Respiration, Compensation point - Gaseous Exchange in Plant | 11th Botany : Chapter 14 : Respiration
Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 14 : Respiration
Gaseous Exchange in Plant
Gaseous Exchange
1. Respiration
The term
respiration was coined by Pepys (1966).
Respiration is a biological process
in which oxidation of various food substances like carbohydrates, proteins and
fats take place and as a result of this, energy is produced where O2
is taken in and CO2 is liberated. The organic substances which are
oxidised during respiration are called respiratory substrates. Among these,
glucose is the commonest respiratory substrate. Breaking of C-C bonds of
complex organic compounds through oxidation within the cells leads to energy
release. The energy released during respiration is stored in the form of ATP (Adenosine Tri Phosphate) as well
as liberated heat. Respiration occurs in all the living cells of organisms. The
overall process of respiration corresponds to a reversal of photosynthesis.
C6H12O6
+ 6O2 → 6CO2
+ 6H2O + Energy (686 K cal
or 2868 KJ)
Depending upon the nature of respiratory
substrate, Blackman divided
respiration into,
1.
Floating respiration
2.
Protoplasmic respiration
When
carbohydrate or fat or organic acid serves as respiratory substrate and it is
called floating respiration. It is a
common mode of respiration and does not produce any toxic product. Whereas
respiration utilizing protein as a respiratory substrate, it is called protoplasmic respiration. Protoplasmic
respiration is rare and it depletes structural and functional proteins of
protoplasm and liberates toxic ammonia.
2. Compensation point
At dawn and dusk the intensity of light is low. The point at which CO2 released in respiration is exactly compensated by CO2 fixed in photosynthesis that means no net gaseous exchange takes place, it is called compensation point. At this moment, the amount of oxygen released from photosynthesis is equal to the amount of oxygen utilized in respiration.
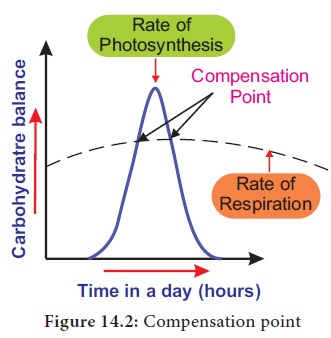
The two common factors associated with
compensation point are CO 2 and light (Figure 14.2) . Based on this
there are two types of compensation point. They are CO2 compensation
point and light compensation point. C3 plants have compensation
points ranging from 40-60 ppm (parts per million) CO2 while those of
C4 plants ranges from 1-5 ppm CO2.
Related Topics