Preparation, Physical and Chemical properties - Acid Halides | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 12 : Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 12 : Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
Acid Halides
Acid Halides:
Methods of Preparation of acid chloride:
Acid chlorides are prepared from carboxylic acid by treating it with
anyone of the chlorinating agent such as SOCl2, PCl5, or
PCl3
1) By reaction with thionyl Chloride (SOCl2)
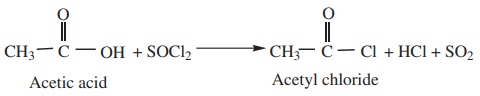
This method is superior to others as the by products being gases escape
leaving the acid chloride in the pure state.
Physical properties:
• They emit pale fumes of hydrogen chloride when
exposed to air on account of their reaction with water vapour.
• They are insoluble in water but slowly begins to dissolve due to
hydrolysis.
Chemical properties:
They react with weak nucleophiles such as water, alcohols, ammonia and
amines to produce the corresponding acid, ester, amide or substituted amides.
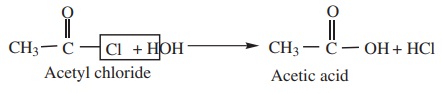
1) Hydrolysis.
Acyl
halides undergo hydrolysis to form corresponding carboxylic acids
2) Reaction with Alcohols (Alcoholysis) gives esters.
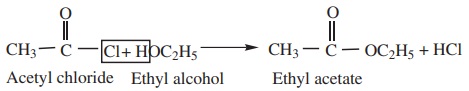
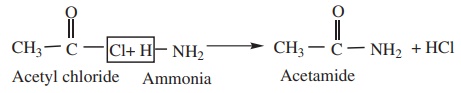
3) Reaction
with Ammonia (Ammonolysis) gives acid
amides.
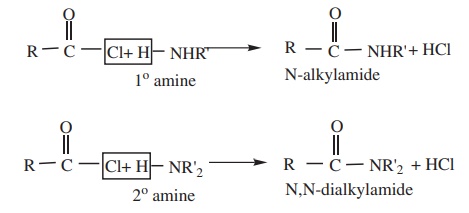
4) Reaction
with 1º and 2º Amines gives N-alkyl amides.
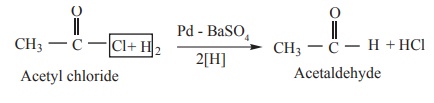
(5) Reduction.
(a) When reduced with hydrogen in the presence of
‘poisoned’ palladium catalyst, they form aldehydes. This reaction is called
Rosenmund reduction. We have already learnt this reaction under the preparation
of aldehydes
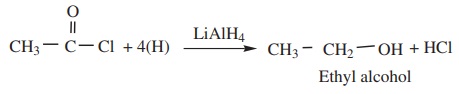
(b) When reduced with LiAlH4 gives primary alcohols.
Related Topics