Ray Optics | Physics - Summary, Concept Map | 12th Physics : UNIT 6 : Ray Optics
Chapter: 12th Physics : UNIT 6 : Ray Optics
Summary, Concept Map
Ray Optics
SUMMARY
▪ A ray of light gives the direction of light.
▪ Law of reflection is, i = r
▪ Paraxial rays are the rays travelling close to
the principal axis of the mirror and make is small angles with it.
▪ The relation between focal length and radius of
curvature in spherical mirror is, 2f
= R (or) f = R/2
▪ Cartesian sign conventions are to be followed to
trace image formed by spherical mirrors.
▪ The mirror equation is, 1/v + 1/u = 1/f
▪ The magnification in spherical mirror is, m = - h’/h = − v/u, m = h’/h = (f−v) / f = f / (f – u)
▪ Light travels with lesser velocity in optically
denser medium.
▪ Refractive index is the ratio of speed of light
in vacuum to speed of light in medium, n=
c/υ
▪ Optical path is the equivalent path travelled in
vacuum in the same time light travels through a optically denser medium. d' = nd
▪ Law of refraction also called as Snell's law in
ratio form is, sin i/sin r = n2/n1.
▪ In product form is, n1, sin i = n2
sin r
▪ The relative refractive index of second medium
with respect to first medium is, n21=
n2/n1
▪ The apparent depth is always lesser than actual
depth. The equation for apparent depth is d’=d/n.
▪ The critical angle of incidence ic for a ray incident from a
denser to rarer medium, is that angle for which the angle of refraction is 90°.
For i > ic, total internal reflection occurs.
▪ Equations for critical angle incidence is, sin ic = 1/n (or) ic = sin-1(1/n).
▪ Snell's window is the restricted area of
circular illumination which appears when seen from water due to critical angle
incidence. The radius of the circular illumination is, R = d [1 / √(n2 −
1) ] (or) R = d / √(n2 − 1)
▪ Optical fibre makes use of critical angle
incidence. The acceptance angle in optical fibre is, . Here, n1, n2,
n3 are the reflactive indices of core, cladding and surrounding
medium respectively.
▪ Glass slabs produce a lateral displacement on
the light falling on it. The equation for lateral shift is, L = t [ sin(i−r) /cos(r) ]
▪ The equation for single spherical surface is, (n/v)
– (1/u) = (n−1) / R
▪ The focal length of the thin lens is positive
for a converging lens and negative for diverging lens. It is not based on the
position of the focal point.
▪ The lens makers formula is, 1/f = (n−1)
( 1/R1 – 1/R2 )
▪ The lens equation is, 1/v – 1/u = 1/f
▪ The
magnification produced by the lens is, m
= h’/h = v/u, m = h’/h = f / (f+u)
(or) m = h’/h = (f – v) / f
▪ The power
of a lens is a measure of the degree of convergence (or) divergence of light
falling on it. Power and focal length are inverse to each other. P = 1/f.
▪ The unit of power is diopter (D) when the focal
length is taken in meter.
▪ The effective focal length of lenses in contact
is, 1/F = 1/f1 + 1/f2
▪ A prism produces deviation on the incident ray.
▪ Angle of deviation depends on angle of prism,
angle of incidence and refractive index of material of prism given by the
equation, d = i1+ i2 − A
▪ At minimum deviation, i1 = i2,
r1 = r₂, and the ray inside the prism is
parallel to the base of the prism.
▪ The refractive index of prism depends on angle
of prism and angle of minimum deviation given by the equation, n = sin([A+D]/2) / sin(A/2)
▪ When white light travels through a medium,
different colours travel with different speeds leading to dispersion of light.
Red colour travels faster than violet colour in a medium. In vacuum all the
colours travel with the same speed.
▪ The angle of deviation produced by the small
angled prism is, δ = (n-1) A
▪ The angular separation between the two extreme
colours (violet and red) in the spectrum is called angular dispersion. δv
− δR = (nV − nR)A
▪ Dispersive power is the measure of ability of
the medium to disperse white light. ω = (nV
– nR) / (n–1)
▪ Rainbow is formed by dispersion of light by
droplets of water.
▪ The scattering of light by particles of size
less than wavelength of light is called Rayleigh scattering. The intensity of
light produced by Rayleigh scattering is, I ∝ 1/λ4
▪ Non-Rayleigh scattering is by suspended dust
particles whose size is greater than the wavelength of light. This scattering
is independent of wavelength of light.
