Plant Respiration - Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle or TCA cycle | 11th Botany : Chapter 14 : Respiration
Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 14 : Respiration
Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle or TCA cycle
Krebs cycle or Citric acid
cycle or TCA cycle:
Two
molecules of acetyl CoA formed from link reaction now enter into Krebs cycle.
It is named after its discoverer, German Biochemist Sir Hans Adolf Krebs (1937). The enzymes necessary for TCA cycle
are found in mitochondrial matrix except succinate dehydrogenase enzyme which
is found in mitochondrial inner membrane (Figure 14.7).
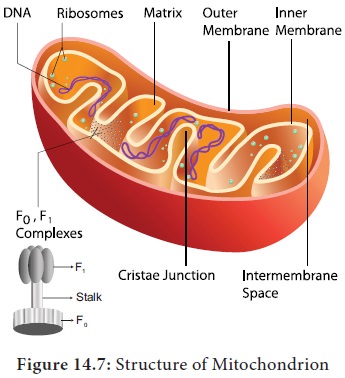
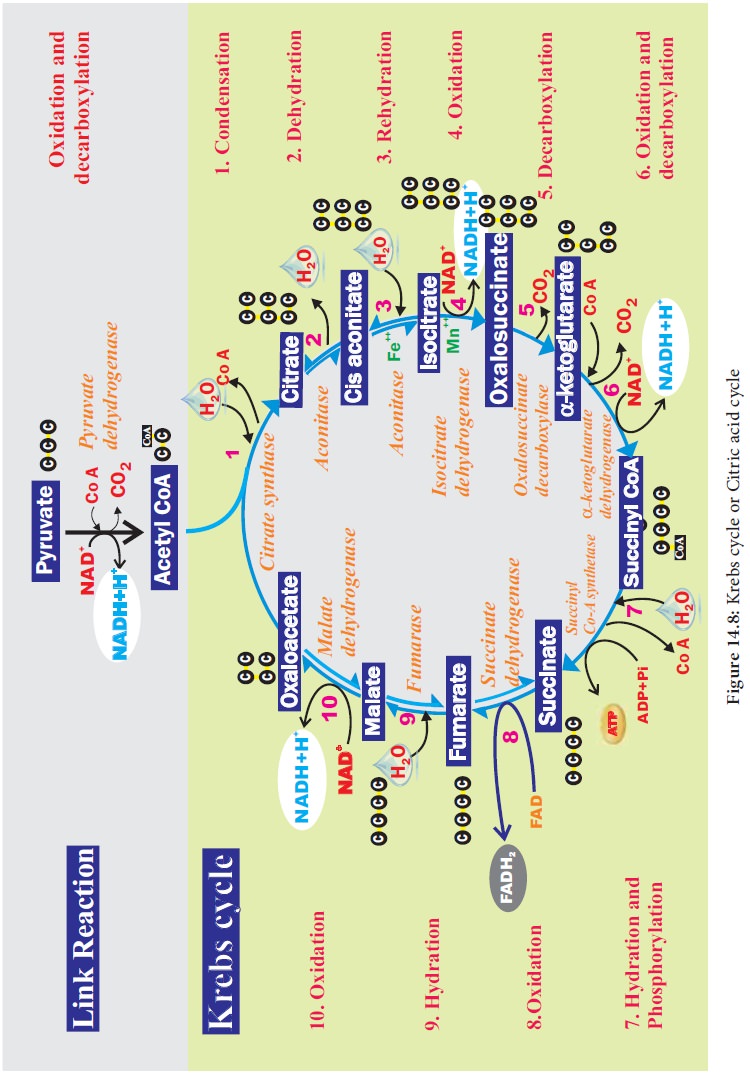
TCA cycle starts with condensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate in the presence of water to yield citrate or citric acid. Therefore, it is also known as Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) or Tri Carboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle. It is followed by the action of different enzymes in cyclic manner. During the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinate by the enzyme succinyl CoA synthetase or succinate thiokinase, a molecule of ATP synthesis from substrate without entering the electron transport chain is called substrate level phosphorylation. In animals a molecule of GTP is synthesized from GDP1Pi. In a coupled reaction GTP is converted to GDP with simultaneous synthesis of ATP from ADP+Pi. In three steps (4, 5, 9) in this cycle NAD1 is reduced to NADH+ H+ and at step 7 (Figure14.8) where FAD is reduced to FADH2.
