Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 1 : Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations
Brief questions and answers: Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations
Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations
Answer the following questions
26) Define relative atomic mass.
The
relative atomic mass is defined as the ratio of the average atomic mass factor
to the unified atomic mass unit.
Relative
atomic mass (Az) :
=
Average mass of the atom / Unified atomic mass
27) What do you understand by the term mole.
One
mole is the amount of substance of a system, which contains elementary
particles as there are atoms in 12g of C-12 isotopes
28) Define equivalent mass.
Gram
equivalent mass of an element, compound or ion is the mass that combines or
displaces 1.008 g hydrogen (or) 8g oxygen or 35.5g chlorine.
29) What do you understand by the term oxidation number.
Oxidation
number is defined as the imaginary charge left on the atom when all other atoms
of the compound have been removed in their usual oxidation states.
30) Distinguish between oxidation and reduction.

Oxidation
1.
Additional of Oxygen
2.
Removal of Hydrogen
3.
Loss of Electron
4.
Increases in Oxidation number
Reduction
1.
Removal of Oxygen
2.
Additional of Hydrogen
3.
Gain of Electron
4.
Decreases in Oxidation number
31) Calculate the molar mass of the following compounds.
i. urea [CO(NH2)2]
ii. acetone [CH3COCH3]
iii. boric acid [H3BO3]
iv. sulphuric acid [H2SO4]
(i)
urea [CO(NH2)2]
N
= 2 × 14 = 28
H
= 4 × 1 = 4
C
= 1 × 12 = 12
O
= 1 × 16 = 16
====
60
=====
Molar
mass of urea : 60g mol−1
(ii)
acetone [CH3COCH3]
C
= 3 × 12 = 36
H
= 6 × 1 = 6
O
= 1 × 16 = 16
=====
58
=====
Molar
mass of acetone = 58g mol−1
(iii)
boric acid [H3BO3]
B
= 1 × 11 = 11
H
= 3 × 1 = 3
O
= 3 × 16 = 48
=========
62
=========
Molar
mass of Boricacid : 62g mol−1
(iv)
sulphuric acid [H2SO4]
S
= 1 × 32 = 32
H
= 2 × 1 = 2
O
= 4 × 16 = 64
==========
98
==========
Molar
mass of H2SO4 = 98g mol−1
32) The density of carbon dioxide is equal to 1.965 kgm-3 at 273 K and 1 atm pressure. Calculate the molar mass of CO2.
Given:
The
density of CO2 at 273K and
1
atm pressure = 1.965 kgm−3
Molar
mass of CO2 = ?
At
273K and 1 atm pressure,
1
mole of CO2 occupies a volume of 22.4l
Mass
of 1 mole of CO2 = ( l.965K.g /1m3 ) × 22.4L
=
[ 1.965 × 103g × 22.4 × 10−3m3 ] / 1m3 =
44.01 g
Molar mass of CO2 = 44.01 g mol−1
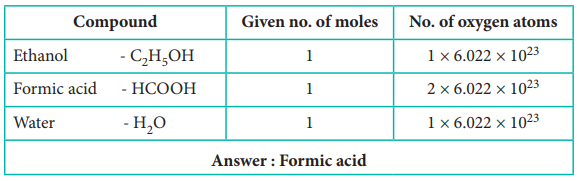
33) Which contains the greatest number of moles of oxygen atoms
i) 1 mol of ethanol
ii) 1 mol of formic acid
iii) 1 mol of H2O
Answer:
34) Calculate the average atomic mass of naturally occurring magnesium using the following data
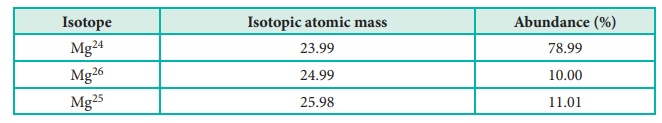
Answer:
Solution:
Average
atomic mass =
[
(78.99 × 23.99) + (10 × 24.99) + (11.01 × 25.98) ] / 100
=
2430.9 / 100 = 24.31u
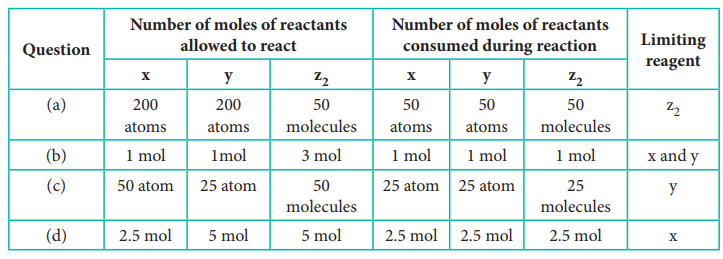
35) In a reaction x + y + z2 → xyz2 identify the Limiting reagent if any, in the following reaction mixtures.
