Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids | Chemistry - Short Answer Questions | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 12 : Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 12 : Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
Short Answer Questions
Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids | Chemistry
Short Answer Questions
1. How is propanoic acid is prepared starting from
(a) an alcohol (b) an alkylhalide (c) an alkene
(a) an alcohol:
Oxidation
of propanol gives propanoic acid
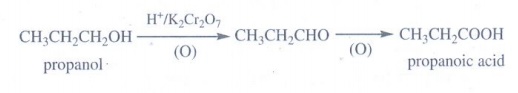
(b) an alkylhalide
Ethyl
bromide treated with KCN gives ethyl cyanide which on further hydrolysis
produce propanoic acid
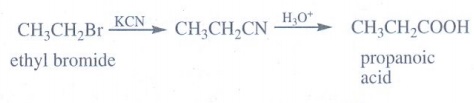
(c) an alkene
Oxidation
of 3-hexene with acidified KMnO4 gives propanoic acid
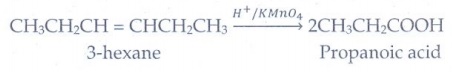
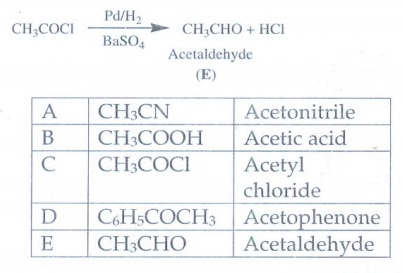
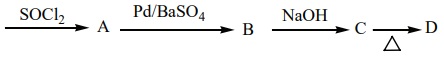
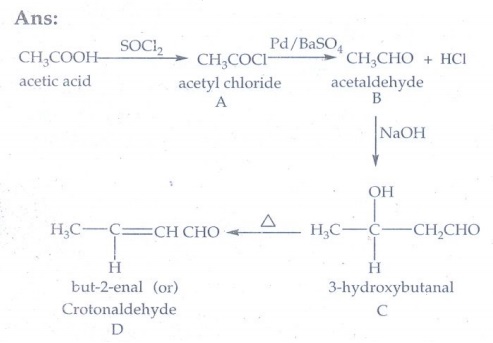
2. A Compound (A) with molecular formula C2H3N on acid hydrolysis gives(B) which reacts with thionylchloride to give compound(C). Benzene reacts with compound (C) in presence of anhydrous AlCl3 to give compound(D). Compound (D) on reduction with Zn/Hg and Conc.HCl gives (E). Identify (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E). Write the equations.
A
Compound (A) with molecular formula C2H3N is CH3CN
on acid hydrolysis gives acetic acid (B).
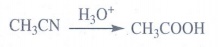
Acetic
acid (B) which reacts with thionylchloride gives acetyl chloride (C)
CH3COOH
+ SOCl2 → CH3COCl
+ HCl + SO2
Benzene
reacts with acetyl chloride (C) in presence of anhydrous AlCl3 gives
acetophenone (D)

Acetylchloride
on reduction gives Acetaldehyde (E)
