Chapter: Biochemistry: Nucleic Acids: How Structure Conveys Information
The Covalent Structure of Polynucleotides
The Covalent Structure of
Polynucleotides
Polymers
can always be broken down into smaller and smaller units until we are left with
the smallest single unit of the polymer, called a monomer. The monomers of
nucleic acids are nucleotides. An
individual nucleotide consists of three parts-a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and
a phosphoric acid residue-all of which are covalently bonded together.
The order of bases in the nucleic acids of DNA contains the information necessary to produce the correct amino acid sequence in the cell’s proteins.
What are the structures and components of the nucleotides?
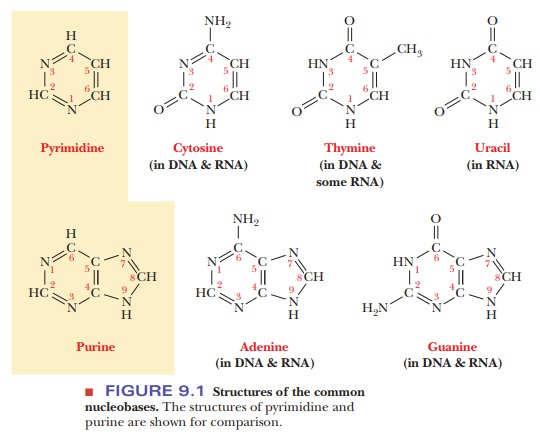
The nucleic acid bases (also called nucleobases) are of two types-pyrimidines and purines (Figure 9.1). In this case, the word base does not refer to an alkaline compound, such as NaOH; rather,
it refers to a one- or two-ring nitrogenous aromatic compound. Three pyrimidine bases (single-ring aromatic
compounds)-cytosine, thymine, and uracil-commonly occur. Cytosine is found
both in RNA and in DNA. Uracil occurs only in RNA. In DNA, thymine is
substituted for uracil; thymine is also found to a small extent in some forms
of RNA. The common purine bases
(double-ring aromatic compounds) are adenine
and guanine, both of which are
found in RNA and in DNA (Figure 9.1).In addition to these five commonly
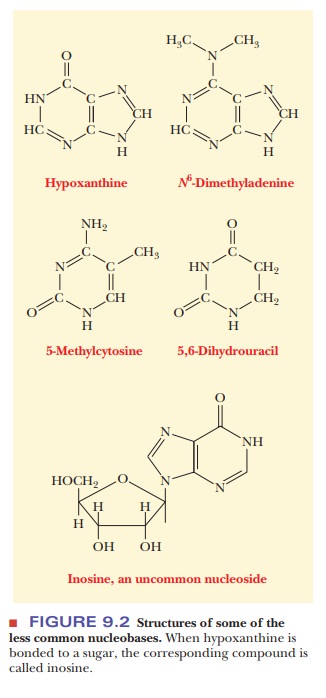
occurring bases, there are “unusual” bases, with slightly different structures,
that are found principally, but not exclusively, in transfer RNA (Figure 9.2).
In many cases, the base is modified by methylation.
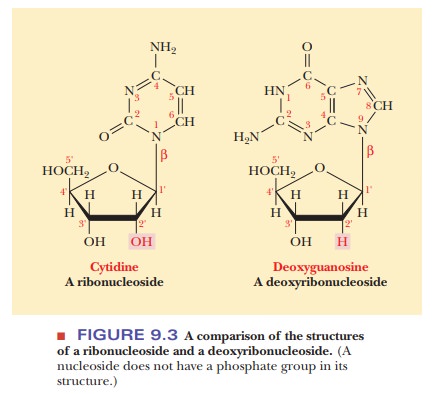
A nucleoside is a compound that consists
of a base and a sugar covalently linked together. It differs from a nucleotide
by lacking a phosphate group in its structure. In a nucleoside, a base forms a
glycosidic linkage with the sugar. Glycosidic linkages. If you wish to look now
at the material on the structure of sugars. For now, it is sufficient to say
that a glycosidic bond links a sugar
and some other moiety. When the sugar is β-D-ribose, the resulting compound is a ribonucleo-side; when the sugar isβ-D-deoxyribose, the resulting
compound is a deoxyri-bonucleoside (Figure
9.3). The glycosidic linkage is from the C-1' carbon of thesugar to the N-1
nitrogen of pyrimidines or to the N-9 nitrogen of purines. The ring atoms of
the base and the carbon atoms of the sugar are both numbered, with the numbers
of the sugar atoms primed to prevent confusion. Note that the sugar is linked
to a nitrogen in both cases (an N-glycosidic
bond).
