Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
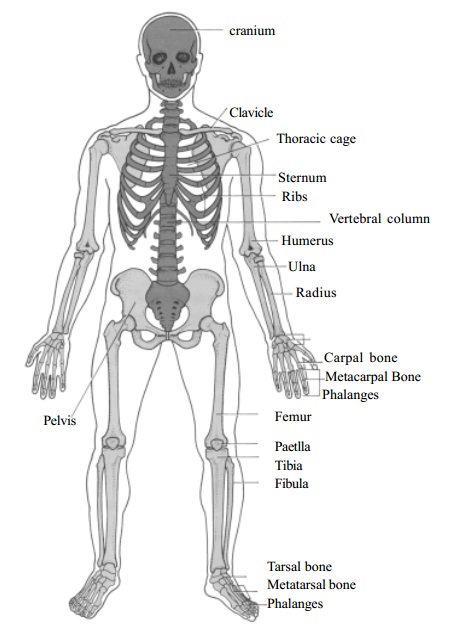
Skeletal System - Axial skeleton
Skeletal
System forms the framework of the body. It provides support and protection for
some of the soft organs. The adult human skeleton consists of approximately two
hundred and six (206) bones grouped in two principal divisions,
The axial skeleton
The appendicular skeleton
The axial
division of the skeleton consists of the bones that lie around the axis. The
parts of the axial skeleton are the skull, hyoid bone, auditory ossicles,
vertebral column, sternum and ribs. Appendicular skeleton consists of the bones
of the girdle and the upper and lower limb.
Axial skeleton
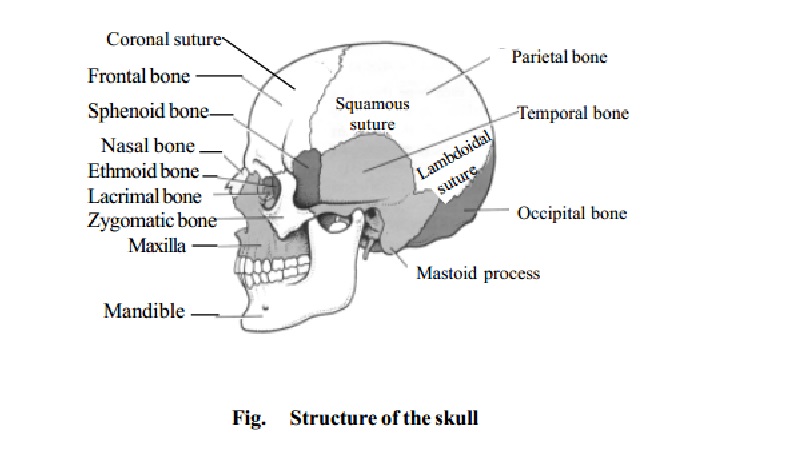
The Skull
It is the
bony framework of the head arranged in two parts - the cranium which consists
of eight bones and the facial skeleton of fourteen bones.
The cavity
of the cranium presents an upper surface known as the vault of the skull. This
is smooth on the outer surface and marked by ridges and depressions to
accommodate the brain and its blood vessels on the inner surface. The lower
surface of the cavity is known as the base of the skull. It has an opening
called the foramen magnum through
which the spinal cord passes.
The bones
which form the Cranium are flat bones which are immovably fixed to each other
by sutures. The cranial bones enclose and protect the brain and organs of
sight, hearing and balance. The 8 cranial bones are:
The
frontal bone (1), Parietal bones (2), temporal bones (2), the occipital bone
(1), sphenoid (1) and ethmoid (1).
The occipital bone is at the back and lower
part of the Cranial cavity. It is pierced by the foramen magnum through which
the medulla oblongata passes to join the spinal cord.
The two parietal bones together form the roof
and sides of the skull. The outer surface is smooth. The inner surface is
marked by deep furrows which lodge the Cranial arteries.
The frontal bone forms the forehead and the
upper part of the orbital cavities.
The two temporal bones form the lower part of
the sides of the skull.
The ethmoid is a light spongy bone, cubical
in shape, situated at the roof of the nose wedged in between the orbits. It is
the principal supporting structure of the nasal cavity.
The sphenoid is situated at the anterior
part of the base of the skull.
Sutures : A
suture is an immovable joint found only between skull bones. Very little connective tissue is found between the
bones of the suture.
The four prominent skull sutures are :
Coronal Suture between the frontal bone and the two parietal bones.
Sagittal Suture between the two parietal bones.
