Example, Preparation, Physical and Chemical properties, Mechanism, Uses - Poly halogen compounds | 11th Chemistry : UNIT 14 : Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 14 : Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Poly halogen compounds
Poly
halogen compounds
Carbon
compounds containing more than one halogen atoms are called poly halogen
compounds. Some of the important poly halogen compounds are described below.
They
are classified as
a) gem – dihalides
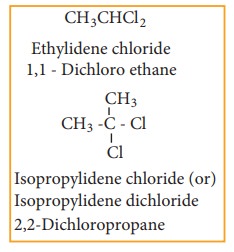
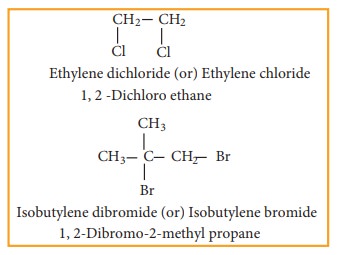
b) vic – dihalides
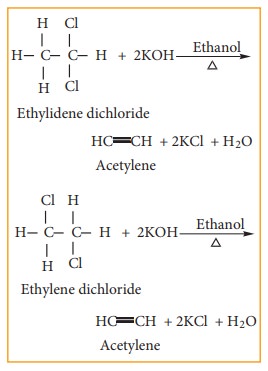
For Example
Preparation
![]()
![]()
a) gem- Dihalides
Ethylidene
dichloride (1, 1 - Dichloro ethane) is prepared by
(i) Treating
acetaldehyde with PCl5
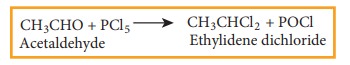
(ii) Adding hydrogen chloride to acetylene
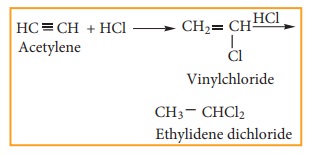
b) vic- Dihalides
Ethylene
dichloride (1, 2 - Dichloro ethane) is prepared by the following methods.
i) Addition of chlorine to ethylene
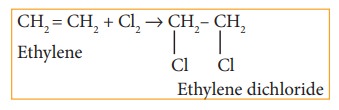
ii) Action of PCl5 (or HCl) on ethylene glycol
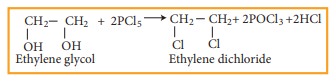
Properties
Physical Properties
i) They are sweet smelling, colourless liquids having relatively high boiling points.
ii) The boiling point of ethylidene chloride is less than
that of ethylene dichloride.
Chemical properties
1) Hydrolysis with aqueous NaOH or KOH
gem-Dihalides,
on hydrolysis with aqueous KOH give an aldehyde or a ketone vic-Dihalides, on
hydrolysis with aqueous KOH gives glycols.
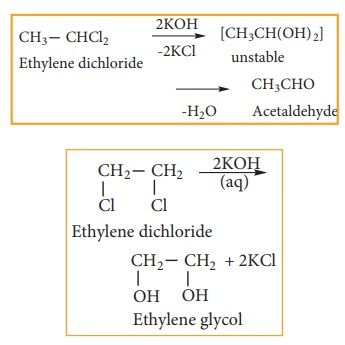
This
reaction can be used to distinguish the gem- Dihalides and vic- Dihalides.
2) Reaction with Zinc (Dehalogenation)
gem-
Dihalides and vic- Dihalides on treatment with zinc dust in methanol give
alkenes.
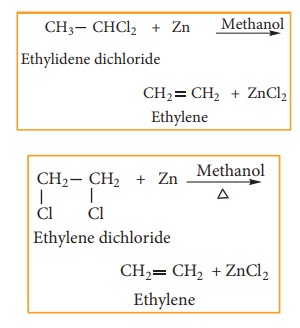
3) Reaction with Alcoholic KOH (Dehydrohalogenation)
gem-
Dihalides and vic- Dihalides on treatment with alcoholic KOH give alkynes.
Methylene chloride (Di chloromethane)
Preparation
Methylene
chloride is prepared by the following methods
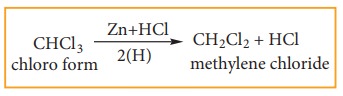
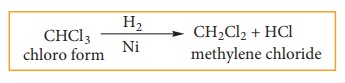
1) Reduction of chloroform
a) Reduction of chloroform in the
presence of Zn + HCl gives methylene chloride.
b) Reduction of chloroform using H2/Ni
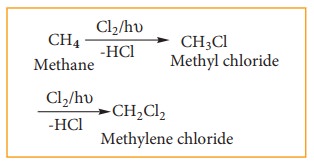
2) Chlorination of methane
Chlorination
of methane gives methylene chloride
Uses of methylene chloride
Methylene
chloride is used as
i.
aerosol spray propellant
ii.
solvent in paint remover
iii.
process solvent in the manufacture of drugs
iv.
a metal cleaning solvent
Trihaloalkane
Trihaloalkanes
are compounds obtained by replacing three hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon by
three halogen atoms.
Example

1) Chloroform
Chloroform
is an important trihaloalkane. Dumas named CHCl3 as chloroform as it
gives formic acid on hydrolysis.
Preparation:
Chloroform
is prepared in the laboratory by the reaction between ethyl alcohol with
bleaching powderfollowed by the distillation of the product chloroform.
