Leaf | Botany - Phyllotaxy | 11th Botany : Chapter 3 : Vegetative Morphology of Angiosperm
Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 3 : Vegetative Morphology of Angiosperm
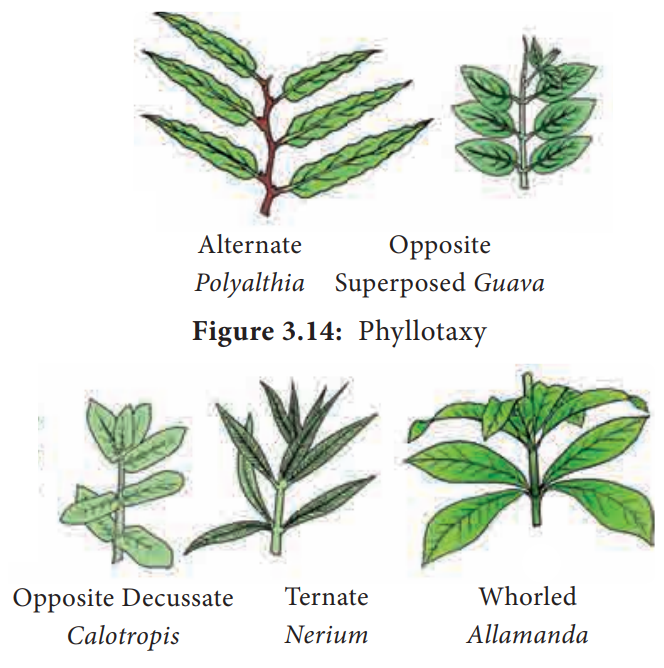
Phyllotaxy
Phyllotaxy
The mode of arrangement of leaves on the stem is
known as phyllotaxy (Gk. Phyllon = leaf ; taxis =
arrangement). Phyllotaxy
is to avoid over crowding of leaves and expose the leaves maximum to the
sunlight for photosynthesis. The four main types of phyllotaxy are
(1) Alternate
(2) Opposite
(3) Ternate
(4) Whorled.
1. Alternate phyllotaxy
In this type there is only one leaf per node and
the leaves on the successive nodes are arranged alternate to each other. Spiral
arrangement of leaves show vertical rows are called orthostichies. They are two types.
i.
Alternate
spiral: In which the leaves are arranged
alternatively in a spiral manner. Example: Hibiscus,
Ficus.
ii.
Alternate
distichous or Bifarious: In which the leaves are organized
alternatively in two rows on either side of the stem. Example: Monoon longifolium (Polyalthia longifolia).
2. Opposite phyllotaxy
In this type each node possess two leaves opposite
to each other. They are organized in two different types.
i.
Opposite
superposed: The pair of leaves
arranged in succession are in the same direction, that is two opposite leaves
at a node lie exactly above those at the lower node. Example: Psidium (Guava), Eugenia jambolana (Jamun), Quisqualis (Rangoon creeper).
ii.
Opposite
decussate: In this type of
phyllotaxy one pair of leaves is placed at right angles to the next upper
or lower pair of leaves. Example: Calotropis, Zinnia, Ocimum
3. Ternate phyllotaxy
In this type there are three leaves attached at
each node. Example: Nerium
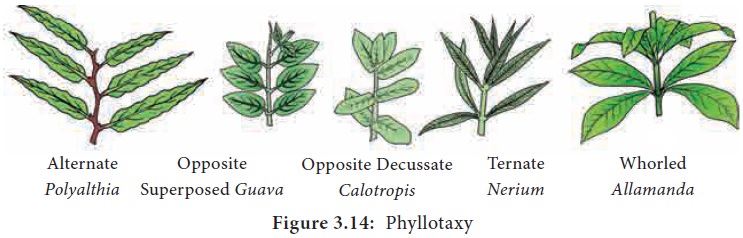
4. Whorled (verticillate) type of phyllotaxy
In this type more than three leaves are present in
a whorl at each node forming a circle or whorl. Example: Allamanda, Alstonia scholaris.
Related Topics