Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 12 : Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
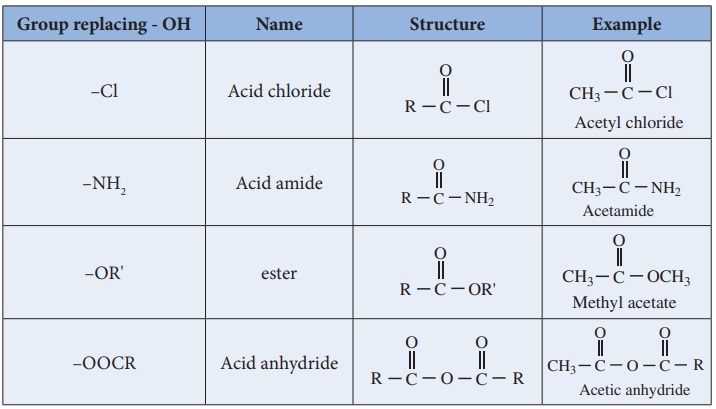
Functional derivatives of carboxylic acids
Functional derivatives of carboxylic acids
Compounds such as acid chlorides, amides, esters etc., are called
carboxylic acid derivatives because they differ from a carboxylic acid only in
the nature of the group or atom that has replaced the -OH group of carboxylic
acid.
Relative reactivity of Acid derivatives
The reactivity of the acid derivatives follows the order
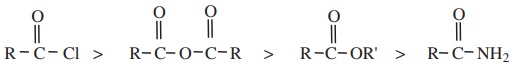
The above order of reactivity can be explained in terms of
i) Basicity of the leaving group ii) Resonance effect
i) Basicity of the leaving group
Weaker bases are good leaving groups. Hence acyl derivatives with weaker
bases as leaving groups (L) can easily rupture the bond and are more reactive.
The correct order of the basicity of the leaving group is 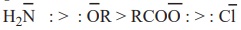
Hence the reverse is the order of reactivity.
ii) Resonance effect
Lesser the electronegativity of the group, greater would be the
resonance stabilization as shown below.
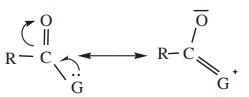
This effect makes the molecule more stable and reduces the R reactivity
of the acyl compound. The order of electronegativity of the leaving groups
follows the order – Cl > - OCOR > - OR > - NH2
Hence the order of reactivity of the acid derivatives with nucleophilic
reagent follows the order
acid halide > acid anhydride > esters > acid amides
Related Topics