Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 14 : Respiration
Fermentation - Anaerobic Respiration in Plants
Anaerobic Respiration
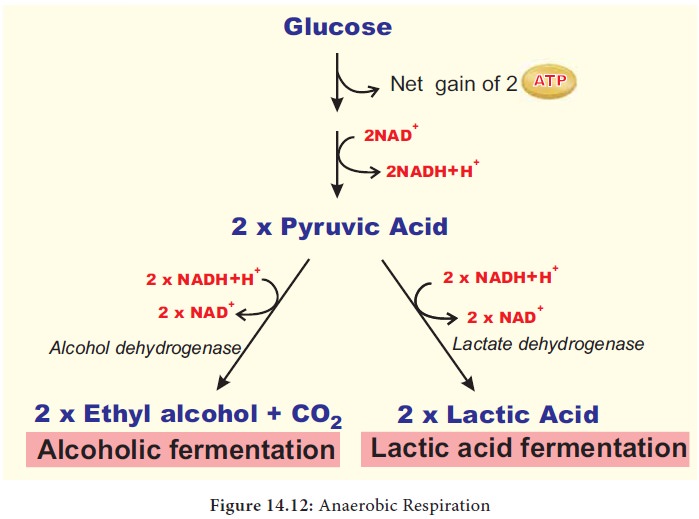
Fermentation
Some
organisms can respire in the absence of oxygen. This process is called fermentation or anaerobic respiration (Figure 14.12). There are three types of
fermentation:
1.
Alcoholic fermentation
2.
Lactic acid fermentation
3.
Mixed acid fermentation
1.
Alcoholic
fermentation
The cells
of roots in water logged soil respire by alcoholic fermentation because of lack
of oxygen by converting pyruvic acid into ethyl alcohol and CO2.
Many species of yeast (Saccharomyces)
also respire anaerobically. This process takes place in two steps:
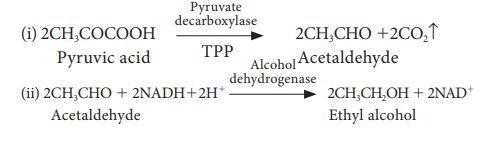
Industrial uses of alcoholic fermentation:
1.
In bakeries, it is used for preparing bread, cakes,
biscuits.
2.
In beverage industries for preparing wine and
alcoholic drinks.
3. In
producing vinegar and in tanning, curing of leather.
4. Ethanol is used to make gasohol (a fuel that is used for cars in Brazil).
2. Lactic acid fermentation
Some
bacteria (Bacillus), fungi and
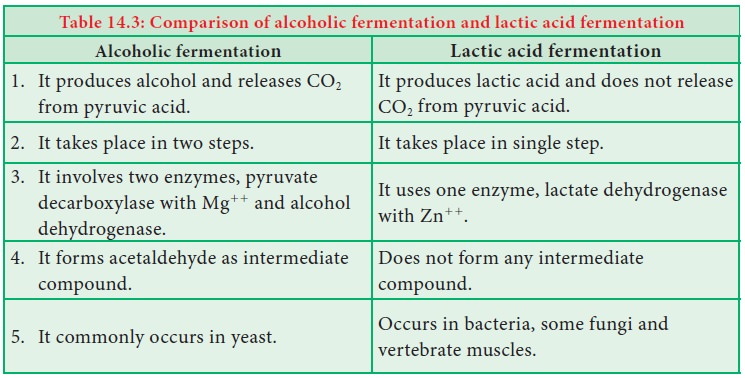
muscles of vertebrates produce lactic acid from pyruvic acid (Table 14.3).
3. Mixed acid fermentation
This type of fermentation is a characteristic feature of Enterobacteriaceae and results in the formation of lactic acid, ethanol, formic acid and gases like CO2 and H2.
Comparison of alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation
Characteristics of Anaerobic Respiration
1.
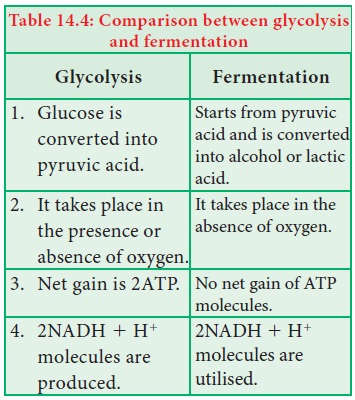
Anaerobic respiration is less efficient than the
aerobic respiration (Figure 14. 12) (Table 14.4).
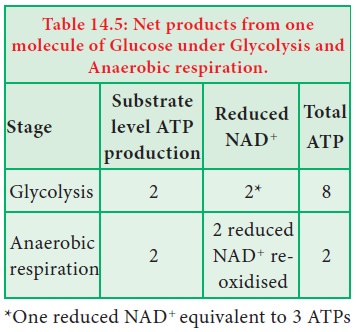
2.
Limited number of ATP molecules is generated per
glucose molecule (Table 14.5).
3.
It is characterized by the production of CO2
and it is used for Carbon fixation in photosynthesis.
Comparison between glycolysis and fermentation
Check your grasp!
•
Why Microorganisms respire
anaerobically?
•
Does anaerobic respiration take place
in higher plants?
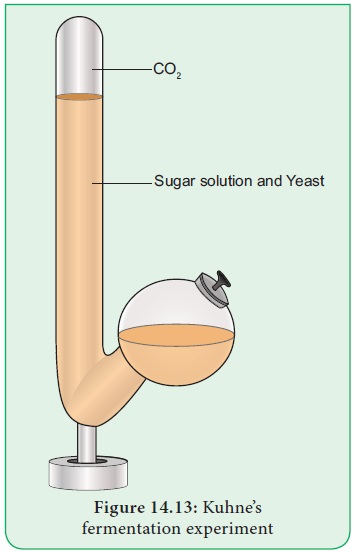
Demonstration of alcoholic fermentation
Take a Kuhne’s fermentation tube which consists of an upright
glass tube with side bulb. Pour 10% sugar solution mixed with baker’s yeast
into the fermentation tube the side tube is filled plug the mouth with lid.
After some time, the glucose solution will be fermented. The solution will give
out an alcoholic smell and level of solution in glass column will fall due to
the accumulation of CO2 gas. It is due to the presence of zymase
enzyme in yeast which converts the glucose solution into alcohol and CO2
. Now introduce a pellet of KOH into the tube, the KOH will absorb CO2
and the level of solution will rise in upright tube (Figure 14.13).
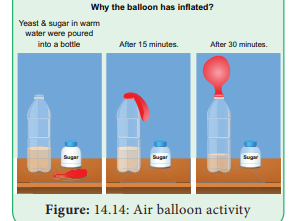
Activity
Take a bottle filled with warm water mixed with baker’s yeast
and sugar. After some time, you will notice water bubbling as yeast produces
carbon dioxide. Attach a balloon to the mouth of the bottle. After 30 minutes
you’ll notice balloon standing upright (Figure 14.14).
Related Topics