When phosphoric acid is esterified to one of the hydroxyl groups of the sugar portion of a nucleoside, a nucleotide is formed (Figure 9.4). A nucleo-tide is named for the parent nucleoside, with the suffix -monophosphate added; the position of the phosphate ester is specified by the number of the carbon atom at the hydroxyl group to which it is esterified-for instance, adenosine 3'-monophosphate or deoxycytidine 5'-monophosphate.
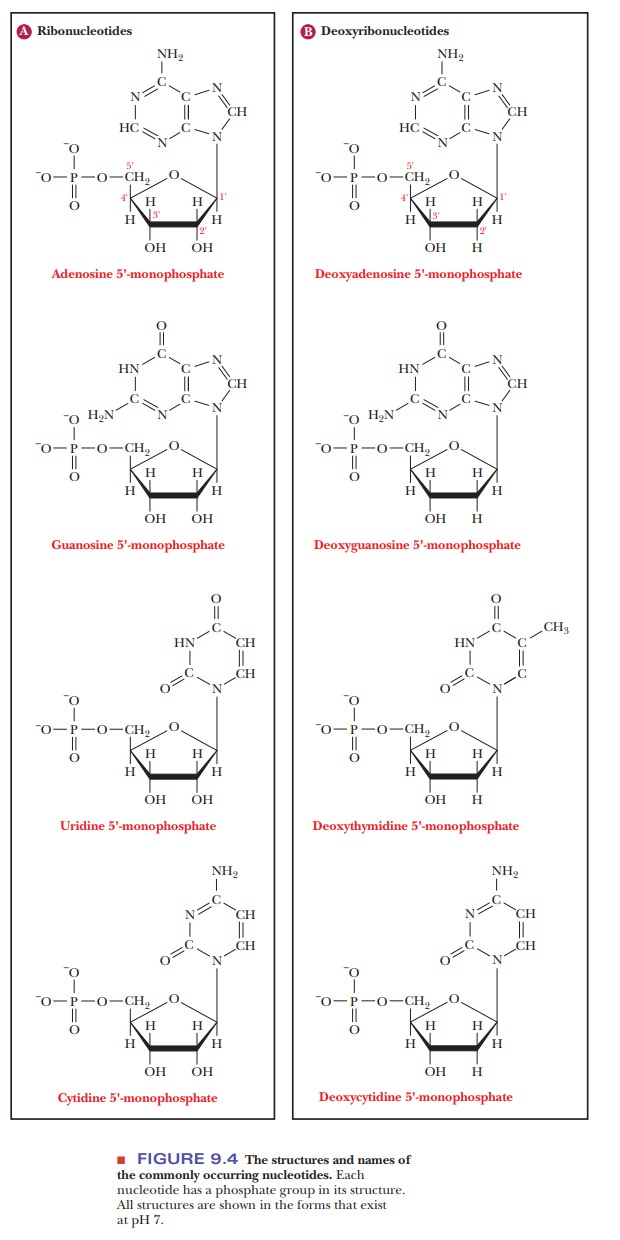
The 5'
nucleotides are most commonly encountered in nature. If additional phosphate groups
form anhydride linkages to the first phosphate, the corre-sponding nucleoside
diphosphates and triphosphates are formed. These compounds are also
nucleotides.
How do nucleotides combine to give nucleic acids?
The
polymerization of nucleotides gives rise to nucleic acids. The linkage between
monomers in nucleic acids involves formation of two ester bonds by phosphoric
acid. The hydroxyl groups to which the phosphoric acid is esterified are those
bonded to the 3' and 5' carbons on adjacent residues. The resulting repeated
linkage is a 3,'5'-phosphodiester bond.
The nucleotide residues of nucleic acids are numbered from the 5' end, which
normally carries a phosphate group, to the 3' end, which normally has a free
hydroxyl group.
