Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Purification of Organic compounds: Crystallisation
Crystallisation
Crystallisation is carried out in four stages
(a) preparation of the solution of the substance in a suitable solvent (b)
filtration of the hot solution (c) crystallisation by cooling the hot filtrate
(d) isolation and drying of the purified substance.
a)
Preparation of the
solution : The powdered organic substance is taken
in a semi-micro round bottom flask and the solvent is added little by little
with constant stirring and heating till the amount added is just sufficient to
dissolve the solute, when the solution is just boiled. If the solvent is
non-inflammable, heating may be done on the wire gauze, while in the case of
inflammable solvents, heating should be done on a water bath.
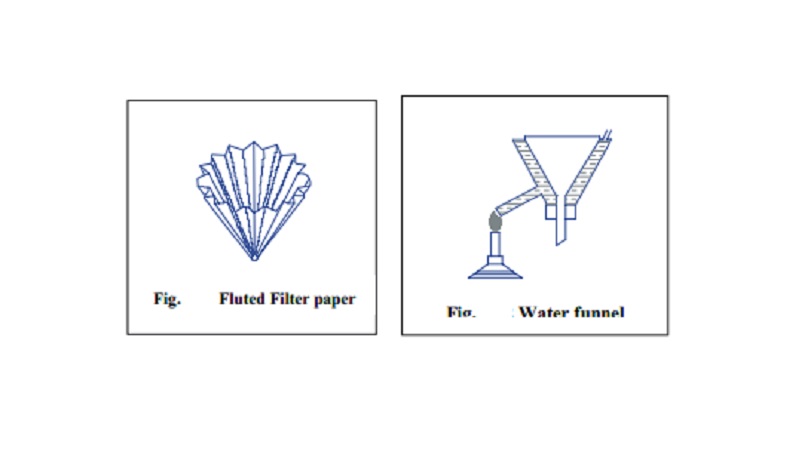
Filtration
of the Solution : The hot saturated solution obtained is filtrated
through a fluted filter paper placed in a hot water funnel.
c)
Crystallisation : When the filtration is over, the beaker containing the solution
is allowed to cool when pure crystals separate. Sometimes the crystals do not
separate due to super cooling of the solution. Crystallisation can be started
in such cases by scratching the sides of the vessel containing the solution
with a glass rod or seeding with a tiny crystal of the substances.
d)Isolation and drying of the purified crystals : The purified crystals are separated from the mother liquor by
filtration using Buchner funnel and a suction pump.
When the whole of the mother liquor has been drained off, the crystals
are washed with small amounts of cold solvent thrice. The crystals are then
transfered to a porous plate, pressed by using filter paper and then dried by
using infra-red light or by keeping in sunlight. If the crystals are coloured,
decolourisation is effected by using animal charcoal.
Fractional
Crystallisation
When the solubility of two substances in any solvent is not much
different from one another, then the two compounds can be separated by
fractional crystallisation, involving a series of repeated crystallisations.
For example, when a solution containing two substances A and B is subjected to
crystallisation, the slightly less soluble substances (say A) containing a
small amount of the other substance (B) crystallises out. The mother liquor
when subjected to crystallisation gives crystals of B containing a small amount
of A.
Now, if these crystals are subjected to
recrystallisation separately and the process is repeated number of times to get
pure A and pure B.
Related Topics