Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Calculation of ionic radii - Pauling's Method, Slater rules
Calculation of ionic radii
Pauling's Method
Pauling has calculated the radii of the ions on the
basis of the observed internuclear distances in four crystals namely NaF, KCl,
RbBr and CsI. In each ionic crystal the cations and anions are isoelectronic
with inert gas configuration.
NaF crystal : Na+ - 2, 8 F- - 2, 8 Ne type configuration
KCl crystal : K+ - 2, 8, 8 Cl- - 2, 8, 8 Ar type configuration
Further the following two
assumptions are made to assign the ionic radii.
i) The cations and anions of an ionic crystal are assumed to be in
contact
with each other and hence the sum of their radii will be equal to the
inter nuclear distance between them.
r(C+) + r(A-) = d (C+-A-)
where
r(C+)
- radius of
cation, C+ r(A-)
-
radius of anion, A-
d(C+-A-)
- internuclear distance between C+ and A- ions in C+A- ionic crystal
ii) For a given noble gas configuration, the radius of
an ion is inversely proportional to its effective nuclear charge. i.e.
r(C+ ) á = 1/ Z (C+ )
r(A- ) á = 1/ Z (A- )
where,
Z*(C+)
& Z*(A-) are the
effective nuclear charges of cation (C+) and anion (A-)
respectively. On combining
r(C+ ) / r(A- ) = Z*(A- ) / Z*(C+ )
Hence the above two equations (1) & (4) can be used
to evaluate the
values of r(C+) and r(A-) provided that the values of d(C+-A-), Z*(C+) and Z*(A-) are known.
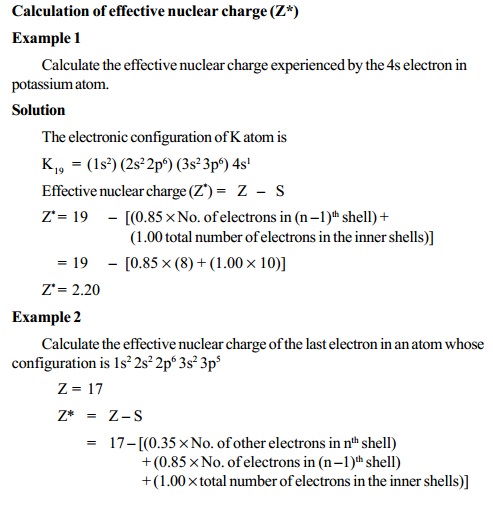
Slater rules
The value of screening constant (S) and effective
nuclear charge (Z*)
can
be calculated by using Slater's rules. According to these rules the
value of "S" for a given electron is estimated as follows.
i) Write down the complete electronic configuration of
the element and divide the electrons into the following orbital groups
starting from the inside of the atom.
(1s) : (2s, 2p) : (3s, 3p) : (3d) : (4s, 4p) :
(4d) : (4f) : (5s, 5p) : (6s, 6p) .......etc.
ii) Select the electron for which the value of S is to be
calculated. For this calculation add up the contributions to S for the other
electrons according to the following rules.
Contribution to S for each electron of this
type
Type of electron
1.
All electrons in groups outside the electron chosen - 0
2.
All other electrons in the same group as the chosen one (n) - 0.35 (or 0.30 for 1s electron)
3. All electrons in shell immediately inside (n-1) - 0.85
All electrons further inside - 1.00

Related Topics