(a) 200 atoms of x + 200 atoms of y + 50 molecules of z2
(b) 1mol of x + 1 mol of y+3 mol of z2
(c) 50 atoms of x + 25 atoms of y+50 molecules of z2
(d) 2.5 mol of x +5 mol of y+5 mol of z2
Answer:
Reaction : x + y + z2 → xyz2
36) Mass of one atom of an element is 6.645 x 10-23 g. How many moles of element are there in 0.320 kg.
Answer:
Solution:
Given
: mass of one atom = 6.645× 10−23 g
∴Mass of 1
mole of atom = 6.645 × 10−23g × 6.022 ×1023 = 40g
∴mole number of moles of element in 0.320 kg = [1 mole / 40 g ] × 0.320kg = 8 mols
37) What is the difference between molecular mass and molar mass? Calculate the molecular mass and molar mass for carbon monoxide.

Molecular
mass
l.
The relative molecular mass is defined as the ratio of the mass of a molecule
to the unified atomic mass unit.
2.
The relative molecular mass of any compound can be calculated by adding the
relative atomic masses of its constituent atoms.
3.
It is expressed in 'u'
Molecular
mass of CO = 12 + 16 = 28 u
Molar
mass
1.
Molar mass is defined as the mass of a one mole of a substance.
2.
molar mass of a compound is equal to sum of the relative masses of its
constituents.
3.
It is expressed in gmol−1
Molar
mass of CO = 28 gmol−1
38) What is the empirical formula of the following ?
i) Fructose (C6H12O6) found in honey
ii) Caffeine (C8H10N4O2) a substance found in tea and coffee.
Answer:

Fructose
Empirical formula : C6H12O6
Molecular formula : CH2O
Caffeine
Empirical formula : C8H10N4O2
Molecular formula : C4H5N2O
39) The reaction between aluminium and ferric oxide can generate temperatures up to 3273 K and is used in welding metals. (Atomic mass of AC = 27 u Atomic mass of 0 = 16 u)
2Al + Fe2O3 → Al2O3 +2Fe; If, in this process, 324 g of aluminium is allowed to react with 1.12 kg of ferric oxide.
i) Calculate the mass of Al2O3 formed.
ii) How much of the excess reagent is left at the end of the reaction?
Answer:
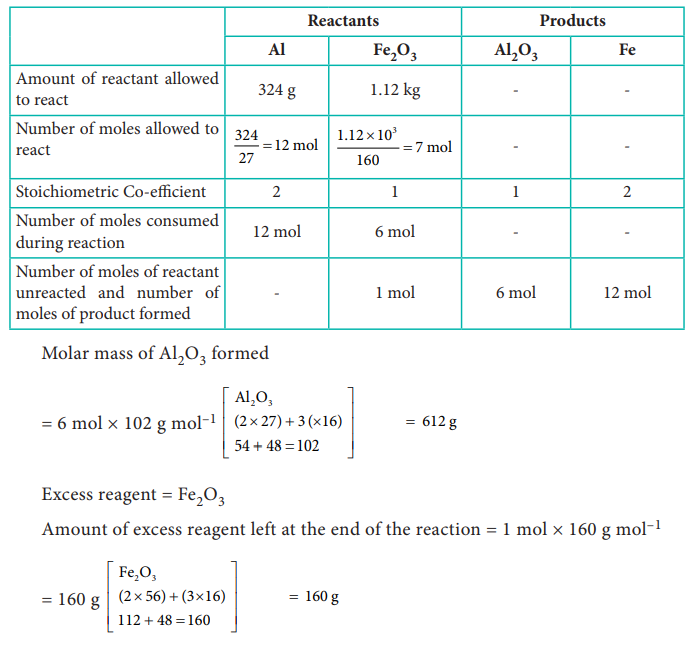
40) How many moles of ethane is required to produce 44 g of CO2 (g) after combustion.
