Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
Pituitary and Sex glands
Endocrines : The glands of the body may be divided into those with an external
secretion (exocrine glands) and those with an internal secretion (endocrine
glands). Example of exocrine glands are the sweat, Lachrymal and mammary glands
which pass their secretion along the ducts to the external surface of the body
and the glands of the mouth, stomach, and intestine which pass their secretions
along ducts into the alimentary tract. The endocrine or ductless gland on the
other hand have no ducts or openings to the exterior.
The secretions are passed directly into the blood stream and transmitted
to the tissues.
A hormone is a chemical substance produced by the endocrine
glands and their overall function is to regulate the activities of various body
organs and their functions. The first hormone was discovered by Bayliss in
1903.
The main endocrine glands in the body are :
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Islets of Langerhans
Adrenal gland
Pituitary and
Sex glands
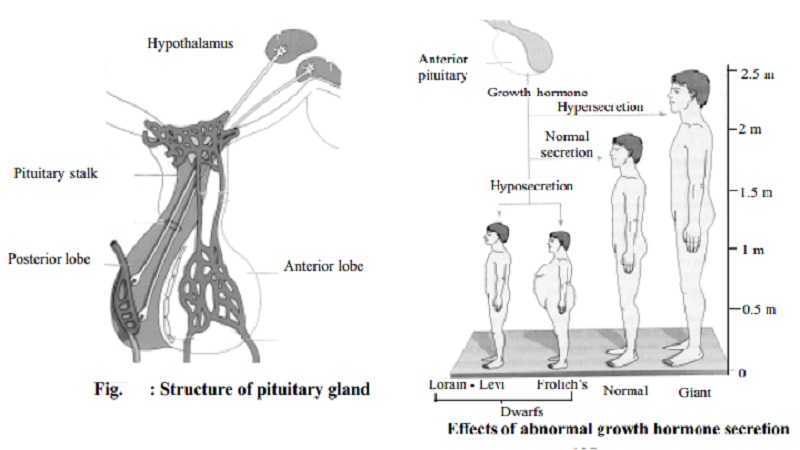
PITUITARY GLAND
The pituitary is a small gland about the size of a cherry. It is
situated at the base of the brain. It plays a peculiar role in the system of
endocrine glands. It is referred to as the 'master' gland of internal secretion
because it controls the activities of other endocrine glands.
The Anterior Pituitary
This part
secretes a large number of hormones. Many of them stimulate other glands. Its
main hormones are:
Growth Hormone: It facilitates the growth of the bone and cartilage tissue. Over activity of the anterior pituitary lobe in
childhood results in excessive growth and height. This condition is known an gigantism. A decreased activity of the
anterior pituitary causes a severe growth retardation leading to dwarfism.
Excessive production of growth hormone in an adult leads to excessive
development of certain regions such as fingers and toes, feet, hands, nose,
lower jaw, tongue, thoracic and abdominal organs. This condition is known as acromegaly.
Thyrotropic Hormone
(TSH): This hormone stimulates the activity of the thyroid gland. Administration of this hormone
causes overgrowth of thyroid tissue.
Adreno Cortico Tropic
Hormone: (ACTH): This hormone
stimulates the cortex of the adrenal gland and increases the production of
the hormones of adrenal cortex.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH): This hormone influences the
growth, development and maturation of the vesicular follicles in the ovary. In
males, the hormone stimulates the formation of sperm in the testes.
Lactogenic Hormone: It acts on the mammary gland and helps in the formation and flow of milk during lactation.
Luteinising Hormone: It is required for the growth of follicle in the ovary and stimulates ovulation. In the absence of the
hormone,
no
ovulation and production of the corpus luteum can occur. In males it stimulates
the interstitial cells of testes to secrete testosterone.
Posterior Lobe of the Pituitary
This lobe
is just behind the anterior lobe, it produces two hormones-Oxytocin and
Vasopressin.
Oxytocin acts on
the smooth muscles especially that of the uterus and produces powerful contractions of the uterus and helps in
parturition.
Vasopressin acts on the smooth muscle of the arterial system and increases the blood pressure. This hormone helps in the
reabsorption of water from the distal convoluted tubule. Vasopressin deficiency
is the cause of diabetes insipidus
in which water is not reabsorbed. So great amounts of urine are excreted with
no sugar in it. Such patients feel constantly thirsty.
THE SEX GLANDS
The sex glands including the ovaries of the female and the testis of the
male are important endocrine structures. The secretion of these glands play an
important part in the development of the sexual characteristics. The male sex
gland secretes hormone called testosterone
and is responsible for secondary sex characteristics. The female sex gland secretes a hormone
called estrogen and it stimulates
the development and functioning of the female reproductive organs.
There is one other hormone produced by the female sex glands and it is
called progesterone. This hormone
assists in normal development of pregnancy.
Related Topics