Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 14 : Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Methods of preparation of Haloalkanes
Methods of preparation
Haloalkanes are prepared by the following methods
1) From alcohols
Alcohols can be converted into halo alkenes by reacting it with any one of the following reagent 1. hydrogen halide 2. Phosphorous halides 3. Thionyl chloride
a) Reaction with hydrogen halide
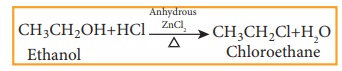
Mixture of con.HCl and anhydrous ZnCl2 is called Lucas reagent.
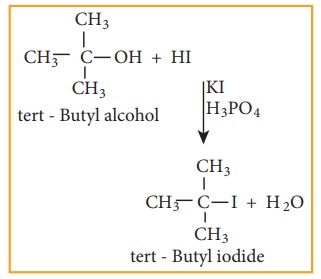
The order of reactivity of halo acids with alcohol is in the order HI > HBr > HCl. The order of reactivity of alcohols with halo acid is tertiary > secondary > primary.
b) Reaction with phosphorous halides
Alcohols react with PX5 or PX3 to form haloalkane. PBr3 and PI 3 are usually generated in situ (produced in the reaction mixture) by the reaction of red phosphorus with bromine and iodine, respectively.
Example
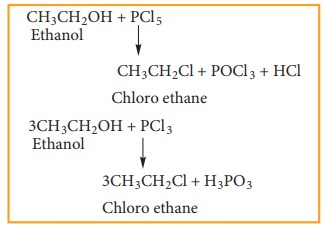
c) Reaction with thionyl chloride (Sulphonyl chloride)
Example
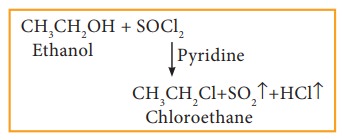
This reaction is known as Darzen's halogenation
2) From alkenes
Alkenes react with halogen acids (HCl, HBr, HI) to give haloalkane. The mode of addition follows Markovnikov’s rule.
3) From alkanes
Alkanes react with halogens (Cl2 or Br2) in the presence of ultra violet light to form haloalkane. This reaction is a free radical substitution reaction and gives a mixture of mono, di or poly substituted haloalkane.
Example
Chlorination of methane gives different products which have differences in the boiling points. Hence, these can be separated by fractional distillation.
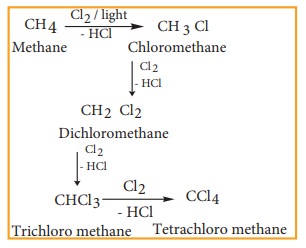
4) Halogen exchange reactions
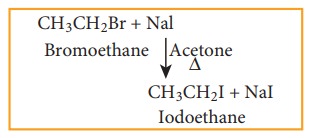
a) Finkelstein reaction
Chloro or bromoalkane on heating with a concentrated solution of sodium iodide in dry acetone gives iodo alkanes. This reaction is called Finkelstein reaction, (SN2 reaction).
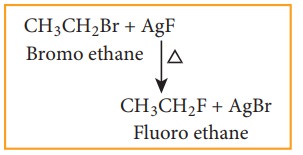
b) Swarts reaction
Chloro or bromo alkanes on heating with metallic fluorides like AgF, SbF3 or Hg2F2 gives fluoro alkanes. This reactions is called Swarts reaction.
Example
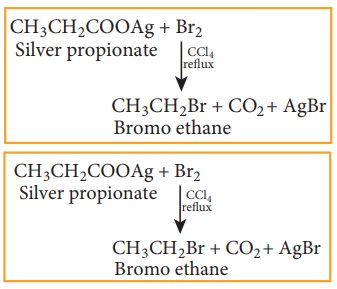
5) From silver salts of fatty acids (Hunsdiccker reaction)
Silver salts of fatty acids when refluxed with bromine in CCl4 gives bromo alkane
Related Topics