Answer:
Solution:
Balanced
equation for the combustion of ethane
C2H6+
7/2O2 → 2CO2+ 3H2O
To
produce 2 moles of CO2, 1 moles of ethane is required
∴To
produce 1 mole 44 g of CO2 required
number
of moles of ethane = [ 1 mol ethane / 2 mole CO2 ] × 1 mol CO2
=
½ mole of ethane
= 0.5 mole of ethane
41) Hydrogen peroxide is an oxidising agent. It oxidises ferrous ion to ferric ion and reduced itself to water. Write a balanced equation.
Answer:
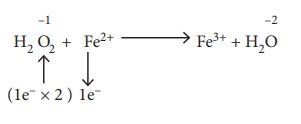
1 H2O2 + 2Fe2+ → Fe3+ + H2O
⇒H2O2 + 2Fe2+ + 2H+ → 2Fe3+ + 2H2O
42) Calculate the empirical and molecular formula of a compound containing 76.6% carbon, 6.38 % hydrogen and rest oxygen its vapour density is 47.
Answer:
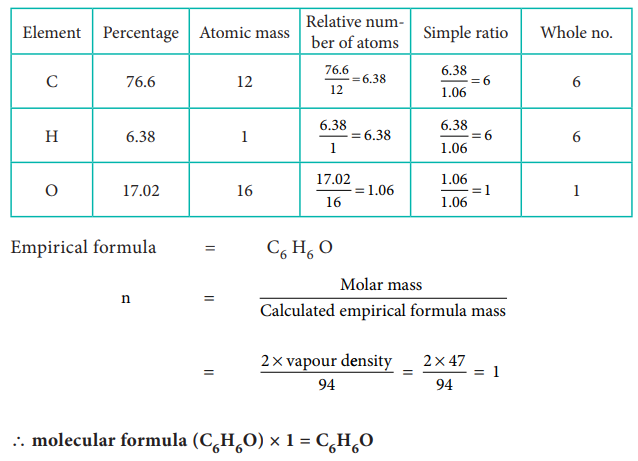
43) A Compound on analysis gave Na = 14.31% S = 9.97% H= 6.22% and O= 69.5% calculate the molecular formula of the compound if all the hydrogen in the compound is present in combination with oxygen as water of crystallization. (molecular mass of the compound is 322).
