Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | Physics - Short Answer Questions | 12th Physics : UNIT 8 : Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Chapter: 12th Physics : UNIT 8 : Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Short Answer Questions
II Short Answer Questions
1. Why do metals have a large number of free electrons?
In
metals, outer most electrons are loosly bound with nucleus.
Even
at room temperature, these electrons are freely moving with in the metal. These
electrons are called free electrons. Hence metals having large number of free
electrons.
2. Define work function of a metal. Give its unit.
The
minimum energy needed for an electron to escape from the metal surface is
called work function of that metal (ŽĢo).
Its
unit is Joule (or) eV.
3. What is photoelectric effect?
The
ejection of electrons from a metal plate
when illuminated by light or any other electromagnetic radiation of
suitable wavelength (or) frequency is called photoelectric effect.
4. How does photocurrent vary with the intensity of the incident light?
The
photocurrent increases as intensity of light increase. Since number of
electrons emitted per second from the surface is directly proportional to the
intensity of the light.
5. Give the definition of intensity of light and its unit.
According
to quantum concept, intensity of light of given wavelength is defined as the number of photons incident per unit
area per unit time, with each photon having same energy. Its unit is Wm-2.
6. How will you define threshold frequency?
For
a given surface, the emission of
photoelectrons takes place only if the frequency of incident light is greater than a certain minimum frequency.
The minimum frequency is called threshold frequency.
7. What is a photo cell? Mention the different types of photocells.
Photocell
is a device which converts light energy into electrical energy. Its Types are
(i)
Photo emissive cell
(ii)
Photo voltaic cell
(iii)
Photo conductive cell
8. Write the expression for the de Broglie wavelength associated with a charged particle of charge q and mass m, when it is accelerated through a potential V.
A
charged particle of charge q and mass m is accelerated through a potential
difference of
V.
The kinetic energy acquired by the charge is
1/2
mv2 = qV
Ōł┤ The speed v of the charge is
v = ŌłÜ[2qV / m]
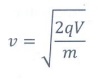
The
momentum of the charge is
p = mv = ŌłÜ[2mqV]
The
de Broglie wavelength of the charge is
╬╗ =h / mv
= h / p
Ōł┤ ╬╗ = h/ ŌłÜ[2mqV]
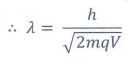
9. State de Broglie hypothesis.
All
material particles like electrons, protons, neutrons in motion are associated
with waves. These waves are called de Broglie waves or matter waves.
10. Why we do not see the wave properties of a baseball?
The
de broglie wavelength
╬╗
= h/p = h/mv
The
average speed of the base ball is about 2.24 m/s.
The
mass of the ball is 0.625 kg.
= [6.62 ├Ś 10-34 ] / [0.625 ├Ś 2.24]
╬╗
= 4.729 x 10-34m
The
wavelength of the base ball is almost very very small. So, we cannot see the
wave properties of the base ball.
11. A proton and an electron have same kinetic energy. Which one has greater de Broglie wavelength. Justify.
The
de Broglie wavelength associated with a charge isŌĆā
╬╗ = h/ ŌłÜ(2mqV)
The
charge of an electron and a proton is same.
ie.,
q = e
The
kinetic energy (K) = eV
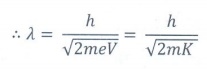
The
kinetic energy of the proton and electron is same. So the de Broglie wavelength
depends only the mass of the particle.
The
wavelength is inversely proportional to
the square root of the mass.
╬╗ ŌłØ 1/ŌłÜm
Ōł┤ ╬╗e
/ ╬╗p = ŌłÜ[mp /me]
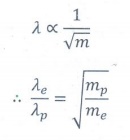
The
mass of an electron is very lesser
than that of proton.
So
the electron has greater de Broglie
wavelength, than proton. ie., ╬╗ e
> ╬╗ p
12. Write the relationship of de Broglie wavelength ╬╗ associated with a particle of mass m in terms of its kinetic energy K.
The
de Broglie wavelength of a particle is
╬╗ = h/mv
= h/p
p is the
momentum of the particle. The kinetic energy of the particle (K) = ┬Į mv2
= p2 /2m
Ōł┤ The momentum (p) = ŌłÜ(2mK)
The
de Broglie wavelength of the particle is ╬╗
= h / ŌłÜ(2mK)
13. An electron and an alpha particle have same kinetic energy. How are the de Broglie wavelengths associated with them related?
The
de Broglie wavelength of an electron is

The
de Broglie wavelength of an alpha particle is

The
electron and the alpha particle have same kinetic energy. ie., Ke =
Ka
The
ratio of ╬╗e and ╬╗ŌłØ is
╬╗e / ╬╗ŌłØ = ŌłÜ[mŌłØ/me]
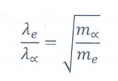
The
mass of the electron is very lesser than
that of the alpha particle. ie., me<<m╬▒
Therefore
the de Broglie wavelength of an electron is greater than that of an alpha
particle. ie., ╬╗e > ╬╗ŌłØ
14. Define stopping potential?
Stopping
potential is that the value of the negative potential given to the collecting
electrode A which is just sufficient to stop the most energetic photoelectrons
emitted and make the photocurrent zero.
The
stopping potential is indepentent of intensity of the incident light.
15. What is surface barrier?
The
potential barrier which prevents the electrons from leaving the metallic
surface is called surface barrier.ŌĆā
16. Mention the two features of X-ray spectra, not
explained by classical electromagnetic theory.
i)
For a given accelerating voltage, the lower limit for the wavelength of
continuous X- ray spectra is same for all targets. This minimum wavelength is
called cut-off wavelength.
ii)
The intensity of X-ray is significantly increased at certain well-defined
wavelengths.
17. What is Bremsstrahlung?
When
a fast moving electron penetrates and approaches a target nucleus, the
interaction between the electron and the nucleus either accelerates or
decelerates it which results in a change of path of the electron. The radiation
produced from such decelerating electron is called Bremsstrahlung or braking
radiation.
Related Topics