Formula, Significance, Experiment - Respiratory Quotient (RQ) in Plant | 11th Botany : Chapter 14 : Respiration
Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 14 : Respiration
Respiratory Quotient (RQ) in Plant
Respiratory Quotient (RQ)
The ratio
of volume of carbon dioxide given out and volume of oxygen taken in during
respiration is called Respiratory Quotient or Respiratory ratio. RQ value depends upon respiratory substrates
and their oxidation.
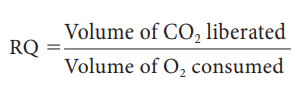
1. The
respiratory substrate is a carbohydrate, it will be completely oxidised in
aerobic respiration and the value of the RQ will be equal to unity.
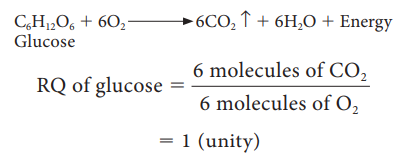
2. If the
respiratory substrate is a carbohydrate it will be incompletely oxidised when
it goes through anaerobic respiration and the RQ value will be infinity.
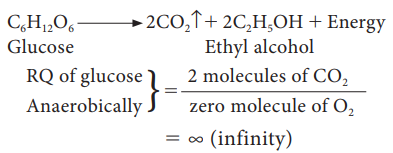
3. In
some succulent plants like Opuntia, Bryophyllum carbohydrates are partially oxidised to organic acid, particularly
malic acid without corresponding release of CO2 but O2 is
consumed hence the RQ value will be zero.
4. When
respiratory substrate is protein or fat, then RQ will be less than unity.
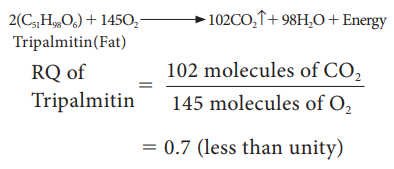
5. When
respiratory substrate is an organic acid the value of RQ will be more than
unity.
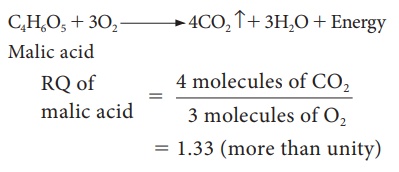
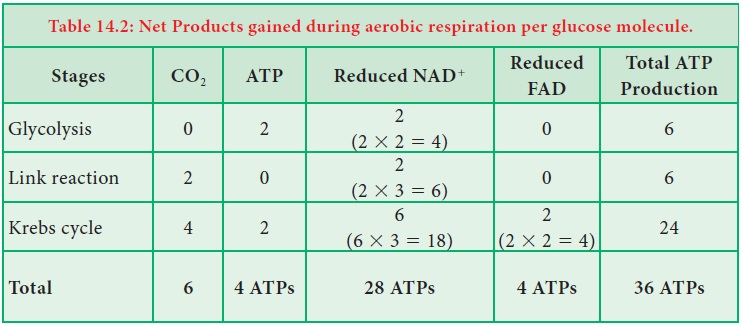
Significance of RQ
1.
RQ value indicates which type of respiration occurs
in living cells, either aerobic or anaerobic.
2.
It also helps to know which type of respiratory
substrate is involved.
Red colour in various parts of plants is due to
the presence of anthocyanin,
synthesis of which require more O2 than CO2 evolved. RQ
will be less than one.
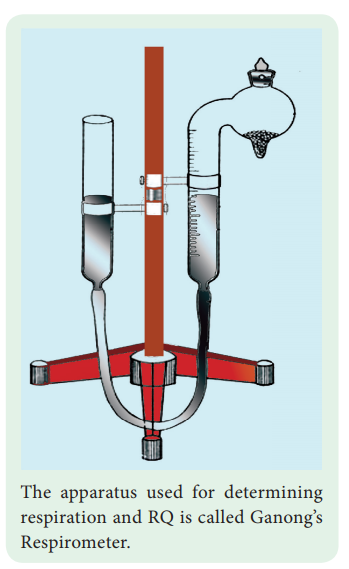
Experiment to demonstrate the production of CO2 in aerobic respiration
Take small quantity of any seed (groundnut or bean seeds) and
allow them to germinate by imbibing them. While they are germinating place them
in a conical flask. A small glass tube containing 4 ml of freshly prepared
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution is hung into the conical flask with the help
of a thread and tightly close the one holed cork (Figure 14.11). Take a bent
glass tube, the shorter end of which is inserted into the conical flask through
the hole in the cork, while the longer end is dipped in a beaker containing
water. Observe the position of initial water level in bent glass tube. This experimental
setup is kept for two hours and the seeds were allowed to germinate. After two
hours, the level of water rises in the glass tube. It is because, the CO2
evolved during aerobic respiration by germinating seeds will be absorbed by KOH
solution and the level of water will rise in the glass tube.
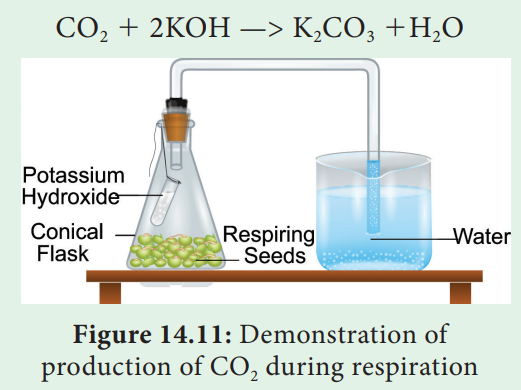
In the case of groundnut or bean seeds, the rise of water is
relatively lesser because these seeds use fat and proteins as respiratory
substrate and release a very small amount of CO2. But in the case of
wheat grains, the rise in water level is greater because they use carbohydrate
as respiratory substrate. When carbohydrates are used as substrate, equal
amounts of CO2 and O2 are evolved and consumed.
Activity
Take a test tube with some germinated seeds and fill with water.
Keep this test tube after some time until liberation of CO2. When the carbon dioxide from
respiration is mixed to water, carbonic acid (H2CO3) is
produced. Therefore, as more carbon dioxide is released, the solution becomes
more acidic. You will see changes in pH as an indicator using blue litmus paper
changed into red that respiration has occurred
CO2+H2O - > H2CO3
Related Topics