Preparation, Physical and Chemical properties - Acid Amides | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 12 : Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 12 : Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
Acid Amides
Acid Amides
Acid amides are derivatives of carboxylic acid in which the – OH part of
carboxyl group has been replaced by – NH2 group. The general formula
of amides are given as follows.
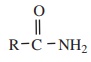
Now, we shall focus our attention mainly on the study of chemistry of
acetamide.
Methods of Preparation
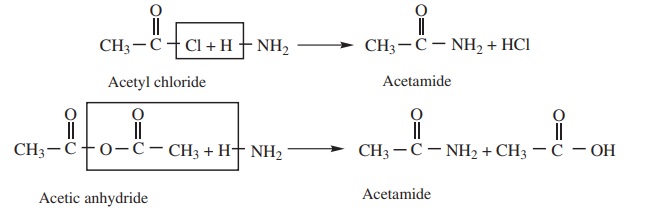
1. Ammonolysis of acid derivatives
Acid amides are prepared by the action of ammonia with acid chlorides or
acid anhydrides.
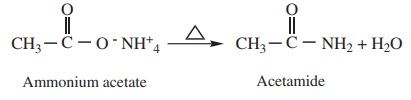
2) Heating ammonium carboxylates
Ammonium salts of carboxylic acids (ammonium carboxylates) on heating,
lose a molecule of water to form amides.
3) Partial hydrolysis of alkyl cyanides (Nitriles)
Partial hydrolysis of alkyl cyanides with cold con HCl gives amides
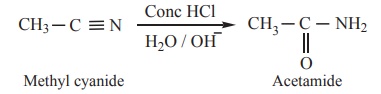
Chemical Properties
1. Amphoteric character
Amides behave both as weak acid as well as weak base and thus show
amphoteric character.
This can be proved by the following reactions.
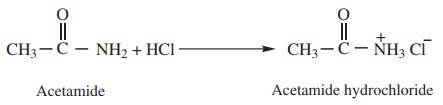
Acetamide (as base) reacts with hydrochloric acid to form salt
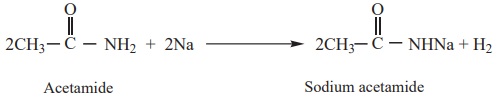
Acetamide (as acid) reacts with sodium to form sodium salt and hydrogen
gas is liberated.
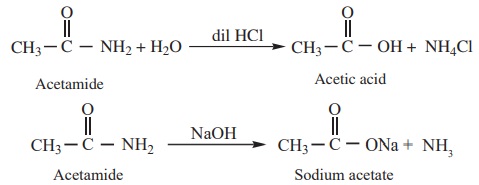
2) Hydrolysis
Amides can be hydrolysed in acid or in alkaline solution on prolonged
heating
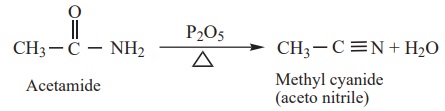
3) Dehydration
Amides on heating with strong dehydrating agents like P2O5
get dehydrated to form cyanides.
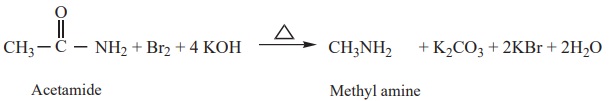
4) Hoff mann’s
degradation
Amides reacts with bromine in the presence of caustic alkali to form a
primary amine carrying one carbon less than the parent amide.
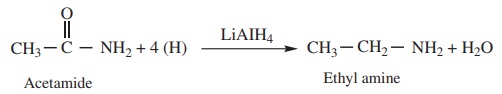
5) Reduction
Amides on reduction with LiAlH4or Sodium and ethyl alcohol to
form corresponding amines.
Related Topics