Bleaching powder act as a source of chlorine and calcium hydroxide. This
reaction is called haloform reaction. The reaction proceeds in three steps as
shown below.
Step – 1: Oxidation
CH3CH2OH
+ Cl2 → CH3CHO + 2HCl
Ethyl alcohol Acetaldehyde
Step – 2: Chlorination
CH3CHO
+ 3Cl2 → CCl3CHO + 3HCl
Acetaldehyde
Trichloro acetaldehyde
Step – 3: Hydrolysis
2CCl3CHO
+ Ca(OH)2 → 2CHCl3 + (HCOO)2 Ca
Chloral   chloroform
Properties
Physical properties
i.
Chloroform is a colourless liquid with peculiar sickly smell and a burning
taste
ii.
The vapours of chloroform when inhaled cause unconsciousness (depress the
central nervous system) and hence it is used as an anaesthetic.
Chemical properties
1) Oxidation
Chloroform
undergoes oxidation in the presence of light and air to form phosgene (carbonyl
chloride)
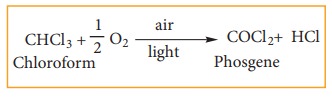
Since
phosgene is very poisonous, its presence makes chloroform unfit for use as
anaesthetic.
2) Reduction
Chloroform
undergoes reduction with zinc and HCl in the presence of ethyl alcohol to form
methylene chloride.

3) Nitration
Chloroform
reacts with nitric acid to form chloropicrin.(Trichloro nitro methane)
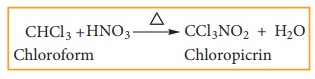
It
used as an insecticide and soil sterilising agent.
4) Carbylamine reaction
Chloroform
reacts with aliphatic or aromatic primary amine and alcoholic caustic potash,
to give foul smelling alkyl isocyanide (carbylamines)
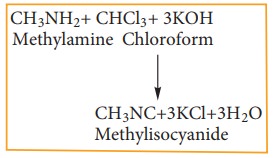
This
reaction is used to test primary amine.
Tetra haloalkane
Carbon
tetrachloride is a good example for tetra haloalkane
Carbon
tetrachloride
Preparation
1. Chlorination of methane
The
reaction of methane with excess of chlorine in the presence of sunlight will
give carbon tetrachloride as the major product.
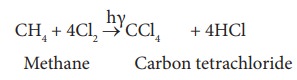
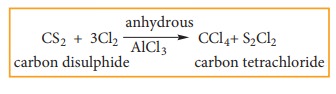
2. Action of carbondisulphide with chlorine gas
Carbon
disulphide reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3
as catalyst giving carbon tetrachloride
Physical properties
i.
Carbon tetrachloride is a colourless liquid with its specific smell
ii.
It is insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents
Chemical properties
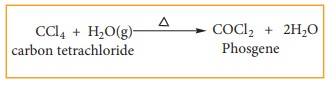
(i) Oxidation
Carbon
tetrachloride reacts with hot water or with hot water vapour producing the
poisonous gas, phosgene.
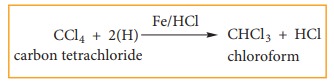
(ii) Reduction
Carbon
tetrachloride is reduced by iron powder in dilute HCl medium to form chloroform
Freons (CFC)
The
chloro fluoro derivatives of methane and ethane are called freons.
Nomenclature
Freon
is represented as Freon-cba
Where
c = number of carbon atoms – 1
b
= number of hydrogen atoms + 1
a
= total number of fluorine atoms
Example
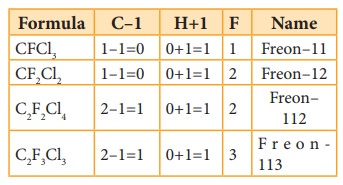
Freon
– 12 is prepared by the action of hydrogen fluoride on carbon tetrachloride in
the presence of catalylic amount of antimony patachloride. This is called
swartz reaction
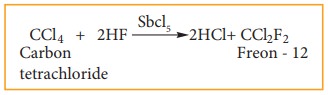
Physical properties
Freons are highly stable, unreactive, non corrosive, non toxic, easily liquefiable gases.
Uses:
i.
Freons are a used as refrigerants in refrigerators and air conditioners.
ii.
It is used as a propellant for aerosols and foams
iii.
It is used as propellant for foams to spray out deodorants, shaving creams, and
insecticides.
DDT (p,p’-dichloro diphenyl tri-chloro ethane)
DDT,
the first chlorinated organic pesticide was prepared in 1873, and in 1939 Paul
Muller discovered the effectiveness of DDT as an insecticide. He was awarded
Noble prize in medicine and physiology in 1948 for this discovery.
DDT
can be prepared by heating a mixture of chlorobenzene with chloral (Trichloro
acetaldehyde) in the presence of con.H2SO4.
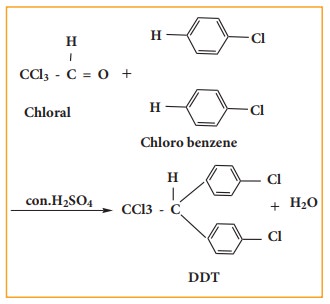
Uses:
i.
DDT is used to control certain insects which carries diseases like malaria and
yellow fever
ii.
It is used in farms to control some agricultural pests
iii.
It is used in building construction as pest control
iv.
It is used to kill various insects like housefly and mosquitoes due to its high
and specific toxicity.
Related Topics