Chapter: 11th Mathematics : UNIT 7 : Matrices and Determinants
Properties of Determinants
Properties of Determinants
We can use one or more of the following properties of the determinants to simplify the evaluation of determinants.
Property 1
The determinant of a matrix remains unaltered if its rows are changed into columns and columns into rows. That is, | A | = | AT | .
Since the row-wise expansion is same as the column-wise expansion, the result holds good.
Property 2
If any two rows / columns of a determinant are interchanged, then the determinant changes in sign but its absolute value remains unaltered.
Verification
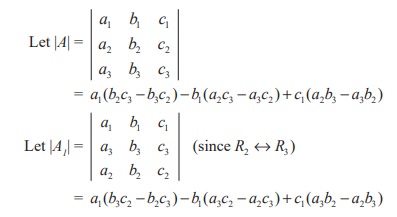
= a1 (b3 c2 − b2 c3 ) − b1 (a3 c2 − a2 c3 ) + c1 (a3 b2 − a2 b3 )
= − a1 (b2 c3 − b3 c2 ) + b1 (a2 c3 − a3 c2 ) − c1 (a2 b3 − a3 b2 )
= −[ a1 (b2 c3 − b3 c2 ) − b1 (a2 c3 − a3 c2 ) + c1 (a2 b3 − a3b2 )]
= - | A |
Therefore, | A1 | = - | A | . Thus the property is verified.
Property 3
If there are n interchanges of rows (columns) of a matrix A then the determinant of the resulting matrix is (- 1)n | A |.
Property 4
If two rows (columns) of a matrix are identical, then its determinant is zero.
Verification
Let |A| = 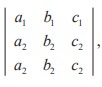
, with 2nd and 3rd rows are identical.
Interchanging second and third rows, we get − | A | = 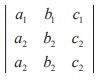 = | A |
= | A |
⇒ 2|A| = 0 ⇒ |A| = 0.
Property 5
If a row (column) of a matrix A is a scalar multiple of another row (or column) of A, then its determinant is zero.
Note 7.8
(i) If all entries of a row or a column are zero, then the determinant is zero.
(ii) The determinant of a triangular matrix is obtained by the product of the principal diagonal elements.
Property 6
If each element in a row (or column) of a matrix is multiplied by a scalar k, then the determinant is multiplied by the same scalar k.
Verification

= ka1 (b2 c3 − b3 c2 ) − kb1 (a2 c3 − a3 c2 ) + kc1 (a2 b3 − a3 b2 ) = k| A |
= k[a1 (b2 c3 − b3 c2 ) − b1 (a2 c3 − a3 c2 ) + c1 (a2 b3 − a3 b2 )] = k| A |
⇒ |A1| = k| A |.
Note 7.9
If A is a square matrix of order n, then
(i) | AB | = | A | | B |
(ii) If AB = O then either | A | = 0 or | B | = 0.
(iii) | An |= (| A |)n
Property 7
If each element of a row (or column) of a determinant is expressed as sum of two or more terms then the whole determinant is expressed as sum of two or more determinants.
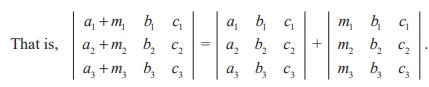
Verification
By taking first column expansion it can be verified easily.
LHS = (a1 + m1 )(b2 c3 − b3 c2 ) − ( a2 + m2 )(b1c3 − b3 c1 ) + ( a3 + m3 )(b1c2 − b2 c1 )
= a1 (b2 c3 − b3 c2 ) − a2 (b1c3 − b3 c1 ) + a3 (b1c2 − b2 c1 ) + m1 (b2 c3 − b3 c2 ) − m2 (b1c3 − b3 c1 ) + m3 (b1c2 − b2 c1 )
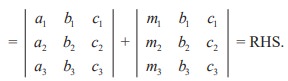
Property 8
If, to each element of any row (column) of a determinant the equi-multiples of the corresponding entries of one or more rows (columns) are added or subtracted, then the value of the determinant remains unchanged.
Verification
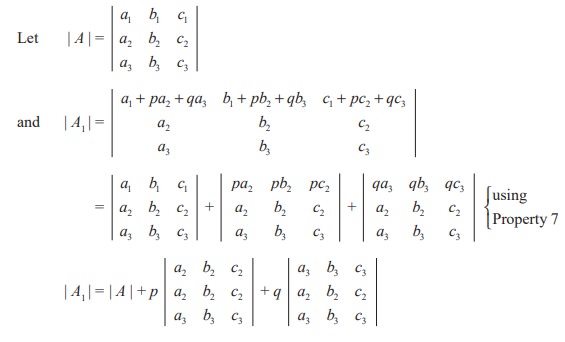
| A1 | = | A | + p(0) + q(0) = | A | (using Property 4)
Therefore | A1 | = | A |
This property is independent of any fixed row or column.

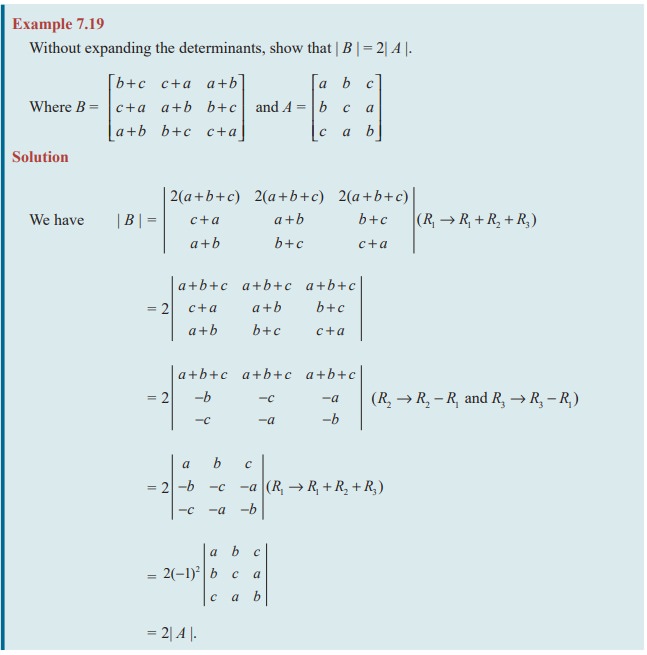



Related Topics