Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Discharge of electricity through gases at low pressure - Discovery of electrons
At atmospheric pressure, air and other gases
are poor conductors of electricity. This is because, they do not have free
charged particles. However, electric current may be passed through a gas if by
some mechanism, charged particles are produced in the gas. This can be done in
many ways, such as (i) by applying a large potential difference across a gas
column at very low pressure and (ii) by allowing X-rays to pass through the
gases.
The study of electric discharge through gases gives valuable
information regarding the structure of atoms. This has led to the discovery of
electrons by J. J. Thomson and later on, to the discovery of X-rays by
Roentgen.
Discharge of electricity through gases at low pressure - Discovery
of electrons
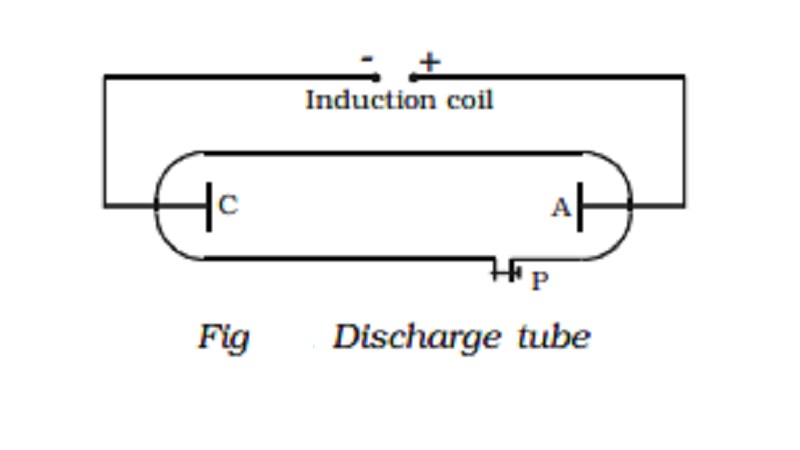
A discharge tube is an arrangement to study the conduction of electricity
through gases. It is a closed,
strong glass tube of length 50 cm
and diameter 4 cm, filled with a gas. Two metal electrodes C and A are fitted
inside the tube at the ends as shown in Fig. The side tube P is connected to a
high vacuum pump and a low pressure gauge. The electrodes C and A are connected
to the secondary of a powerful induction coil, which maintains a potential difference
of 50,000 V. The electrode C connected to the negative terminal of the
induction coil is called the cathode and the electrode A connected to the
positive terminal is called the anode.
When the pressure of the gas inside the
discharge tube is reduced by working the vacuum pump, to about 110 mm of Hg, no
discharge occurs through the tube. At a pressure of about 100 mm of Hg, the
discharge of electricity through the gas begins and irregular streaks of light
appear, accompanied by a crackling sound. As the pressure is reduced to the
order of 10 mm of Hg, the irregular streaks broaden out into a luminous column
extending from the anode, almost upto the cathode. This column is known as the
positive column. With further reduction in pressure to around 0.01 mm of Hg,
the positive column disappears and Crooke's dark space fills the whole tube. At
this stage, the walls of the glass tube fluoresce with green colour. This
greenish glow in the final stage of the gaseous discharge is found to be a
fluorescence of the glass produced by some invisible rays emanating from the
cathode (shown in the wrapper). These rays are called cathode rays and are
found to be electrons.
Related Topics