Answer:
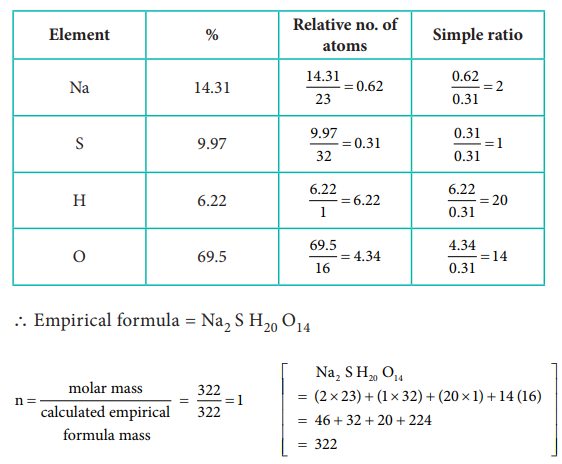
Molecular formula = Na2 S H20 O14
Since all the hydrogen in the compound present as water
∴ Molecular formula is Na2 SO4 . 10H2O
44) Balance the following equations by oxidation number method
i) K2Cr2O7 + KI + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 +I2+H2O
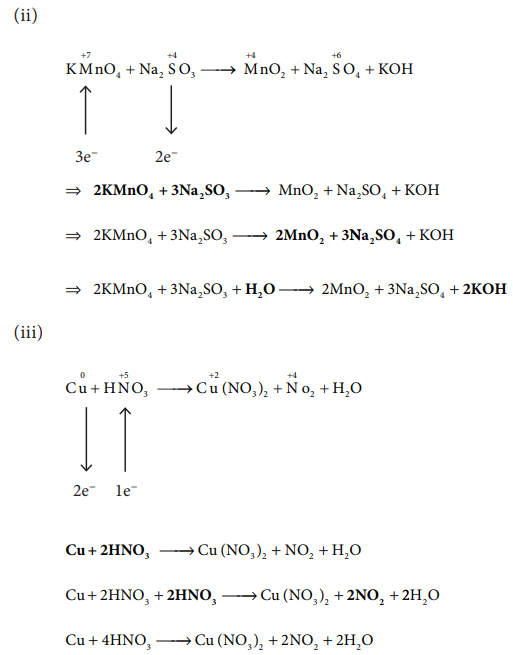
ii) KMnO4 + Na2SO3 → MnO2 + Na2SO4 + KOH
iii) Cu+ HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + NO2+ H2O
iv) KMnO4+H2C2O4 + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + MnSO4 + CO2 + H2O
Answer:
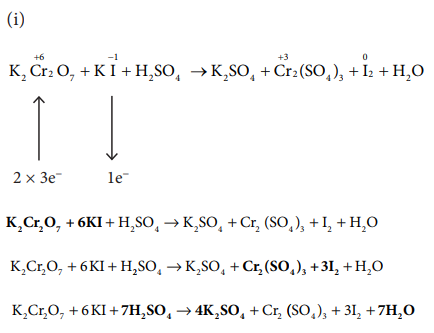
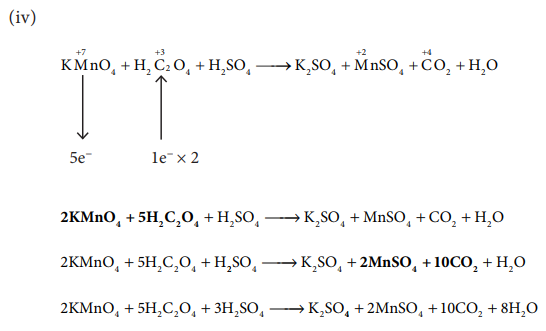
45) Balance the following equations by ion electron method.
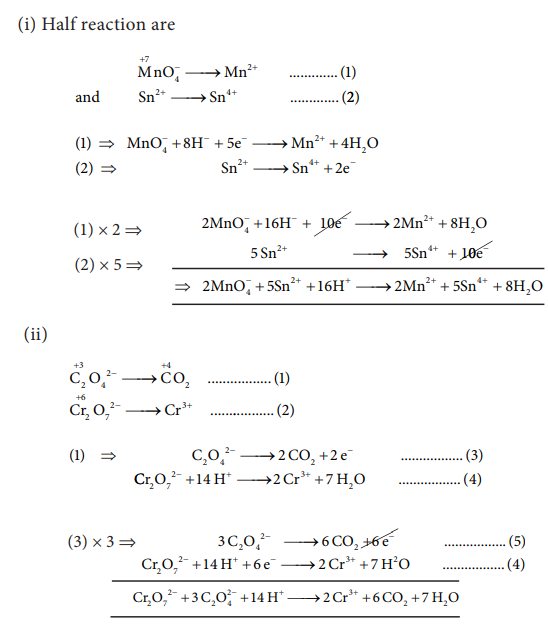
i) KMnO4 + SnCl2+HCl → MnCl2 + SnCl4 + H2O + KCl
ii) C2O42_ + Cr2 O72_ → Cr3+ + CO2 (in acid medium)
iii) Na2S2O3 + I2 → Na2S4O6 + NaI ( in acid medium)
iv) Zn +NO3_ → Zn2+ + NO
Answer:
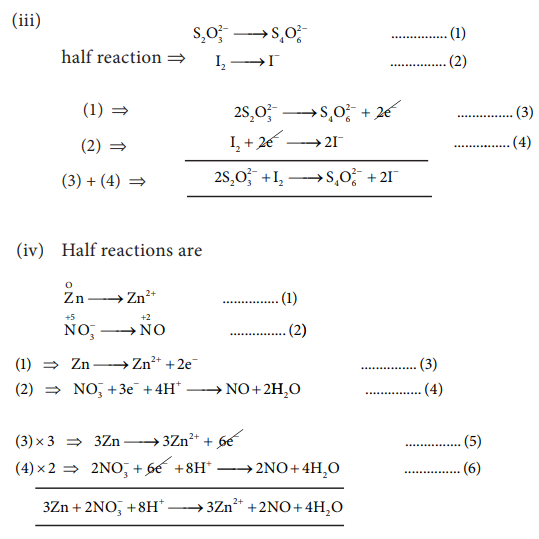
Related Topics