Chapter: Electronic Devices : Power Devices and Display Devices
Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR)
SILICON CONTROLLED RECTIFIER (SCR)
Introduction
The SCR
stand for Silicon Control Rectifier, it is used in industries because it can
handle high values of current and voltage.
Three
terminals
·
Anode - P-layer
·
Cathode - N-layer (opposite end)
·
Gate - P-layer near the cathode
Three
junctions - four layers
Connect
power such that the anode is positive with respect to the cathode - no current
will flow
A silicon
controlled rectifier i s a semiconductor device that acts as a true electronic
switch. It can change alternating current and at the same time can control the
amount of power fed to the load. SCR combines the features of a rectifier and a
transistor.
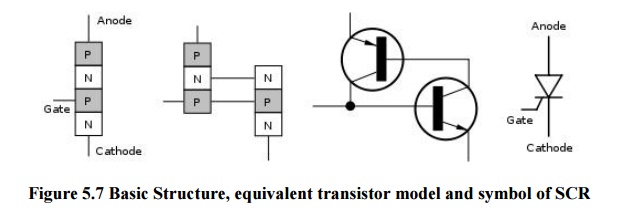
Figure 5.7 Basic Structure,
equivalent transistor model and sy mbol of SCR
Construction
When a pn junction i s added to a junction
transistor the resulting three pn junction device is called a SCR. ordin ary
rectifier (pn) and a junction transistor (npn) combined in one unit to form
pnpn device.
Three terminals are taken : one from the outer p-
type material called anode a second from the outer n- type material called
cathode K and the third from the base o f transistor called Gate. GSCR is a
solid state e quivalent of thyratron. The gate anode and cathode of SCR
correspond to the grid plate and cathode of thyratron SCR is called thyristor.
Working Principle
Load is connected in series with anode the anode is
always ke pt at positive potential w.r.t cathode.
1 SCR Operation / Working
The
Silicon Control Rectifier SCR start conduction when it is forwa rd biased. For
this purpose the cathode is kept at negative and anode at positive. When
positivee clock pulse is applied at the gate the SCR turns ON.
When
forward bias volt age is applied to the Silicon Control Rectifier SCR, the
junction J1 and J3 become forward bias w hile the junction J2 become reverse
bias.
When we
apply a clock pulse at the gate terminal, the junction J2 become forward bias
and the Silicon Control Rectifier SCR start conduction.The Silicon Control
Rectifier SCR turn ON and OFF very quickly, At the OFF state the Silicon
Control Rectifier SCR provide infinity resistance and in ON state, it offers
very low resistance, which is in the range of 0.01O to 1O.
2 SCR Firing & Triggering
The
Silicon Control Rectifier SCR is normally operated below the forward break over
voltage (VBO). To turn ON the Silicon Control Rectifier SCR we apply clock
pulse at the gate terminal which called triggering of Silicon Control
Rectifier, but when the Silicon Control Rectifier SCR turned ON, now if we
remove the triggering voltage, the Silicon Control Rectifier SCR will remain in
ON state. This voltage is called Firing voltage.
3 When Gate is Open
No voltage applied to the gate, j2 is reverse
biased while j1 and j3 are FB . J1 and J3 is just in npn transistor with base
open .no current flows through the load RL and SCR is cut off. If the applied
voltage is gradually increased a stage is reached when RB junction J2 breakdown
.the SCR now conducts heavily and is said to be ON state. the applied voltage
at which SCR conducts heavily without gate voltage is called Break over
Voltage.
4 When Gate is Positive w.r.to
Cathode:-
The SCR can be made to conduct heavily at smaller
applied voltage by applying small positive potential to the gate.J3 is FB and
J2 is RB the electron from n type material start moving across J3 towards left
holes from p type toward right. Electrons from j3 are attracted across junction
J2 and gate current starts flowing. as soon as gate current flows anode current
increases. the increased anode current in turn makes more electrons available
at J2 breakdown and SCR starts conducting heavily. the gate loses all control
if the gate voltage is removed anode current does not decrease at all. The only
way to stop conduction is to reduce the applied voltage to zero.
Break over Voltage
It is the minimum forward voltage gate being open
at which SCR starts conducting heavily i.e turned on.
Peak Reverse Voltage ( PRV)
It is the
maximum reverse voltage applied to an SCR without conducting in the reverse
direction.
Holding Current
It is the maximum anode current gate being open at
which SCR is turned off from on conditions.
Forward Current Rating
It is the maximum anode current that an SCR is
capable of passing without destruction
Circuit Fusing Rating
It is the
product of of square of forward surge current and the time of duration of the
surge.
Turning OFF methods of Silicon Control Rectifier -
SCR
There are
two methods through which Silicon Control Rectifier SCR can be turned OFF,
1 Anode current interruption method
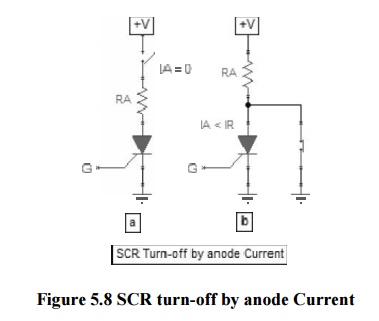
Figure 5.8 SCR turn-off by anode
Current
In this
method a paralle l or a series switch is used to turn OFF the S ilicon Control
Rectifier (SCR electronics) by turning O FF the switch.
2 Forced Commutation method
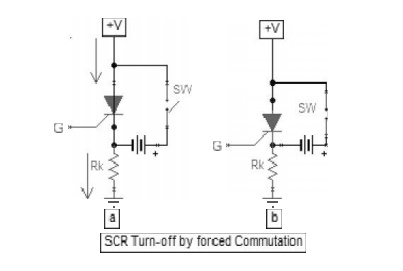
Figure 5.8 SCR turn-off by forced
communicatio n
In this
method a revers ed polarity battery is connected, so the cur rent through the
Silicon Control Rectifier SCR is reduced and it turn OFF.
V-I Characteristics of SCR
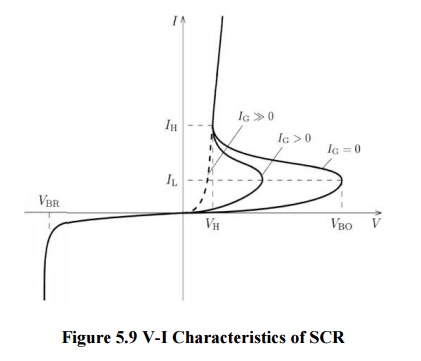
Figure 5.9 V-I Characteristics of SCR
1 Forward Characteristics
When
anode is +ve w.r.t cathode the curve between V & I is called Forward
characteristics. OABC is the forward characteristics of the SCR at Ig =0. if
the supplied voltage is increased from zer o point A is reached .SCR starts
conducti ng voltage across SCR suddenly drops (dotted curve AB) most of supply
voltage appears across RL.
2 Reverse Characteristi cs
When anode is –ve w.r.t cathode the curve b/w
V&I is known as reverse characteristics reverse voltage come across S CR
when it is operated with ac supply reve rse voltage is increased anode current
remains small avalanche breakdown occurs and SCR start s conducting heavily is
known as reverse breakdown voltage.
3 Application
·
SCR as a switch
·
SCR Half and Full wave rectifier
·
SCR as a static contactor
·
SCR for power control
·
SCR for speed control of d.c.shunt motor
·
Over light detector
Related Topics