Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 3 : Vegetative Morphology of Angiosperm
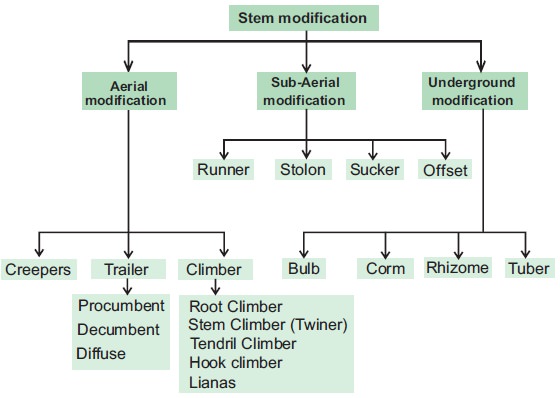
Underground stem modifications

Perennial and some biennial herbs have underground
stems, which are generally known as root
stocks. Rootstock functions as a storage and protective organ. It remains
alive below the ground during unfavourable conditions and resumes growth during
the favourable conditions.
Underground stems are not roots because they
possess nodes, internodes, scale-leaves and buds. Rootstock also lack root cap
and root hairs but they possess terminal bud which is a characteristics of stem.
1. Bulb
It is a condensed conical or convex stem surrounded
by fleshy scale leaves. They are of two types 1. Tunicated (coated) bulb: In
which the stem is much condensed and surrounded by several concentric layers of
scale leaves. The inner scales commonly fleshy, the outer ones dry. These are
two types (a) Simple Tunicated bulb Example: Allium cepa (b) Compound Tunicated bulb. Example: Allium
sativum. 2. Scaly bulb: They are narrow, partially overlap each other by
their margins only. Example:![]()
![]()
![]() Tulipa spp.
Tulipa spp.
Pseudobulb is a short erect aerial storage or
propagating stem of certain epiphytic and terrestrial sympodial orchids.
Example: Bulbophyllum.
2. Corm
This is a succulent underground stem with an erect
growing tip. The corm is surrounded by scale leaves and exhibit nodes and
internodes. Example: Amorphophallus, Gladiolus, Colocasia, Crocus, Colchicum

3. Rhizome
This is an underground stem growing horizontally with several lateral growing tips. Rhizome posses conspiquous nodes and internodes covered by scale leaves. Example: Zingiber officinale, Canna, Curcuma longa, Maranta arundinacea, Nymphaea, Nelumbo.
4. Tuber
This is a succulent underground spherical or globose stem with many embedded axillary buds called “eyes”. Example: Solanum tuberosum, Helianthus tuberosus
Related Topics