SUMMARY
• In ray optics, light is treated as a ray in the direction of light.
• Light undergoes reflection at polished surfaces and it is governed by laws of reflection.
• In general, plane mirrors form virtual and laterally inverted images at equal distance inside the mirror.
• The height of plane mirror needed to see a person fully in a mirror is half of the height of person.
• Spherical mirrors form a part of a sphere.
• Paraxial rays are the rays travelling close to the principal axis of the mirror and make small angles withit.
• There is a relation between f and R in spherical mirrors for paraxial rays.
• Image formation in spherical mirrors is based on mirror equation.
• There is a set of Cartesian sign conventions to be followed to trace image formed by spherical mirrors.
• Light travels with lesser velocity in optically denser medium.
• Optical path is the equivalent path travelled in vacuum in the same time light travels through a optically denser medium.
• The phenomenon of refraction is governed by laws of refraction (Snell’s law).
• The apparent depth is always lesser than actual depth.
• Refraction takes place in atmosphere due to different layers of air with varying refractive indices.
• Total internal reflection takes place when light travels from denser to rarer medium with the angle of incidence greater than critical angle.
• There are several applications of total internal reflection.
• A glass slab produces lateral displacement or shift of ray entering into it.
• Thin lenses are formed by two spherical refracting surfaces.
• The image tracing in thin lenses is done with the Cartesian sign conventions and with the help of lens equation.
• Power and focal length are inverse to each other.
• There is effective focal length for lenses in contact and out of contact.
• Prism produces deviation on the incident ray.
• Angle of deviation depends on angle of prism, angle of incidence and refractive index of material of prism.
• The refractive index of prism depends on angle of prism and angle of minimum deviation.
• When white light travels through a medium, different colours travel with different speeds leading to dispersion of light.
• Dispersive power is the measure of ability of the medium to disperse white light.
• Rainbow is formed by dispersion of light by droplets of water.
•![]() Light can be scattered by the particles present in atmosphere.
Light can be scattered by the particles present in atmosphere.
• The scattering of light by particles of size less than wavelength of light is called Rayleigh scattering which is inversely proportional to fourth power of wavelength.
• If the scattering is by suspended dust particles whose size is greater than wavelength of light, the scattering is independent of wavelength.
• There are four theories on light each explaining few aspects of light.
• Light has wave and particle nature.
• In wave optics we treat light propagating as a wavefront.
• Huygens’ principle explains the propagation of light as wavefront.
• Laws of reflection and refraction are proved by Huygens’ principle.
• In interference, two light waves are added to get varying intensities at different points.
• Coherent sources produce monochromatic light waves in phase or with constant phase difference.
• Coherent sources are obtained by intensity division, wavefront division and real and virtual images of light source.
• Young’s double slit uses wavefront division to obtain coherent sources.
• Interference with polychromatic (white) light produces coloured interference fringes.
• Thin films appear coloured due to interference of white light.
• Bending of light around sharp edges is called diffraction.
• There are two types of diffractions called Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffractions
• Diffraction takes place at single slit which has a width comparable to the wavelength of light.
• Fresnel’s distance is the distance up to which ray optics is obeyed.
• Diffraction can also happen in grating which has multiple slits of thickness comparable to wavelength of light used.
• Using diffraction grating and spectrometer wavelength of monochromatic light and also different colours of polychromatic light can be determined.
• Resolution is the quality of image which is decided by diffraction effect and Rayleigh criterion.
• Resolution is measured by the smallest distance which could be seen clearly without the blur due to diffraction.
• Polarisation is restricting electric or magnetic field vibrations to one plane.
• Polarisation is obtained by selective absorption, reflection, double refraction and scattering.
• Malus’ law gives the intensity of emerging light when a polarised light enters two polaroids kept at an angle.
• Brewster’s law relates angle of polarisation and refractive index of the medium.
• Optically active crystals can be classified as uniaxial and biaxial crystals.
• When light enters in to optically active crystals, double refraction takes place.
•![]() In double refraction, ordinary ray obeys laws of refraction and extraordinary ray does not obey laws of refraction.
In double refraction, ordinary ray obeys laws of refraction and extraordinary ray does not obey laws of refraction.
• Nicol prism separates ordinary and extraordinary rays by transparent cement called Canada balsam.
