Chapter: Biochemistry: Nucleic Acids
Structure of DNA
Structure of DNA
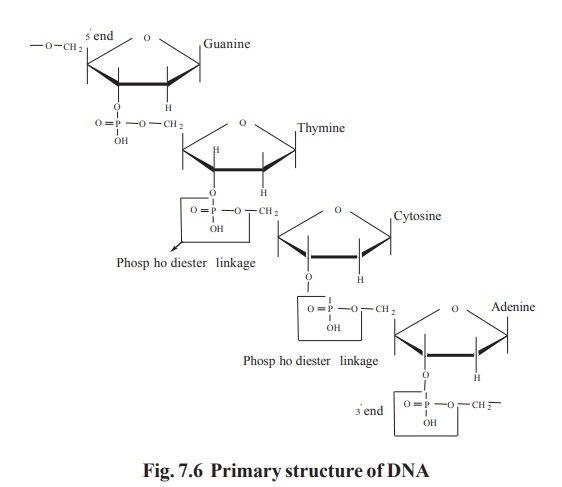
Primary structure
Nucleotide sequence of a nucleic acid is known
as its primary structure which confers individuality to the polynucleotide
chain. Polynucleotide chain has direction. They are represented in 5’---> 3’
and 3’----> 5’ directions. Each polynucleotide chain has 2 ends. The 5’ end
carrying a phosphate group and 3’ end carrying an unreacted hydroxyl group (Fig
7.6).
In 1953, J.D. Watson and F.H.C. Crick proposed
a precise three dimensional model of DNA structure based on model building
studies, base composition and X-ray diffraction studies. This model is
popularly known as the DNA double helix (Fig.7.7).
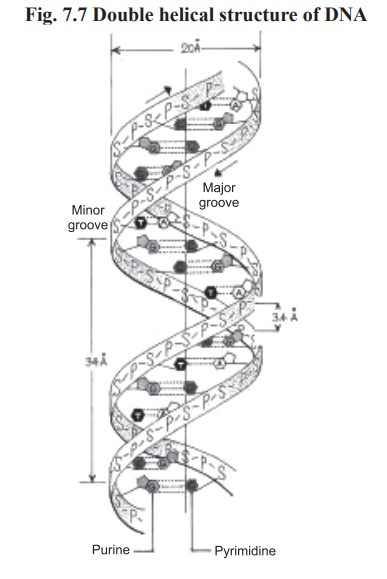
The purine bases present in DNA are adenine and
guanine and the pyrimidine bases present are thymine and cytosine. The purine
and pyrimidine bases of DNA carry genetic information where as the sugar and
phosphate groups perform the structural role.
Salient features of double helix
·
Two
polynuleotide chains are coiled around a central axis in the form of a right
handed double helix.
·
Each
polynucleotide chain is made up of 4 types of nucleotides. They are adenylate,
guanidylate, thymidylate and cytidinilate.
·
Each
polynucleotide chain has direction or polarity. Further each polynucleotide
chain has 5’ phosphorylated and 3’ hydroxyl ends.
·
The
backbone of each strand consists of alternating sugar and phosphate. The bases
project inwards and they are perpendicular to the central axis.
·
The 2
strands run in opposite direction (ie.) they are antiparallel.
·
The
strands are complementary to each other. Base composition of one strand is
complementary to the opposite strand. If adenine appears in one strand, thymine
is found in the opposite strand and vice versa. When guanine is found in one
strand, cytosine is present in the opposite strand and vice versa.
·
Bases of
opposite strands are involved in pairing. Pairing occurs through hydrogen
bonding and it is specific. Adenine pairs with thymine through two hydrogen bonds.
·
Guanine
pairs with cytosine with three hydrogen bonds.
·
Major
and minor grooves are present on the double helix. They arise because
glycosidic linkages of base pairs are not opposite to each other. Protein
interact with DNA through the minor and major grooves without disrupting the
DNA strands.
·
According
to Chargaff’s observation, the number of adenine base is equal to thymine base
and the number of quanine base is equal to number of cytocine base ie. A = T
and G = C. Also A + T = G + C and the ratio of A+T /G+C = nearly 1.0. The total
number of purine bases = the total number of pyrimidine bases.
Related Topics