The
summary of link reaction and Krebs cycle in Mitochondria is
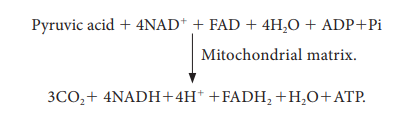
Two
molecules of pyruvic acid formed at the end of glycolysis enter into the
mitochondrial matrix. Therefore, Krebs cycle is repeated twice for every
glucose molecule where two molecules of pyruvic acid produces six molecules of
CO2, eight molecules of NADH + H+, two molecules of FADH2
and two molecules of ATP.
1. Significance of Krebs cycle:
1.
TCA cycle is to provide energy in the form of ATP
for metabolism in plants.
2.
It provides carbon skeleton or raw material for
various anabolic processes.
3.
Many intermediates of TCA cycle are further
metabolised to produce amino acids, proteins and nucleic acids.
4.
Succinyl CoA is raw material for formation of
chlorophylls, cytochrome, phytochrome and other pyrrole substances.
5.
α-ketoglutarate and oxaloacetate undergo reductive
amination and produce amino acids.
6.
It acts as metabolic sink which plays a central
role in intermediary metabolism.
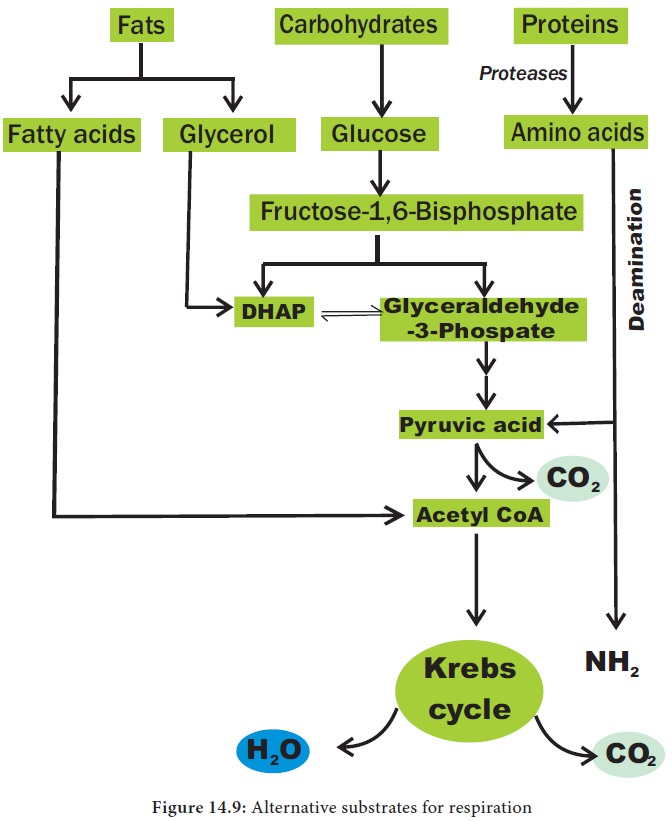
2. Amphibolic nature
Krebs
cycle is primarily a catabolic pathway, but it provides precursors for various
biosynthetic pathways there by an anabolic pathway too. Hence, it is called amphibolic pathway. It serves as a
pathway for oxidation of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. When fats are
respiratory substrate they are first broken down into glycerol and fatty acid.
Glycerol is converted into DHAP and acetyl CoA. This acetyl CoA enter into the
Krebs cycle. When proteins are the respiratory substrate they are degraded into
amino acids by proteases. The amino acids after deamination enter into the
Krebs cycle through pyruvic acid or acetyl CoA and it depends upon the
structure. So respiratory intermediates form the link between synthesis as well
as breakdown. The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for oxidation
of fuel molecules like amino acids, fatty acids and carbohydrates. Therefore,
respiratory pathway is an amphibolic pathway (Figure 14.9).
Related Topics