Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
Simple fleshy fruits : baccate,drupaceous - Berry, Drupe, Hesperidium, Pepo, Pomo
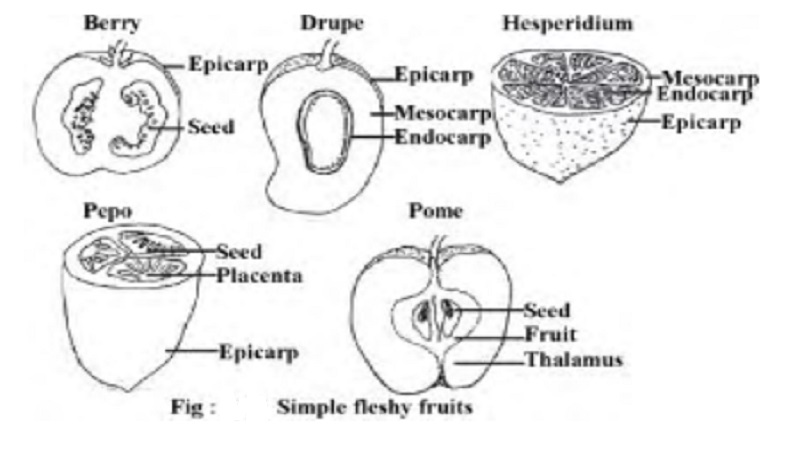
In these fruits either the entire pericarp or part of the pericarp is succulent and juicy when fully ripe. Normally the fruit wall may be differentiated into three layers - an outer epicarp, a middle mesocarp and an iWhen a single fruit develops from a single ovary of a single flower, it is called simple fruit. The ovary may be monocarpellary or multicarpellary syncarpous. On the nature of pericarp, simple fruits are divisible into two types
i) Fleshy fruits and ii) Dry fruitsnner endocarp. As a general rule, the fleshy fruits are indehiscent.
Simple fruits
When a single fruit develops from a single ovary of a single flower, it is called simple fruit. The ovary may be monocarpellary or multicarpellary syncarpous. On the nature of pericarp, simple fruits are divisible into two types
i) Fleshy fruits and ii) Dry fruits
Fleshy fruits are broadly divided into two kinds, baccate and drupaceous. Baccate fruits are fleshy fruits with no hard part except the seeds. Berry is an example for the first category while drupe falls under the second type.
When a single fruit develops from a single ovary of a single flower, it is called simple fruit. The ovary may be monocarpellary or multicarpellary syncarpous. On the nature of pericarp, simple fruits are divisible into two types
i) Fleshy fruits and ii) Dry fruits
Simple fleshy fruits
In these fruits either the entire pericarp or part of the pericarp is succulent and juicy when fully ripe. Normally the fruit wall may be differentiated into three layers - an outer epicarp, a middle mesocarp and an inner endocarp. As a general rule, the fleshy fruits are indehiscent.Fleshy fruits are broadly divided into two kinds, baccate and drupaceous. Baccate fruits are fleshy fruits with no hard part except the seeds. Berry is an example for the first category while drupe falls under the second type.
1. Berry: It is a many seeded fruit. Here the epicarp is thin, the mesocarp and endocarp remain undifferentiated. They form a pulp in which the seeds are embedded. In these fruits, all parts including the epicarp with the seeds are edible eg. tomato
2. Drupe: This is normally a one-seeded fruit. In these fruits the pericarp is differentiated into an outer skinny epicarp, a middle fleshy and juicy mesocarp and an inner hard and stony endocarp. Drupes are called stone fruits because of the stony hard endocarp. The endocarp encloses F o llic le a single seed. The edible portion, i. Basifixed (Innate): Filament is attached to the base of the anther, eg. Brassica.
of the fruit is the fleshy mesocarp eg. mango. In coconut, the mesocarp is fibrous, the edible part is the endosperm.3. Hesperidium: It is a skind of baccate fruit that develops from a superior multicarpellary and syncarpous ovary. The fruit wall is differentiated into three layers - an outer glandular skin or epicarp, a middle fibrous mesocarp, and an inner membranous endocarp. The latter divides the fruit chamber into a number of compartments. The seeds arise on axial placentae and are covered by juicy hairs or outgrowths from the lacentae that are edible.
It is characteristic fruit of the genus Citrus (Fam. Rutaceae)4. Pepo: A large fleshy fruit developing from a tricarpellary, syncarpous, unilocular and inferior ovary with parietal placentation. The fruit is many seeded with pulpy interior; eg. Cucumber, Melon, Bottle gourd etc.
5. Pome: It is a fleshy and a false fruit or Pseudocarp. It develops from a multicarpellary syncarpous inferior ovary in which the receptacle also develops along with the ovary to become fleshy and enclosing the true fruit. The true fruit containing seeds remains inside. The edible part is fleshy thalamus. eg. Apple, Pear etc.
Study Material, Lecturing Notes, Assignment, Reference, Wiki description explanation, brief detail
11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes : Simple fleshy fruits : baccate,drupaceous - Berry, Drupe, Hesperidium, Pepo, Pomo |
Related Topics
11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes