Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 12 : Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
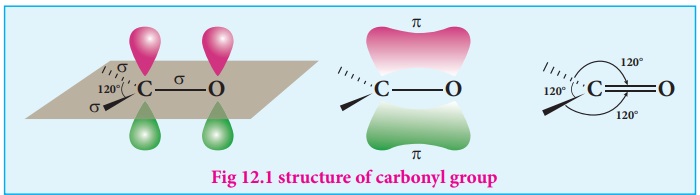
Structure of carbonyl group
Structure of carbonyl group
The carbonyl carbon

is sp2 hybridised and the carbon – oxygen bond is similar to
carbon – carbon double bond in alkenes. The carbonyl carbon forms three σ bonds
using their three sp2 hybridised orbital. One of the sigma bond is
formed with oxygen and the other two with hydrogen and carbon (in aldehydes) or
with two carbons (in ketones). All the three 'σ' bonded atoms are lying on the same plane as shown
in the fig (12.1). The fourth valence electron of carbon remains in its
unhybridised ‘2p’ orbital which lies perpendicular to the plane and it overlaps
with 2p orbital of oxygen to form a carbon – oxygen p bond.
The oxygen atom has two nonbonding pairs of electrons, which occupy its
remaining two p-orbitals. Oxygen, the second most electro negative atom
attracts the shaired pair of electron between the carbon and oxygen towards
itself and hence the bond is polar. This polarisation contributes to the
reactivity of aldehydes and ketones.

Fig 12.1 structure of carbonyl group
Related Topics