Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
Demonstration of Osmosis - Potato Osmoscope
Osmosis
Osmosis is a special type of diffusion of liquids. When two solutions of different concentrations are separated by a selectively permeable membrane, diffusion of water or solvent molecules takes place from the solution of lower concentration to the solution of higher concentration. This process is called Osmosis. In other words Osmosis is the diffusion of water or solvent from a region of its higher concentration to a region of its lower concentration through a selectively permeable membrane. This can also be expressed as the movement of water from a region of higher free energy of water or water potential to a region of lower free energy of water potential through a selectively permeable membrane.
Hypertonic, Hypotonic and Isotonic solutions
Imagine a system in which an aqueous solution A with high concentration of solute is separated by a selectively permeable membrane from an aqueous solution B with a low concentration of solute. Solution A is said to be hypertonic to solution B, and solution B hypotonic to solution A. In this situation, there will be a net movement of water or solvent molecules through the membrane from the hypotonic solution to the hypertonic solution by osmosis. This will continue until equilibrium is reached, at which point there is no further movement of water and the two solutions are described as isotonic.
Demonstration of Osmosis
The process of osmosis may be demonstrated by the simple osmometer which is the thistle funnel experiment.
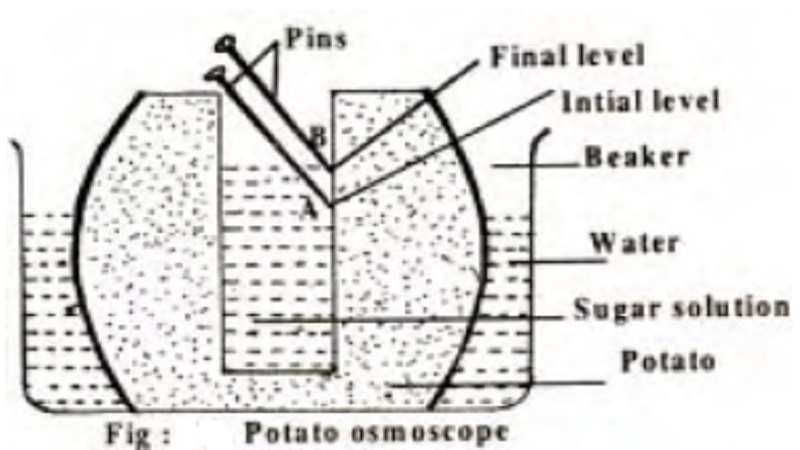
Potato Osmoscope
Demonstration of osmosis in a living system can be one using the potato osmoscope.
A potato is peeled and one side is flattened which serves as the base. A cavity is made in the potato and is filled with concentrated sugar solution and a pin mark is made to indicate the initial level. This potato is then placed in a beaker containing coloured water for some time.
Observation
It is observed that the sugar solution in the cavity of the potato becomes coloured and level rises
Inference
This proves the entry of water into the sugar solution through the potato tissues which serve as the selective permeable membrane.
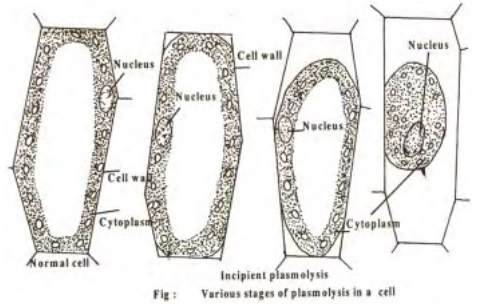
Plasmolysis
When a plant cell is placed in hypertonic solution, the process of exosmosis starts and water from the cell sap diffuses out into the solution of external medium. This causes a reduction in the tension of the cell wall and brings about the contraction of protoplasm due to the continuous loss of water. The protoplasm becomes rounded in shape due to contraction and such a cell is said to beplasmolysed and the phenomenon is referred to as plasmolysis. The initial stage of plasmolysis where the protoplasm just starts leaving the cell wall is called incipient plasmolysis.
When a completely plasmolysed cell is again placed in water or a hypotonic solution, endosmosis takes place and the protoplasm regains its original state and shape. i.e., the cell becomes fully turgid. This phenomenon is the reverse of plasmolysis and is calleddeplasmolysis.
Significance of Plasmolysis
1. Helps to understand the living nature of a cell.
2. Helps to preserve meat, jellies and used in pickling as their salting kills bacteria by plasmolysis.
3. Used to prove the permeability of cell wall and selectively permeable nature of plasma membrane.
Osmotic Pressure
Osmotic pressure of a solution is the pressure which must be applied to it in order to prevent the passage of solvent due to osmosis. In other words, it is that pressure which is needed to check the process of osmosis. The term osmotic potential is also used in place of osmotic pressure.
Turgor Pressure
When the plant cell is placed in water, it will swell but will not burst. Due to the negative osmotic potential of the cell sap, water moves into the cell and causes the plasma membrane to press against the cell wall. This pressure responsible for pressing the plasma membrane against cell wall is called turgor pressure.
Turgor pressure may also be defined as the hydrostatic pressure developed inside the cell on the cell wall due to endosmosis.
Wall Pressure
As a result of turgor pressure on the cell wall, the rigid cell wall exerts an equal pressure in the opposite direction called wall pressure. Under these conditions, the plant cell is said to be turgid.
When wall pressure becomes equal to turgor pressure, entry of water into the cell stops and the water potential (Psi denoted as �) becomes equal to that of the environment.
Diffusion Pressure Deficit (DPD) or Suction Pressure
The pressure exerted by diffusing particles is called diffusion pressure. When solute is added, the diffusion pressure of a solution is lowered. The amount by which diffusion pressure of a solution is lower than that of its pure solvent is known as diffusion pressure deficit which was described as suction pressure by Renner (1915). Recently a new term called water potential is used for DPD but with a negative value.
Related Topics