Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
Ground or fundamental tissue system
Ground or fundamental tissue system
The ground or fundamental tissue system constitutes the main body of the plants. It includes all the tissues except epidermis and vascular bundles. In monocot stem, ground tissue system is a continuous mass of parenchymatous tissue in which vascular bundles are found scattered. Here ground tissue is not differentiated into cortex, endodermis, pericycle and pith. Generally in dicot stem, ground tissue system is differentiated into three main zones - cortex, pericycle and pith.
The cortex occurs between the epidermis and pericycle. Cortex may be a few to many layers in thickness. In most cases, cortex is made up of parenchyma tissues. Intercellular spaces may or may not be present..
Cortical cells may contain non-living inclusions like starch grains, oils, tannins and crystal.
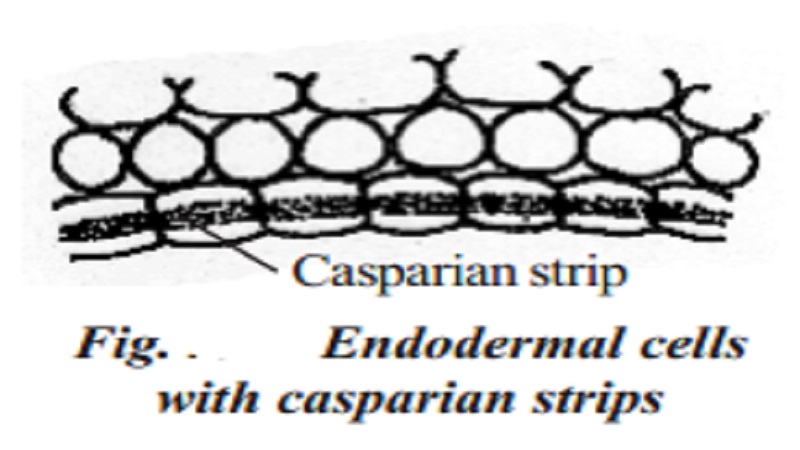
In the leaves, the ground tissue consists of chlorenchyma tissues. This region is called mesophyll. The inner most layer of the cortex is called endodermis. Generally endodermis is made up of barrel shaped parenchyma cells. These cells are arranged in a single layer without intercellular spaces. Pericycle occurs between the endodermis and the vascular bundles. It is generally made up of parenchyma cells. Lateral roots originate from the pericycle. Thus their origin is endogenous. The central part of the ground tissue is known as pith or medulla. Generally this is made up of thin walled parenchyma cells which may be with or without intercellular spaces. The cells in the pith generally store starch, fatty substances, tannins, phenols, calcium oxalate crystals, etc.
Related Topics