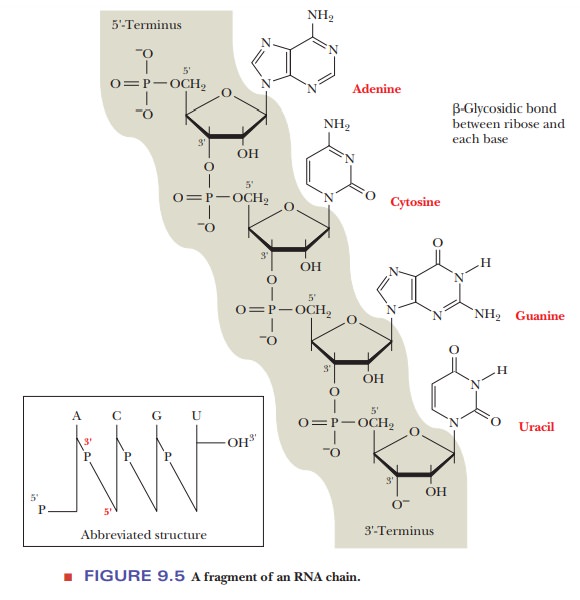
Figure
9.5 shows the structure of a fragment of an RNA chain. The sugar–phosphate backbone repeats itself down the length of the
chain. The most importantfeatures of the structure of nucleic acids are the
identities of the bases. Abbreviated forms of the structure can be written to convey
this essential information. In one system of notation, single letters, such as
A, G, C, U, and T, represent the individual bases. Vertical lines show the
positions of the sugar moieties to which the individual bases are attached, and
a diagonal line through the letter P represents a phospho-diester bond (Figure
9.5). However, an even more common system of notation uses only the single
letters to show the order of the bases. When it is necessary to indicate the
position on the sugar to which the phosphate group is bonded, the letter p is
written to the left of the single-letter code for the base to represent a 5'
nucleotide and to the right to represent a 3' nucleotide. For example, pA
signifies 5'-adenosine monophosphate (5'-AMP), and Ap signifies 3'-AMP. The
sequence of an oligonucleotide can be represented as pGpApCpApU or, even more
simply, as GACAU, with the phosphates understood.
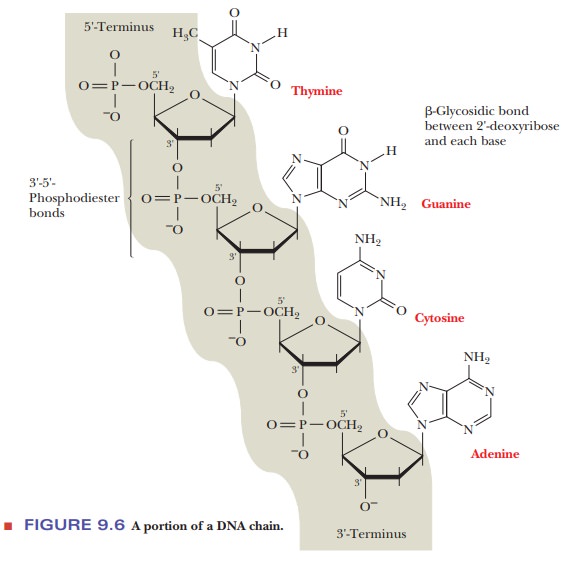
A portion of a DNA chain differs from the RNA chain just described only in the fact that the sugar is 2'-deoxyribose rather than ribose (Figure 9.6). In abbreviated notation, the deoxyribonucleotide is specified in the usual man-ner. Sometimes a letter d is added to indicate a deoxyribonucleotide residue; for example, dG is substituted for G, and the deoxy analogue of the ribooligo-nucleotide in the preceding paragraph would be d(GACAT). However, given that the sequence must refer to DNA because of the presence of thymine, the sequence GACAT is not ambiguous and would also be a suitable abbreviation.
Summary
Two kinds of nitrogen-containing nucleobases,
pyrimidines and purines, are joined to sugars to form nucleosides.
The sugar is deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in
RNA.
Addition of phosphate groups to nucleotides
gives rise to nucleotides, which are the monomers of nucleic acids.
When nucleotides are joined by phosphodiester
bonds, they form a sugar–phosphate backbone, giving rise to DNA and RNA.
The
sequence of bases is a very important feature of the primary structure of
nucleic acids, because the sequence is the genetic information that ultimately
leads to the sequence of RNA and protein.
Related Topics