Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
Plant Respiration : Electron transport chain
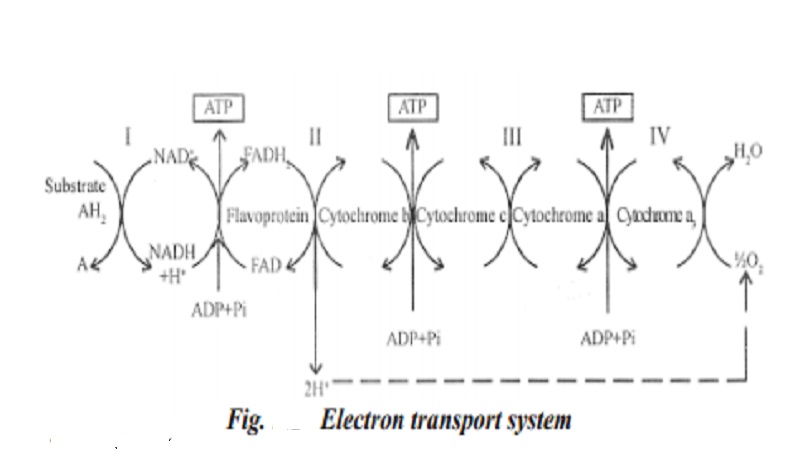
Electron transport chain
Electron transport system (ETS) is a chain of electron carriers consisting of NAD+, FAD+, CoQ and cytochromes (cyt. b, cyt. c, cyt. a and cyt. a3). The glucose molecule is completely oxidized by the end of the citric acid cycle. But, energy is not released, unless NADH2 and FADH2 are oxidized through electron transport system. Transfer of electrons and protons from NADH2 and FADH2 to oxygen through a series of components like flavoprotein, cytochrome is called electron transport chain. This process leads to coupling of electrons to form high-energy phosphate bonds in the form of ATP from ADP is called oxidative phosphorylation. The electron transport components are arranged in the inner membrane of mitochondria.
According to modern concept, the electron carriers in the electron transport system are arranged in four complexes - complex I, complex II, complex III and complex IV. When NAD+ is a primary acceptor of electrons, the electrons are transported from complex I to II, II to III and then to complex IV. When electrons are transported from one complex to next complex, an ATP is produced. Thus, one molecule of NADH2 generates three ATPs. When FAD+ is a primary acceptor of electrons, the electrons are transported from complex II to III and then to complex IV. Thus, one molecule of FADH2 generates two ATPs.
The molecular oxygen forms the terminal constituent of the electron transport system. It is the ultimate recipient of electrons and picks up the protons from the substrate to form water.
Energy yield
Complete oxidation of one glucose molecule yields a net gain of 38ATP. Out of 38ATP molecules, 4ATP are obtained by direct substrate level phosphorylation, 30ATP through oxidation of NADH2 and 4ATP through oxidation of FADH2. Since, a large number of ATP molecules are produced in the mitochondria, they are called the 'power houses of the cell'. Demonstration of respiration by anong's respiroscope
The aim of this experiment is to demonstrate liberation of carbon dioxide during respiration. The respiroscope is a glass apparatus consisting of a bulb like part with a bent neck and vertical tube. Germinating seeds are taken in the bulb and the mouth of the tube is kept immersed in the beaker containing KOH solution as shown in the figure. The respiroscope is fixed in the vertical position with the help of a stand. Thus, the enclosed air in the bulb is completely cut off from the atmosphere. The apparatus is kept undisturbed for few hours.
It is observed that the level of KOH solution in the limb is raised. The KOH solution absorbs carbondioxide released by the seeds and a vacuum is created. It results in the raise of KOH level.
Related Topics