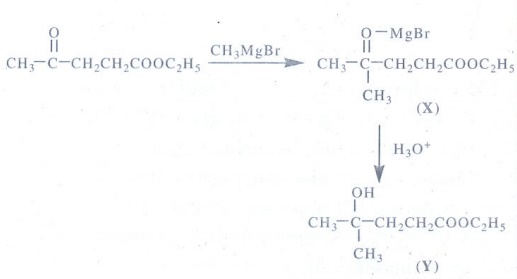
3. Identify X and Y.
CH3 COCH2CH2 COOC2H5 -----CH3 MgBr→ X ----H3O+→Y
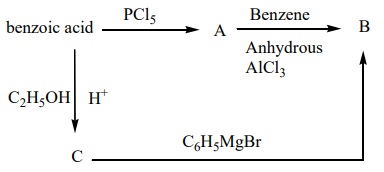
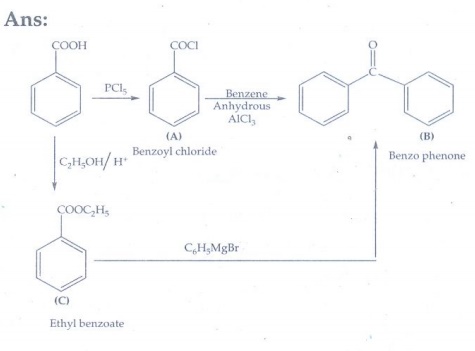
4. Identify A, B and C
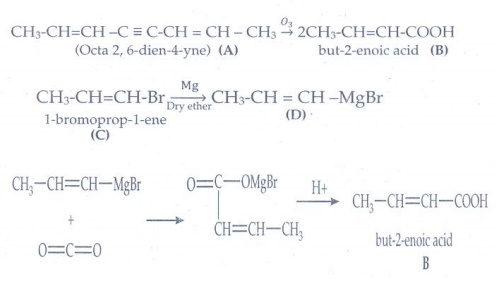
5. A hydrocarbon A
(molecular formula C8H10) on ozonolysis gives B(C4H6O2)
only. Compound C (C3H5Br) on treatment with magnesium in
dry ether gives (D) which on treatment with CO2 followed by acidification
gives(B). Identify A, B and C.
Answer:
6. Identify A, B, C and D
7. An alkene (A) on ozonolysis gives propanone and aldehyde (B). When (B) is oxidised (C) is obtained. (C) is treated with Br2/P gives (D) which on hydrolysis gives (E). When propanone is treated with HCN followed by hydrolysis gives (E). Identify A, B, C, D and E.
Answer:
2, 4-dimethylpent-2-ene on ozonolysis gives propanone and isobutyraldehyde.
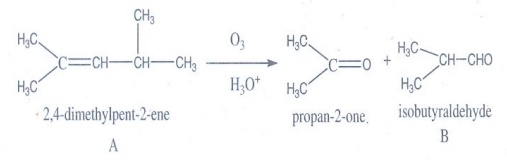
Oxidation of isobutyraldehyde (B) gives isobutyric acid.
