Chapter: Introduction to Human Nutrition: The Vitamins
Vitamers and units of activity - Vitamin E
Vitamers and units of activity
Vitamin E is the generic descriptor for two families of compounds, the tocopherols and the tocotrienols (Figure 8.5). The different vitamers have different biological potency. The most active is α-tocopherol, and it is usual to express vitamin E intake in terms of mg α-tocopherol equivalents. This is the sum of mg α-tocopherol + 0.5 × mg β-tocopherol + 0.1 × mg γ-tocopherol + 0.3 × mg α-tocotrienol. The other vitamers have negligible vitamin activity.
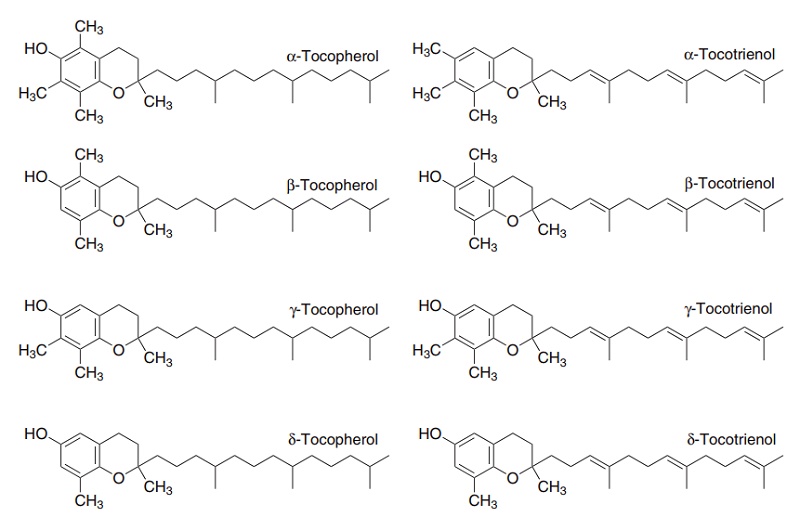
Figure 8.5 The vitamin E vitamers, tocopherols and tocotrienols.
The obsolete international unit of vitamin E activ-ity is still sometimes used: 1 IU = 0.67 mg α-tocopherol equivalent; 1 mg α-tocopherol = 1.49 IU.
Synthetic α-tocopherol does not have the same biological potency as the naturally occurring com-pound. This is because the side-chain of tocopherol has three centers of asymmetry and when it is synthe-sized chemically the result is a mixture of the various isomers. In the naturally occurring compound all three centers of asymmetry have the R-configuration, and naturally occurring α-tocopherol is called all-R, or RRR-α-tocopherol.
Related Topics