• Light scattered by molecules at perpendicular direction to the incident light is found to be plane polarised.
• Single convex lens can act as a simple microscope when object is within the focal length.
• Two focusing namely, near point focusing and normal focusing are possible.
• In near point focusing, the image is formed at 25 cm which is the distance of distinct vision for normal eye. Whereas, in normal focusing the image is formed at infinity.
• To find magnification in near point focusing we use lateral magnification and for normal focusing we use angular magnification.
• Resolution of microscope could be improved by using oil immersed eye piece.
• Compound microscope has improved magnification.
• Astronomical telescope has an eye piece of long focal length and eye piece of short focal length.
• Terrestrial telescopes have one addition lens for producing erect image.
• Reflecting telescopes have advantages as well as disadvantages.
• Eye has three problems (i) nearsightedness, (ii) farsightedness, (iii) astigmatism.
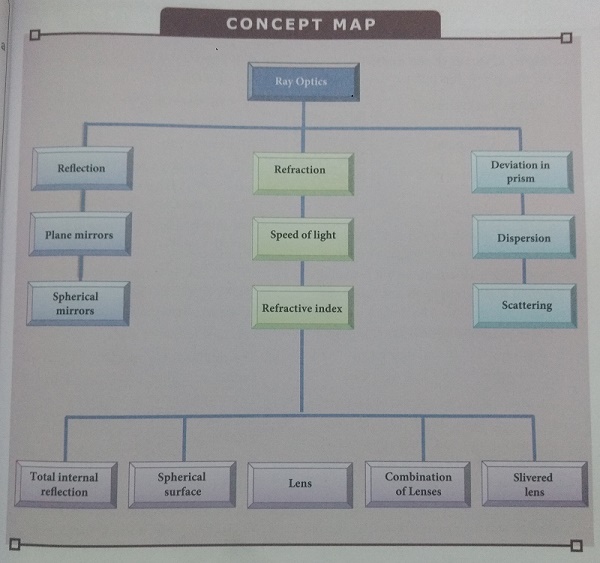
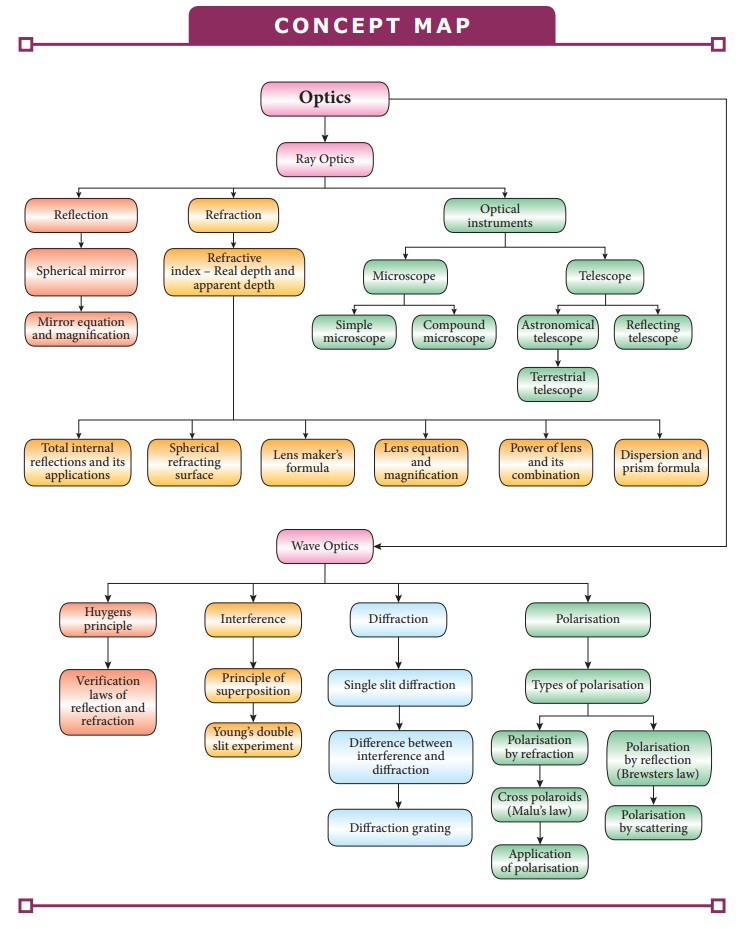
CONCEPT MAP

Related Topics