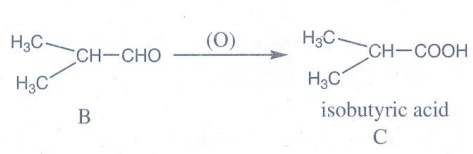
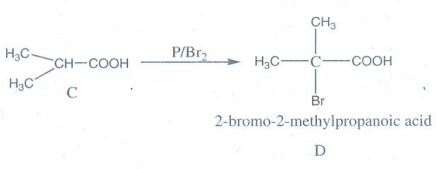
isobutyric acid with P / Br2 gives α – bromo substituted compound D
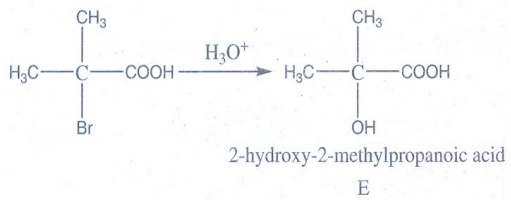
Hydrolysis of D gives 2- hydroxyl – 2 – methylpropanoic acid
A → 2,4 – dimethyl pent-2-ene
B → Isobutyraldehyde
C → Isobutyric acid
D → 2-bromo-2-methylpropanoic acid
E → 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanoic acid
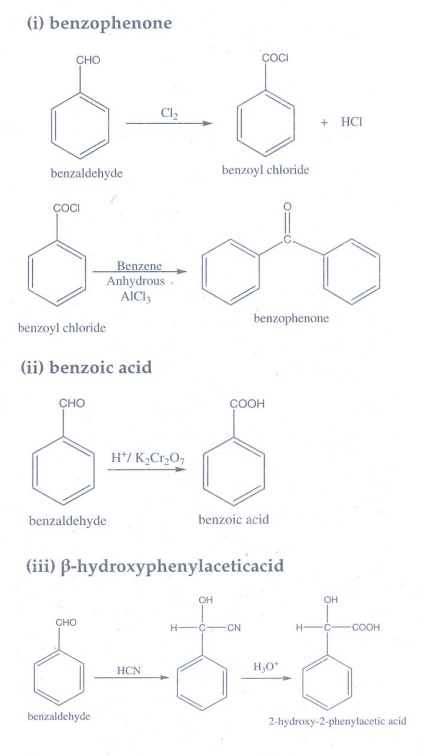
8. How will you convert benzaldehyde into the following compounds?
(i) benzophenone (ii) benzoic acid (iii) β-hydroxyphenylaceticacid.
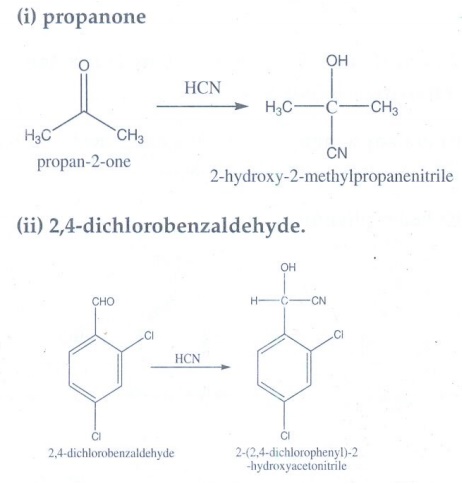
9. What is the action of HCN on
(i) propanone (ii) 2,4-dichlorobenzaldehyde. iii) ethanol
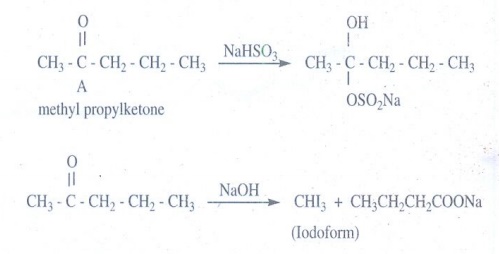
10. A carbonyl compound A having molecular formula C5H10O forms crystalline precipitate with sodium bisulphate and gives positive iodoform test. A does not reduce Fehling solution. Identify A.
• A does not reduce Fehling
solution.
Therefore
A is ketone.
• A gives positive iodoform test. A
contains -COCH3 group.
• A has molecular formula C5H10O
and one - COCH3 group. Hence A is 2-pentanone.
CH3—CO—CH2—CH2—CH3
2-pentanone
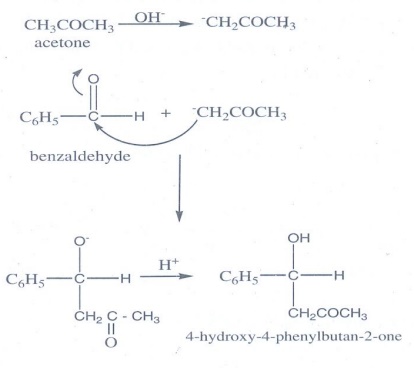
11. Write the structure of the major product of the aldol condensation of benzaldehyde with acetone.
CH3COCH3 --OH- →
-CH2COCH3
acetone
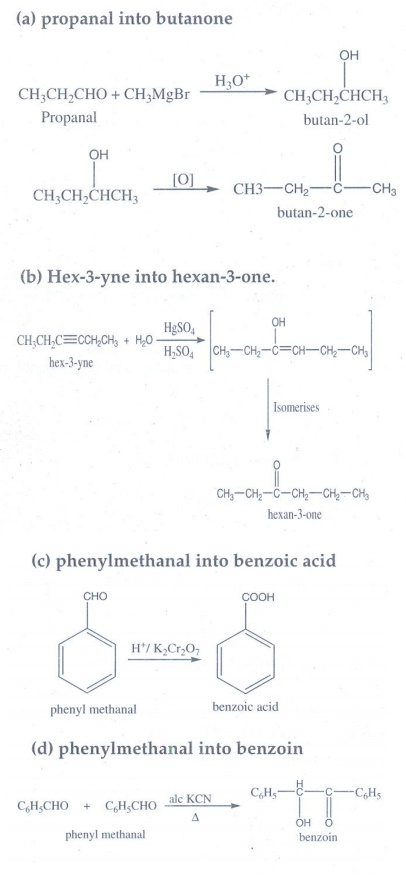
12. How are the following conversions effected
(a) propanal into butanone
(b) Hex-3-yne into hexan-3-one.
