Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 1 : Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Chemical Calculations
Atomic Masses
Atomic
Masses
How much does an individual atom weigh? As atoms are too
small with diameter of 10–10 m and weigh approximately 10–27
kg, it is not possible to measure their mass directly. Hence it is proposed to
have relative scale based on a standard atom.
The C-12 atom is considered as standard by the IUPAC
(International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry), and it's mass is fixed as
12 amu (or) u. The amu (or) unified atomic mass is defined as one twelfth of
the mass of a Carbon-12 atom in its ground state.
i.e. 1 amu (or) 1u ≈ 1.6605 × 10–27 kg.
In this scale, the relative atomic mass is defined as the
ratio of the average atomic mass factor to the unified atomic mass unit.
Relative atomic mass (Ar)
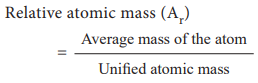
For example,
Relative atomic mass of hydrogen (Ar)H

Since most of the elements consist of isotopes that differ
in mass, we use average atomic mass. Average atomic mass is defined as the
average of the atomic masses of all atoms in their naturally occurring
isotopes. For example, chlorine consists of two naturally occurring isotopes 17Cl35
and 17Cl37 in the ratio 77 : 23, the average relative
atomic mass of chlorine is
= [ (35 × 77) + (37 × 23) ] / 100
= 35.46 u
Related Topics