Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 14 : Respiration
Glycolysis - Stages of Respiration in plants
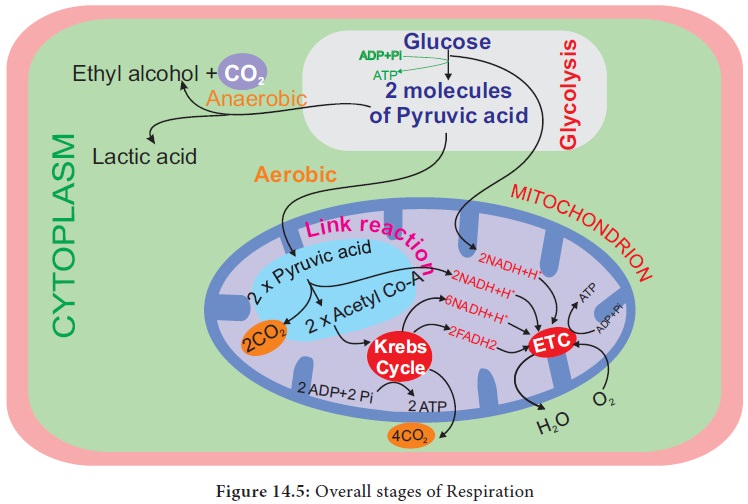
Glycolysis
(Gr: Glykos 5 Glucose, Lysis 5 Splitting) Glycolysis is a
linear series of reactions in which 6-carbon glucose is split into two
molecules of 3-carbon pyruvic acid. The enzymes which are required for
glycolysis are present in the cytoplasm (Figure 14.6). The reactions of
glycolysis were worked out in yeast cells by three scientists Gustav Embden (German), Otto Meyerhoff
(German) and J Parnas (Polish)
and so it is also called as EMP pathway.
It is the first and common stage for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It
is divided into two phases.
1.
Preparatory
phase or endergonic phase or hexose
phase (steps 1-5).
2.
Pay off
phase or oxidative phase or exergonic
phase or triose phase (steps 6-10).
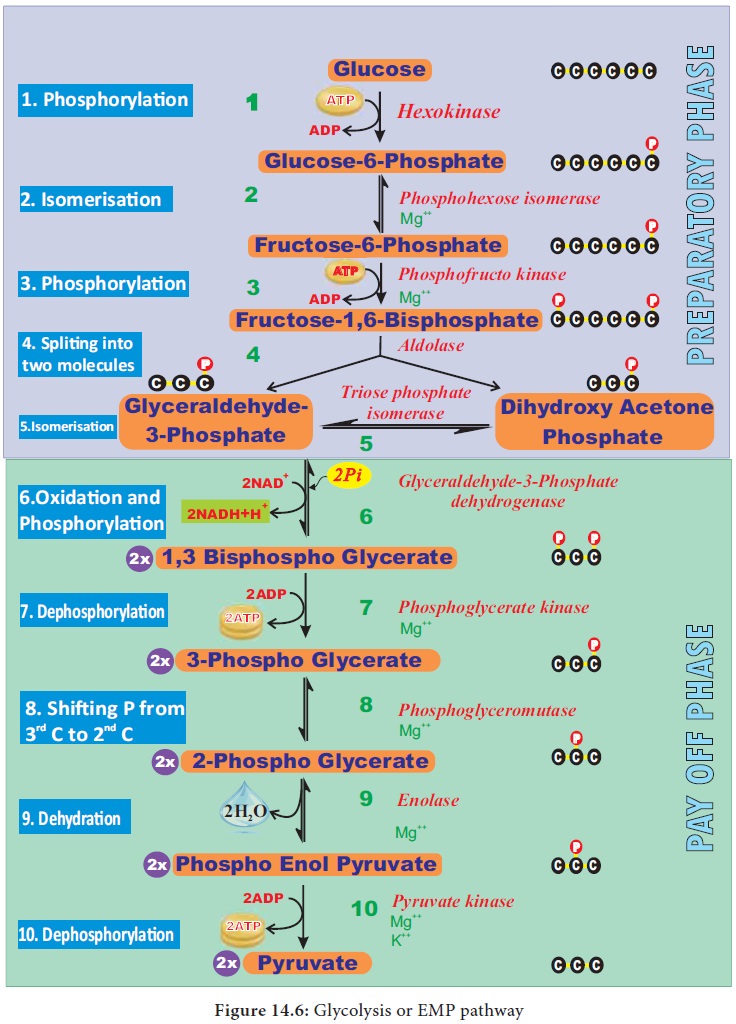
1. Preparatory phase
Glucose
enters the glycolysis from sucrose which is the end product of photosynthesis.
Glucose is phosphorylated into glucose-6-phosphate by the enzyme hexokinase,
and subsequent reactions are carried out by different enzymes (Figure 14.6). At
the end of this phase fructose-1, 6 - bisphosphate is cleaved into
glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate and dihydroxy acetone phosphate by the enzyme
aldolase. These two are isomers. Dihydroxy acetone phosphate is isomerised into
glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate by the enzyme triose phosphate isomerase, now two
molecules of glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate enter into pay off phase. During
preparatory phase two ATP molecules are consumed in step-1 and step-3 (Figure
14.6).
2. Pay off phase
Two
molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate oxidatively phosphorylated into two
molecules of 1,3 - bisphospho glycerate. During this reaction 2NAD1 is reduced
to 2NADH + H+ by glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate dehydrogenase at step
6. Further reactions are carried out by
different enzymes and at the end two molecules of pyruvate are produced. In
this phase, 2ATPs are produced at step 7 and 2 ATPs at step10 (Figure 14.6).
Direct transfer of phosphate moiety from substrate molecule to ADP and is
converted into ATP is called substrate
phosphorylation or direct
phosphorylation or trans phosphorylation . During the reaction
at step 9, 2phospho glycerate
dehydrated into Phospho enol pyruvate a water molecule is removed by the enzyme
enolase. As a result, enol group is formed within the molecule. This process is
called Enolation.
3. Energy Budget
In the
pay off phase totally 4ATP and 2NADH + H+ molecules are produced.
Since 2ATP molecules are already consumed in the preparatory phase, the net
products in glycolysis are 2ATPs and 2NADH + H+.
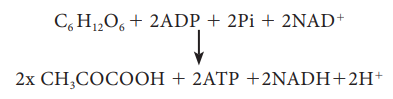
The
overall net reaction of glycolysis
Related Topics