(c) phenylmethanal into benzoic acid
(d) phenylmethanal into benzoin
13. Complete the following reaction.
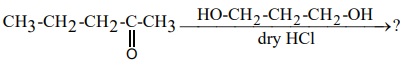
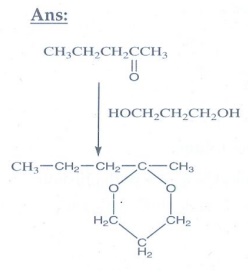
14. Identify A, B and C
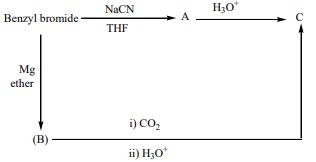
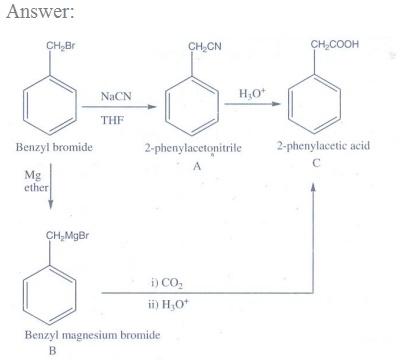
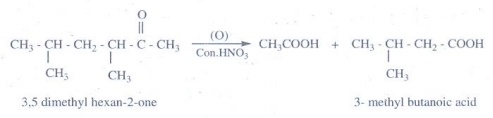
15. Oxidation of ketones involves carbon – carbon bond cleavage. Name the product (s) is / are formed on oxidising 2,5 – dimethyhexan – 3- one using strong oxidising agent.
Ketones
are not easily oxidized under drastic condition (or) with powerful oxidizing
agent like con.HNO3, H+/KMnO4, H+/ K2Cr2O7,
cleavage of carbon - carbon bond takes place to give mixture of carboxylic
acids having less number of carbon atom than the parent ketone.

The
oxidation of unsymmetrical ketones is governed by popoff's rule. It states that
during the oxidation of an unsymmetrical ketone, a (C -CO) bond is cleaved in
such a way that the keto group stays with the smaller alkyl group.
16. How will you prepare
i. Acetic anhydride from acetic acid
ii. Ethylacetate from methylacetate
iii. Acetamide from methylcyanide
iv. Lactic acid from ethanal
v. Acetophenone from acetylchloride
vi. Ethane from sodium acetate
vii. Benzoic acid from toluene
viii. Malachitegreen from benzaldehyde
ix. Cinnamic acid from benzaldehyde
x. Acetaldehyde from ethyne
Answer:
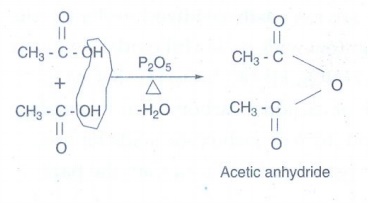
i) Acetic anhydride from acetic
acid:
Acetic
acid on heating in the presence of a strong dehydrating agent such as P2O5
forms acid anhydride.
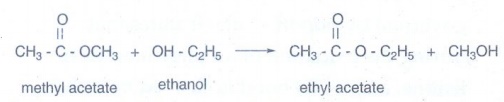
ii) Ethyl acetate from methyl
acetate:
Methyl
acetate is treated with ethanol to form ethyl acetate.
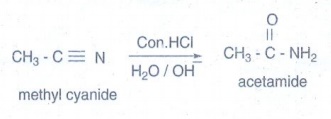
iii) Acetamide from methyl
cyanide:
Partial
hydrolysis of alkyl cyanides with cold con.HCl gives amides.
