Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Nernst equation - Thermodynamics of a reversible cell
Thermodynamics of a
reversible cell
Nernst equation : Suppose the reaction occurring in a reversible
cell is represented by the equation
A + B < -- -- > C + D
The decrease in free energy, - DG,
accompanying the process is given by the well known thermodynamic equation
- DG = - D Go
- RT ln J
where - DGo is the decrease in free energy
accompanying the same process when all the reactants and products are in their
standard states of unit activity and J stands for the reaction quotient of the
activities of the products and reactants at any given stage of the reaction.
Substituting the value of J, we have
- D G = - DGo -
RT ln (aCxaD
/aAxaB )
If E is the E.M.F. of the cell in volts and the
cell reaction involves the passage of ' n'
faradays (i.e.,) nF coulombs, the electrical work done by the cell is in nFE
volt-coulombs or Joules. Hence free energy decrease of the system, - DG, is given by the expression
- DG = nFE
nFE
= - DGo - RT ln (aCxaD /aAxaB
)
nFE = - nFE o - RT ln (aCxaD /aAxaB )
E =Eo -
RT/nF ln (aCxaD
/aAxaB )
where Eo is the E.M.F. of the cell
in which the activity, or as an approximation, the concentration of each
reactant and each product of the cell reaction is equal to unity. Eo is known
as the standard E.M.F. of the cell.
E =Eo -
RT/nF ln (aCxaD
/aAxaB ) is often referred to as the
Nernst equation
Replacing activities by
concentrations, as an approximation, the Nernst equation may be written as
E =Eo - 2.303RT/nF
log K
where Eo
= standard electrode potential
R = gas constant
T = Kelvin temperature
n = number of electrons transferred in the half-reaction
F = Faraday of electricity
= equilibrium constant for
the half-cell reaction as in equilibrium law.
Calculation of Half-cell
potential
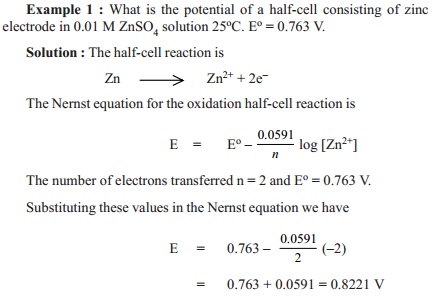
For an oxidation half-cell
reaction when the metal electrode M gives Mn+ ion,
M -- -- -- > Mn+ + ne-
the Nernst equation takes the form
E =Eo - 2.303RT/nF
log ( [Mn+] / [M] )
The activity of solid metal [M] is equal to
unity. Therefore, the Nernst equation can be written as
E =Eo - 2.303RT/nF
log ( [Mn+] )
Substituting the values of R, F and T at 25oC,
the quantity 2.303 RT/F comes to be 0.0591. Thus the Nernst equation can be written in its simplified form as
E =Eo - 0.0591 /n log ( [Mn+])
This is the equation for a half-cell in which
oxidation occurs. In case it is a reduction, the sign of E will have to be
reversed.
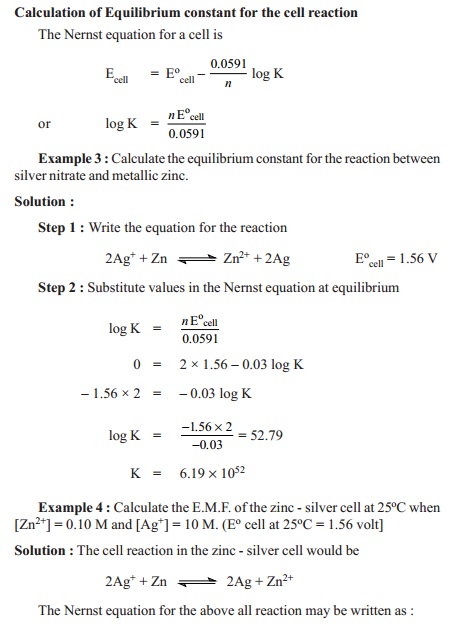
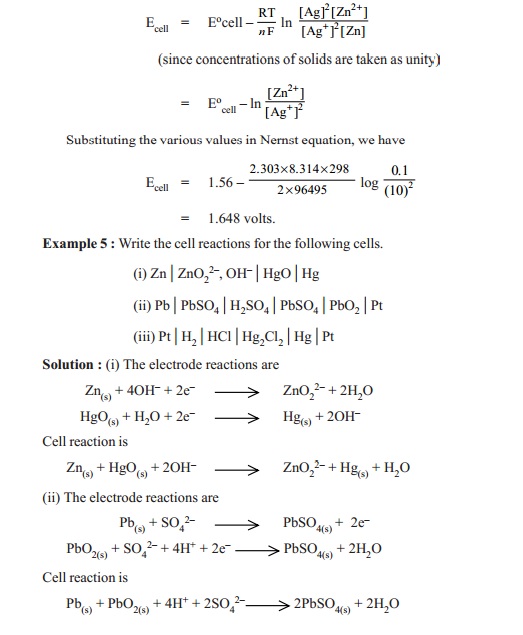
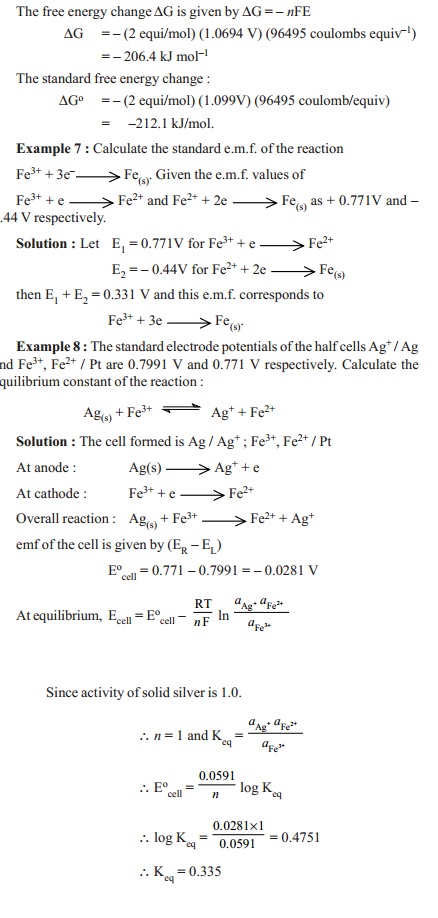
Calculation of Cell potential
The Nernst equation is applicable to cell
potentials as well. Thus,
Ecell =Ecello
- 0.0591 /n log ( [Mn+])
K is the equilibrium constant of the redox cell
reaction.


Related Topics