Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
Vascular tissue system
Vascular tissue system
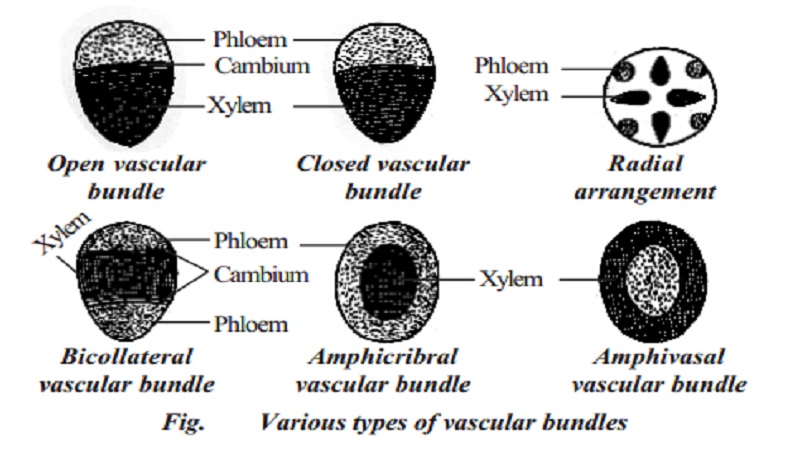
The vascular tissue system consists of xylem and phloem. The elements of xylem and phloem are always organized in groups. They are called vascular bundles. In dicot stem, the vascular bundle consists of cambial tissue in between xylem and phloem. Such vascular bundle is called open vascular bundle. In monocot stem, cambium is absent in the vascular bundle, hence it is known as closed vascular bundle
In roots, xylem and phloem are arranged in an alternate manner on different radii. It is called radial arrangement. In stems and leaves, xylem and phloem are arranged at the same radius and form a vascular bundle together. Such vascular bundle is called conjoint vascular bundle. Depending upon the mutual relationship of xylem and phloem, conjoint vascular bundles are divided into three types. They are collateral, bicollateral and concentric.
If xylem and phloem in a vascular bundle are arranged along the same radius with phloem towards the outside, such vascular bundle is called collateral vascular bundle. If phloem occurs on both the outer and inner sides of xylem, the bundle is called bicollateral. Bicollateral vascular bundles are most typically seen in Cucurbitaceae.
The bundle in which either phloem surrounds the xylem or xylem surrounds the phloem completely is known as concentric vascular bundle.
This is of two types amphicribral and amphivasal. In amphicribral concentric vascular bundles, the phloem completely surrounds the xylem. eg. Polypodium. In amphivasal concentric vascular bundles, the xylem completely surrounds the phloem. eg. Acorus. In roots, protoxylem vessels are present towards the periphery and the metaxylem vessels towards the centre. This arrangement of xylem is called exarch. In stem, protoxylem vessels are towards the centre, while metaxylem towards the periphery. This condition is known as endarch.
Related Topics