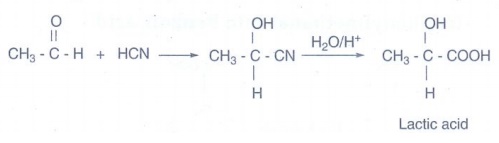
iv) Lactic acid from ethanal:
Ethanol
is treated with HCN to form acetaldehyde cyanohydrins and then hydrolysed with
H3O+ gives lactic acid.
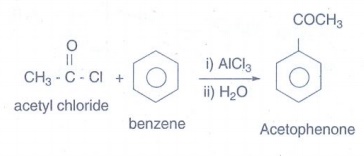
v) acetophenone from acetyl
chloride:
Acetyl
chloride is treated with benzene in presence of AlCl3 and H2O
gives acetophenone.
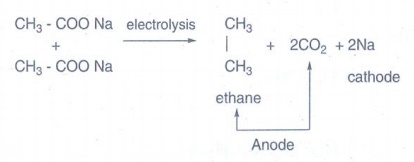
vi) Ethane from sodium acetate:
The
aqueous solutions sodium or potassium salts of carboxylic acid on hydrolysis
gives alkanes at anode. This reaction is called Kolbes electrolysis.
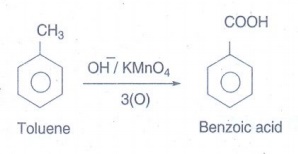
vii) Benzoic acid from toluene:
The
oxidation of alkyl benzene with chromic acid or acidic or alkaline KMnO4
to form benzoic acid.
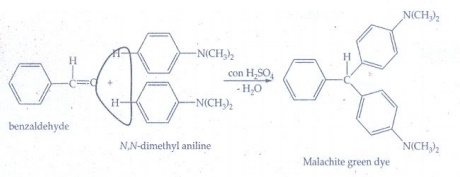
viii) Malachite green from
benzaldehyde:
Benzaldehyde
condenses with N, N - dimethyl aniline in the presence of strong acids forms
malachite green.
ix) Cinnamic acid from
benzaldehyde: (Perkin's reaction)
Benzaldehyde
is treated with acetic anhydride, condensation takes place and cinnamic acid is
obtained.

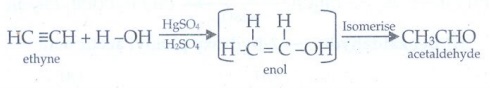
x) Acetaldehyde from ethyne:
The
hydration of alkynes in presence of 40% dilute H2SO4 and
1% HgSO4 to give corresponding aldehyde.
EVALUATE YOURSELF:
1. Write the IUPAC
name for the following compound
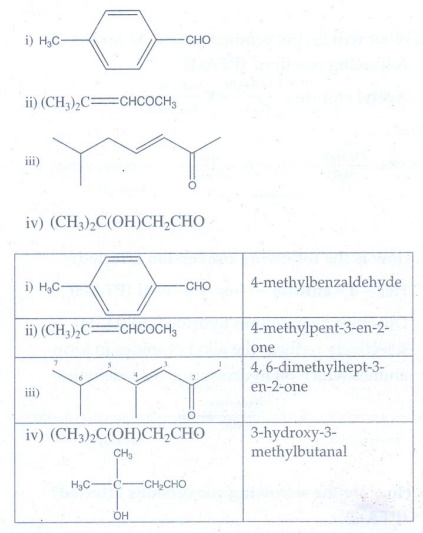
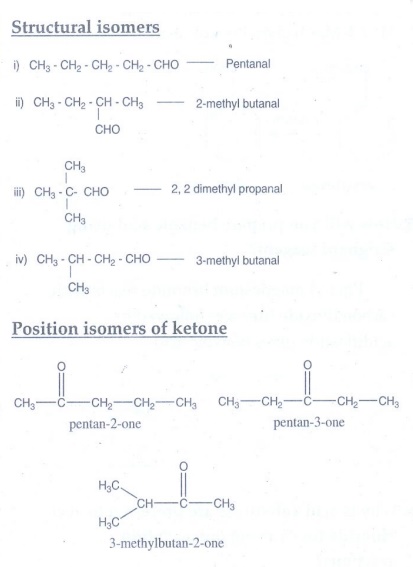
2. Write all
possible structural isomers and position isomers for the ketone represented by
the molecular formula C5H10O.
