Chapter: Biochemistry: Nucleic Acids
Purine bases: Structure and Properties
Purine bases
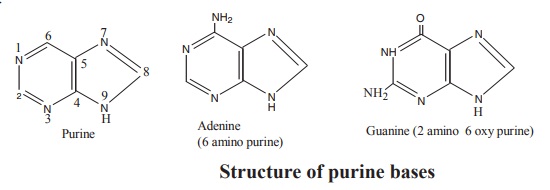
Structure of purine bases
Purine bases are derived from the parent
compound purine. Purine contains the heterocyclic ring system. Fusion of the
pyrimidine ring with imidazole yields the purine ring (Fig. 7.2).
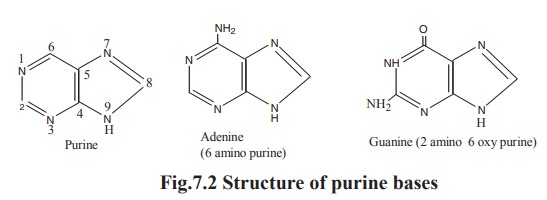
The purine bases present in nucleic acids are
adenine and guanine. Other purine bases are hypoxanthine and xanthine. They are
intermediates in the formation of adenine and guanine nucleotides.
Properties of purine bases
·
Purine
bases are sparingly soluble in water.
·
They
absorb light in UV region at 260 nm. This property is used for the detection of
and the quantification of purine nucleotides.
·
They are
capable of forming hydrogen bonds.
·
They
exhibit keto-enol tautomerism at body pH.
Related Topics