Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Characteristic parameters and seven classes of unit cell
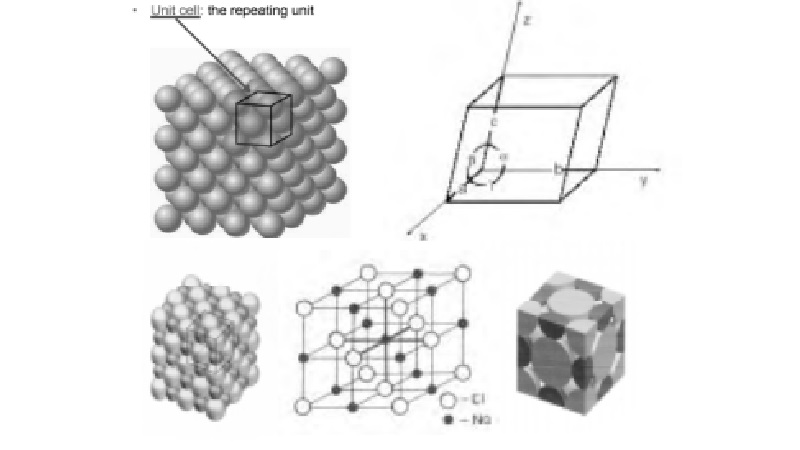
Unit Cell
Crystals
are built up of a regular arrangement of atoms or ions in three dimensions. The smallest structure of which the
crystalline solid (or crystal) is
built by its repetition in three dimensions is called as unit cell. A unit cell may be considered as the
brick of a wall depends upon the shape of brick, the shape of crystal also
depends upon the shape of unit cell. Therefore, a unit cell is the fundamental
elementary pattern of a crystalline solid. The characterization of the crystal
involves the identification of its unit cell.
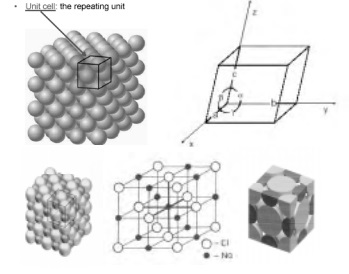
Characteristic parameters of unit cell
1.
Crystallographic axes: The lines drawn parallel
to the lines of intersection of any three faces of the unit cell which do not
lie in the same plane are called crystallographic axes.
2.
Interfacial angles: The angles between the three
crystallographic axes are known as interfacial angles.
3.
Primitives: The three sides a, b and c (as shown
in figure ) of a unit cell are known as primitives or characteristic
intercepts.
Crystallographic axes : OX, OY, OZ Interfacial angles : a, b, g
Primitives (distances) : a, b, c
The unit cell is characterized by the distances a, b and c and angles a, b & g.
The size
(edge length) of a unit cell depends on the size of the atoms or ions and their
arrangement. Because a unit cell is representative of the entire structure, the
ratio of ions in the unit cell is the same as the ratio in the overall
structure.
There
are seven classes
of unit cells.
1.
Cubic ,
2.
Triclinic,
3. Monoclinic,
4. Orthorhombic,
5. Tetragonal,
6.Hexagonal and
7. Rhombohedral.
Packing arrangement variations exist in each of the classes, yet here we
will only explore the cubic system because it is the simplest.
Cubic unit cells
Three types of cubic unit cells are discussed in this chapter. Each unit
cell is defined by one type of atom. Consequently, whichever atom you choose
when defining that unit cell is the only atom used in defining the unit
cell. (Ignore all other types.)
Simple cubic
The most
simple unit cell is known as a simple cubic unit cell. This is where one atom
occupies each of the eight corners of a cube. The distance from atom to atom
along the lattice is the same in every direction, and the angle between each of
axes is 90 o .
Body-centred cubic
The next unit cell is known as the body-centred cubic. In this form of
crystal, there is an atom at each corner of the unit cell and also there is an
additional atom in the center of the cube. This packing can fit more atoms into
less space than the simple cubic unit cell.
Face-centred cubic
A slightly more tightly packed unit cell is the
face-centred cubic unit cell. In this form of crystal, there is an atom at each
corner of the unit cell. And there is an atom at the center of each of the six
faces of the cubic unit cell. This crystal packing form has an even higher
density than the body-centred cubic unit cell.
Atoms or ions are shared between adjacent unit
cells. The lattice position of the atom or ion determines the number of unit
cells involved in the share. There are four different lattice positions an atom
or ion can occupy.
Body: Not
shared
Face:
Shared by two unit cells
Edge:
Shared by four unit cells
Corner:
Shared by eight unit cells.
Sodium chloride crystal
Space
lattice of sodium chloride is known to consist of a face-centered cubic lattice
of Na+ ions interlocked with a similar lattice of Cl-ions.
A unit cell of this combined lattice is shown in figure. This unit cell repeats
itself in three dimensions throughout the entire crystal. The yellow spheres
indicate chloride ions and red spheres represent sodium ions. The lattices are
constituted entirely by ions are known as ionic
lattices. All electrovalent
compounds show such lattices.
There are
four units of NaCl in each unit cube with atoms in the positions
Cl: 0 0 0; ½½0; ½0½; 0½½;
Na: ½½½; 00½; o½0; ½00;
As will be seen figure, the unit cell of sodium chloride consists of 14
chloride ions and 13 sodium ions. Each chloride ion is surrounded by 6 sodium
ions and similarly, each sodium ion is surrounded by 6 chloride ions.
Notice that the particles at corners, edges and faces do not lie wholly
within the unit cell. Instead these particles are shared by other unit cells. A
particle at a corner is shared by eight unit cells, one at the centre of face
is shared by two and one at the edge is shared by four. The unit cell of sodium
chloride has 4 sodium ions and 4 chloride ions as shown below;
No. of Sodium ions
12 (At edge centers) x (1/4) + 1 ( At body center) x 1
=Ncc / 4 + Nb / 1 + Nf / 2 + Nc / 8 = = 12 x ¼ + 1x 1 =3 + 1 =4
No. of Chloride ions
8 (At corners) x (1/8) + 6 ( At face centre) x (1/2 )
8 x (1/8) + 6 x (1/2) =1+ 3 = 4
Thus, number of NaCl units per unit cell is 4.
The sodium chloride structure is also called rock-salt structure.
Representative crystals having the NaCl arrangements includes: LiH, NaI,
KCl, RbF, RbI, PbS etc.
Cesium Chloride structure
The cesium chloride, CsCl, structure has body-centred cubic system and is shown in figure. The body-centred cubic arrangement of atoms is not a close packed structure. There is one molecule per primitive cell, with atoms at the corners (000) and body-centred positions 1/2 1/2 1/2 of the simple cubic space lattice.
1. The Cl- ions are at the corners of a cube where as Cs+ ion is at the centre of the cube or vice versa
2. Each Cs+ ion is connected eight Cl- ions and each Cl- ion is connected eight Cs+ ions i.e., 8:8 coordination. Thus each atom is at the center of a cube of atoms of the opposite kind, so that the coordination number is eight.
The unit cell of cesium chloride has one Cs+ ion and one Cl- ion as shown below
No. of Cl- ions
8(At corners) x 1/8 (common to eight unit cell)
8 x 1/8 = 1
No. of Cs+ ion = 1 (At the body center) x 1
= 1 x 1 = 1
Thus number of CsCl units per unit cell is 1.
Representative crystals having the CsCl arrangements include: CsBr, CsI, TlBr, TlI, NH4Cl etc.
Related Topics