Lambdoidal suture between the parietal and the occipital bone.
Squamosal suture between the parietal and the temporal bones.
Bones of the face
There are
14 facial bones, which are the nasal bones (2), Maxillae (2), Zygomatic bones
(2), Mandible (1), Lacrimal bones (2), Palatine bones (2), Inferior nasal
conchae (2) and Vomer (1).
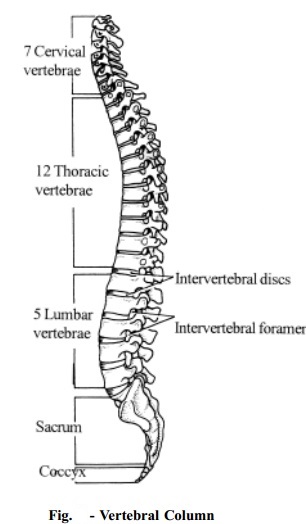
The
Vertebral Column or the spinal column is a flexible structure formed by a
number of bones called Vertebrae.
They are the back bone which forms the main axis of the body to which all other
skeletal parts are attached.
The vertebral column has three functions.
It supports the flexible body.
It provides attachments for muscles which permits flexible movements.
It provides protection for the spinal cord.
There are
33 vertebral bones. 24 of which are separate bones and the remaining vertebrae
are fused to form two bones, the sacrum and the coccyx. The vertebrae are
grouped and named according to the region they occupy. There are,
Seven Cervical Vertebrae that
form the neck or Cervical region.
Twelve thoracic vertebrae
that form the back of the thorax or chest.
Five lumbar vertebrae that
form the lumbar region or lions.
Five Sacral vertebrae that
are fused to form the sacrum.
Four Coccygeal vertebrae that
are fused to form the Coccyx or tail.
The vertebrae in the three upper regions that remain separate are called
movable vertebrae.
Those in the two lower regions the Sacrum and Coccyx are united in the
adult to form two bones called the fixed vertebrae.
The
vertebral Column consists of primary curves (thoracic and sacral) and secondary
curves (cervical and lumbar). The curves give strength, support and balance.
Fig-5 gives the detailed description of various parts of the vertebral
column which includes the cervical vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae, lumbar
vertebrae, the sacrum and coccyx.
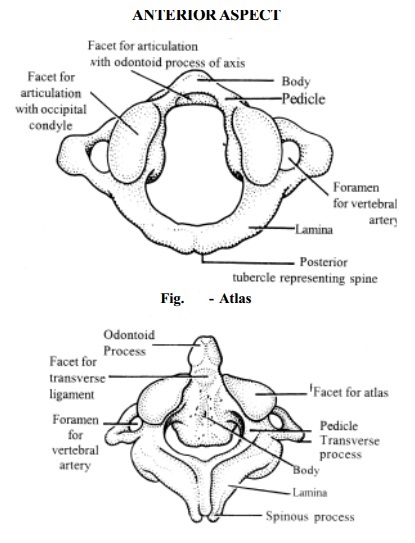
The first
two cervical vertebrae are called Atlas
or Axis.
The Atlas
is a mere ring of bone with surface for resting the skull. The second cervical
vertebra is the Axis. It has an upward projection called the odontoid-process which projects through
the ring of the Atlas and forms a pivot on which the head turns from side to
side. The skeletal framework of the neck consists of five cervical vertebrae
which are designed with shape of flat discs placed one on the other.
Ribs and Sternum
The
thoracic vertebrae, ribs and sternum make up the thoracic basket. The skeleton
of the thorax acts as a protective cage around the heart and lungs.
There are
12 pairs of movable ribs on the sides of the chest cavity. A rib is a flattened
curved bone. The first upper seven pairs of ribs are the true ribs. These ribs articulate with the thoracic vertebrae at the
back and are attached directly (separately) to the sternum by coastal
cartilages in front. The last five pairs of ribs are the false ribs. They also articulate with the thoracic vertebrae at the
back, but all are not attached with the sternum in front. The 8th, 9th
and 10th pairs of ribs on each side are attached with the cartilages
of the rib just above to it and are joined to the sternum indirectly. The 11th
and 12th pairs are free in front and do not attach to the sternum. They
are called the floating ribs.
Sternum (or) Breast Bone
The
Sternum or breast bone is a flat bone divided into three parts
the upper manubrium, the middle body gladiolus and the lower small
cartilaginous xiphoid process. The collar bone articulate with the manubrium of
the sternum.
Related Topics