Chapter: Introduction to Human Nutrition: The Vitamins
Vitamers and dietary equivalence - Folic acid
Vitamers and dietary equivalence
As shown in Figure 8.14, folic acid consists of a reduced pterin linked to p-aminobenzoic acid, forming pteroic acid. The carboxyl group of the p-aminobenzoic acid moiety is linked by a peptide bond to the α-amino group of glutamate, forming pteroyl-glutamate (PteGlu). The coenzymes may have up to seven additional glutamate residues linked by γ-peptide bonds, forming pteroyldiglutamate (PteGlu2), pteroyltriglutamate (PteGlu3), etc., collectively known as folate or pteroyl polyglutamate conjugates (PteGlun).
“Folate” is the preferred trivial name for pteroyl-glutamate, although both “folate” and “folic acid” may be used as a generic descriptor to include various polyglutamates. PteGlu2 is sometimes referred to as folic acid diglutamate, PteGlu3 as folic acid trigluta-mate, and so on.
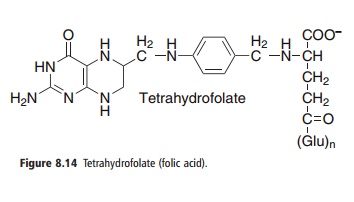
Figure 8.14 Tetrahydrofolate (folic acid).
Tetrahydrofolate can carry one-carbon fragments attached to N-5 (formyl, formimino, or methyl groups), N-10 (formyl), or bridging N-5–N-10 (methy-lene or methenyl groups). 5-Formyl-tetrahydrofolate is more stable to atmospheric oxidation than is folate, and is therefore commonly used in pharmaceutical preparations; it is also known as folinic acid, and the synthetic (racemic) compound as leucovorin.
The extent to which the different forms of folate can be absorbed varies; on average only about half of the folate in the diet is available, compared with more or less complete availability of the monoglutamate. To permit calculation of folate intakes, the dietary folate equivalent has been defined as 1 μg mixed food folates or 0.6 μg free folic acid. On this basis, total dietary folate equivalents = μg food folate + 1.7 × synthetic (free) folic acid.
Related Topics