Definition, Theorem, Solved Example Problems - Symmetric and Skew-symmetric Matrices | 11th Mathematics : UNIT 7 : Matrices and Determinants
Chapter: 11th Mathematics : UNIT 7 : Matrices and Determinants
Symmetric and Skew-symmetric Matrices
Symmetric and Skew-symmetric Matrices
Definition 7.17
A square matrix A is said to be symmetric if AT = A.
That is, A = [ aij ]n×n is a symmetric matrix, then aij = a ji for all i and j.
For instance, 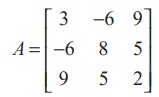 is a symmetric matrix since AT =A.
is a symmetric matrix since AT =A.
Observe that transpose of AT is the matrix A itself. That is ( AT )T=A.
Definition 7.18
A square matrix A is said to be skew-symmetric if AT = − A.
If A = [aij ]n×n is a skew-symmetric matrix, then aij = −a j for all i and j.
Now, if we put i = j, then 2aii = 0 or aii = 0 for all i. This means that all the diagonal elements of a skew-symmetric matrix are zero.
For instance, A =
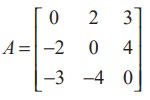
is a skew-symmetric matrix since AT= - A
It is interesting to note that any square matrix can be written as the sum of symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices.
Theorem 7.1
For any square matrix A with real number entries, A + AT is a symmetric matrix and A − AT is a skew-symmetric matrix.
Proof
Let B = A + AT.
BT = ( A + AT )T = AT + ( AT )T = AT + A = A + AT = B .
This implies A + AT is a symmetric matrix.
Next, we let C = A − AT . Then we see that
C T = ( A + ( − AT ))T = AT + ( − AT )T = AT − ( AT )T = AT − A = − ( A − AT ) = − C
This implies A − AT is a skew-symmetric matrix.
Theorem 7.2
Any square matrix can be expressed as the sum of a symmetric matrix and a skew-symmetric matrix.
Proof
Let A be a square matrix. Then, we can write
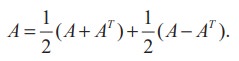
From Theorem 7.1, it follows that (A+AT) and (A-AT) are symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices respectively. Since (kA)T = kAT , it follows that 1/2( A + AT ) and 1/2( A − AT ) are symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices, respectively. Now, the desired result follows.
Note 7.4
A matrix which is both symmetric and skew-symmetric is a zero matrix.
Example 7.13
Express the matrix 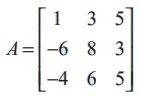 as the sum of a symmetric and a skew-symmetric matrices.
as the sum of a symmetric and a skew-symmetric matrices.
Solution
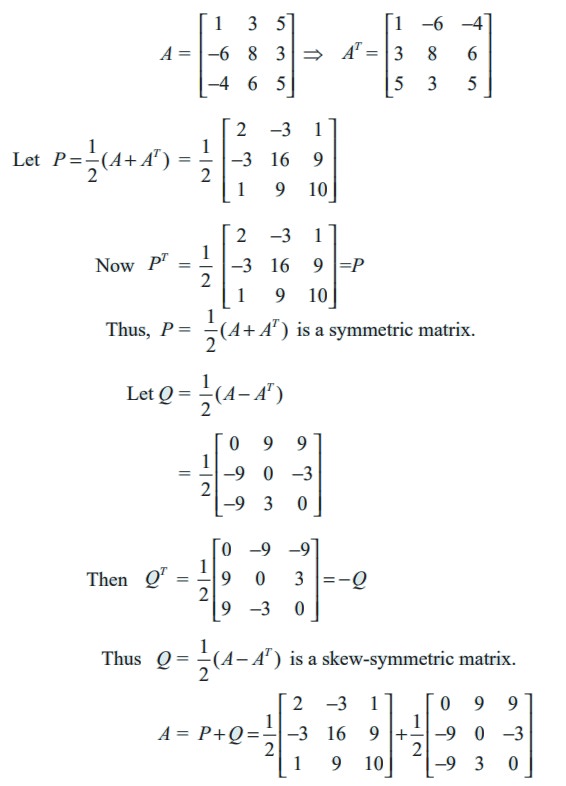
Thus A is expressed as the sum of symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices.
Related Topics