Preparation, Properties, Structure, Uses - Potassium permanganate | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 4 : Transition and Inner Transition Elements
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 4 : Transition and Inner Transition Elements
Potassium permanganate
Potassium
permanganate - KMnO4
Preparation:
Potassium permanganate
is prepared from pyrolusite (MnO2) ore. The preparation involves the
following steps.
i) Conversion of MnO2
to potassium manganate:
Powdered ore is fused
with KOH in the presence of air or oxidising agents like KNO3 or
KClO3. A green coloured potassium manganate is formed.
2MnO2 + 2KOH
+ O2 → K2MnO4 + 2H2O
K2MnO4 = potassium manganate (Green)
ii) Oxidation of potassium manganate to potassium permanganate: Potassium
manganate thus obtained can be oxidised in two ways , either by chemical
oxidation or electrolytic oxidation.
Chemical oxidation:
In this method potassium
manganate is treated with ozone (O3) or chlorine to get potassium
permanganate.
2MnO42− + O3 + H2O
→ 2MnO4− + 2OH− + O2
2MnO42− + Cl2 → 2MnO4− + 2Cl−
Electrolytic
oxidation
In this method aqueous
solution of potassium manganate is electrolyzed in the presence of little
alkali.
K2MnO4
↔ 2K+ + MnO42−
H2O ↔ H+
+ OH−
Manganate ions are
converted into permanganate ions at anode.
MnO42− ↔ MnO4− + e−
Green purple
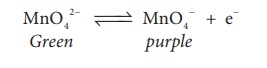
H2is
liberated at the cathode.
2H+ + 2e− → H2 ↑
The purple coloured
solution is concentrated by evaporation and forms crystals of potassium
permanganate on cooling.
Physical properties:
Potassium permanganate
exists in the form of dark purple crystals which melts at 513 K.
It is sparingly soluble
in cold water but, fairly soluble in hot water.
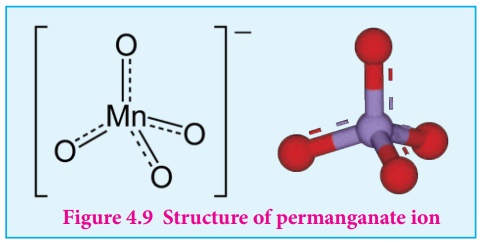
Structure of permanganate ion
Permanganate ion has tetrahedral geometry in which the central Mn7+ is sp3 hybridised.
Chemical properties:
1. Action of heat:
When heated, potassium permanganate
decomposes to form potassium manganate and manganese dioxide.
2KMnO4 → 2K2MnO4
+ MnO2 + O2
2. Action of conc H2SO4
On treating with cold
conc H2SO4, it decomposes to form manganese heptoxide,
which subsequently decomposes explosively.
2KMnO4 + 2H2SO4
(cold) → Mn2O7 + 2KHSO4 + H2O
(cold)
Mn2O7
→Δ→ 2MnO2 + 3O2
But with hot conc H2SO4,
potassium permanganate give MnSO4
4KMnO4 + 6H2SO4(hot) → 4MnSO4 +
2K2SO4 + 6H2O + 5O2 (hot)
3. Oxidising property:
Potassium permanganate
is a strong oxidising agent, its oxidising action differs in different reaction
medium.
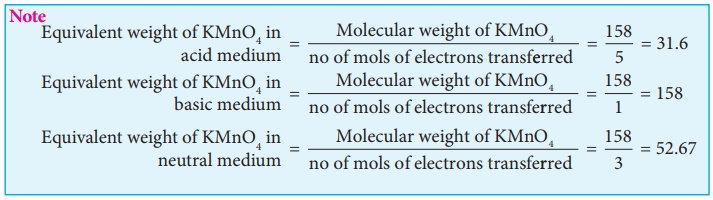
a) In neutral medium:
In neutral medium, it is
reduced to MnO2.
MnO4− + 2H2O + 3e− → MnO2 + 4OH−
(i) It oxidises H2S
to sulphur
2MnO4− + 3H2S → 2MnO2
+ 3S + 2OH− + 2H2O
(ii) It oxidises
thiosulphate into sulphate
8MnO4− + 3S2O32− + H2O → 6SO42− + 8MnO2 +
2OH−
b) In alkaline medium:
In the presence of
alkali metal hydroxides, the permanganate ion is converted into manganate.
MnO4− + e− → MnO42−
This manganate is
further reduced to MnO2 by some reducing agents.
MnO42− + H2O → MnO2
+ 2OH− + [O]
So the overall reaction
can be written as follows.
MnO4− + 2H2O + 3e− → MnO2 + 4OH−
This reaction is similar
as that for neutral medium.
Bayer’s reagent:
Cold dilute alkaline
KMnO4 is known as Bayer’s reagent. It is used to oxidise alkenes
into diols. For example, ethylene can be converted into ethylene glycol and
this reaction is used as a test for unsaturation.
c) In acid medium:
In the presence of
dilute sulphuric acid, potassium permanganate acts as a very strong oxidising
agent. Permanganate ions is converted into Mn2+ ion.
MnO4− + 8H+ + 5e− → Mn2+ + 4H2O
The oxidising nature of
potassium permanganate (permanganate ion) in acid medium is illustrated in the
following examples.
(i) It oxidises ferrous
salts to ferric salts.
2MnO4− + 10Fe2+ +
16H+ → 2Mn2+ +
10Fe3+ + 8H2O
(ii) It oxidises iodide
ions to iodine
2MnO4− + 10I− + 16H+ → 2Mn2+ + 5I2
+ 8H2O
(iii) It oxidises oxalic
acid to CO2
2MnO4− + 5( COO)2− + 16H+ → 2Mn2+ +
10CO2 + 8H2O
(iv) It oxidises
sulphide ion to sulphur
2MnO4− + 5 S2− + 16H+ → 2Mn2+ + 5
S + 8H2O
(vi) It oxidises nitrites
to nitrates
2MnO4− + 5NO2− + 6H+ → 2Mn2+ +
5NO3− + 3H2O
(vi) It oxidises
alcohols to aldehydes.
2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4
+ 5CH3CH2OH → 2K2SO4 + 2MnSO4
+ 5CH3CHO + 8H2O
(vii) It oxidises
sulphite to sulphate
2MnO4− + 5SO32− + 6H+ → 2Mn2+ +
5SO42− + 3H2O
Uses of potassium permanganate:
Some important uses of
potassium permanganate are listed below.
1.
It is used as a strong oxidizing agent.
2. It is used for the
treatment of various skin infections and fungal infections of the foot.
3. It used in water
treatment industries to remove iron and hydrogen sulphide from well water.
4. It is used as a Bayer’s
reagent for detecting unsaturation in an organic compound.
5.
It is used in quantitative analysis for the estimation of ferrous
salts, oxalates, hydrogen peroxide and iodides.

Related Topics