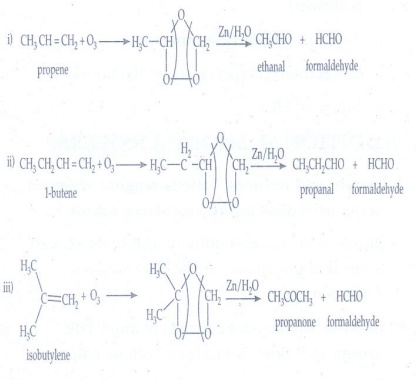
3. What happens
when the following alkenes are subjected to reductive ozonolysis?
1) propene 2) 1 -
Butene 3) Isobutylene
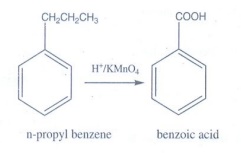
4. What happens
when n-propyl benzene is oxidised using H+ / KMnO4?
n-propyl
benzene is oxidised using H+ / KMnO4 gives benzoic acid
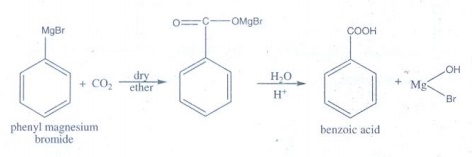
5. How will you
prepare benzoic acid using Grignard reagent?
Phenyl
magnesium bromide reacts with carbon dioxide (dry ice) followed by
acidification gives benzoic acid
6. Why is acid
anhydride are preferred to acyl chloride for carrying out acylation reactions?
i)
Acid anhydride is safer to use than acyl chloride. It is less corrosive and not
so readily hydrolysed (Its reaction with water is slower)
ii) Acid anhydride does not produce dangerous (corrosive and poisonous) fumes of HCl
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS
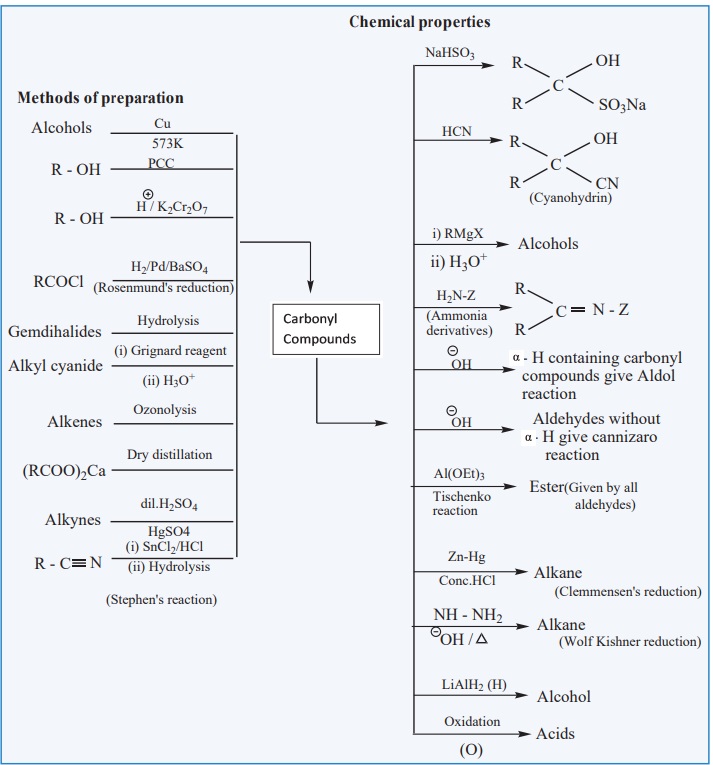
Related Topics