of pressure increases adsorption.
7. Forms
multimolecular layers on adsorbent surface.
Chemical
adsorption
1. It
is due to chemical bond formation.
2. More
specific than the physical adsorption.
3. Heat
of adsorption is large.
4. Irreversible.
5. Increases
with increase of temperature.
6. Change
of pressure has no effect.
7. Forms unimolecular layer
Factors affecting adsorption
The magnitude of gaseous adsorption
depends upon the following factors:
1.
Temperature
2.
Pressure
3.
Nature of the gas and
4.
Nature of the adsorbent.
Effect of temperature and pressure
Adsorption
is invariably accompanied by evolution of heat. Therefore, in accordance with
Le chatelier's principle, the magnitude of adsorption increases with decrease
in temperature. Further, since adsorption of a gas leads to decrease of
pressure, the magnitude of adsorption increases with increase in pressure.
Thus, decrease of temperature and increase of pressure both tend to cause
increase in the magnitude of adsorption of a gas on a solid.
Nature of the gas
It
is observed that the more readily soluble and easily liquefiable gases such as
ammonia, chlorine and sulphur dioxide are adsorbed more than the hydrogen,
nitrogen and oxygen. The reason is that Vander waal's or intermolecular forces
which are involved in adsorption are more predominant in the former than in the
latter.
Nature of the adsorbent
Adsorption is a surface
phenomenon. Therefore, the greater the surface area per unit mass of the
adsorbent, the greater is its capacity for adsorption under the given
conditions of temperature and pressure.
Related Topics