Chapter: Electronic Devices : Power Devices and Display Devices
Optocoupler
OPTOCOUPLER
In
electronics, an opto-isolator, also called an optocoupler, photocoupler, or
optical isolator, is a component that transfers electrical signals between two
isolated circuits by using light. Opto - isolators prevent high voltages from
affecting the system receiving the signal. Commercially available
opto-isolators withstand input-to-output voltages up to 10 kV and voltage
transients with sppeds upto 10kV/µs. A common type of opto-isolator consists of
an LED and a phototransistor in the same package. Opto-isolators are usually
used for transmission of digital (on/off) signals, but some techniques allow
use with analog (proportional) signals.
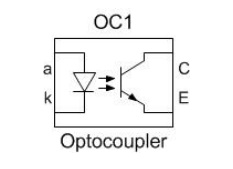
Figure 5.46 Optocoupler Symbol
An opto-isolator contains a source (emitter) of
light, almost always a near infrared light-emitting diode (LED), that converts
electrical input signal into light, a closed optical channel (also called
dielectrical channel), and a photosensor, which detects incoming light and
either generates electric energy directly, or modulates electric current
flowing from an external power supply.The sensor can be a photoresistor, a
photodiode, a phototransistor, a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) or a triac.
Because LEDs can sense light in addition to emitting it, construction of
symmetrical, bidirectional opto-isolators is possible.
An optocoupled solid state relay contains a
photodiode opto-isolator which drives a power switch, usually a complementary
pair of MOSFETs. A slotted optical switch contains a source of light and a
sensor, but its optical channel is open, allowing modulation of light by
external objects obstructing the path of light or reflecting light into the
sensor.
Related Topics