Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
Stucture of Animal Cell
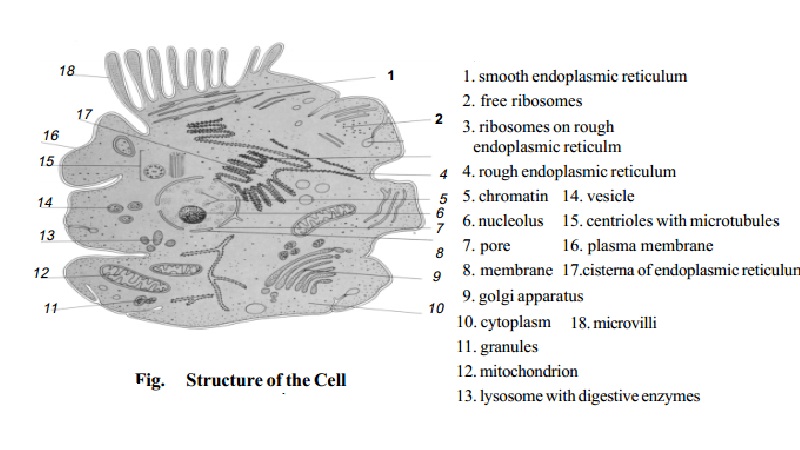
CELL
The basic functional unit of the body is the cell. The cells are the building blocks of the organs and each of these organs performs its own specialized function.
1. smooth endoplasmic reticulum
2. free ribosomes
3. ribosomes on rough endoplasmic reticulm
4. rough endoplasmic reticulum
5. chromatin
6. nucleolus
7. pore
8. membrane
9. golgi apparatus
10. cytoplasm
11. granules
12. mitochondrion
13. lysosome with digestive enzymes
14. vesicle
15. centrioles with microtubules
16. plasma membrane
17.cisterna of endoplasmic reticulum
18. microvilli
A typical cell is composed of nucleus and various organelles. The cell is filled with a colloid type of material called protoplasm. This is divided between 2 separate compartments. The nuclear compartment that contains nucleoplasm and the compartment outside the nucleus containing cytoplasm. The nucleoplasm is separated from the cytoplasm by the nuclear membrane. The cytoplasm is separated from the surrounding fluids by the cell membrane.
The protoplasm is composed mainly of 5 basic substances
water,
electrolytes such as potassium, magnesium, phosphate, bicarbonates and small amounts of sodium and chloride,
proteins,
lipids and
carbohydrates.
The cell contains highly organized physical structures called organelles which are important for the functions of the cell. Someprincipal organelles of the cell are the cell membrane, nuclear membrane, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi complex, mitochondria and lysosomes.
Cell membrane
The cell membrane is thin and elastic, composed entirely of proteins and lipids. The structure shows a central layer of lipid covered by protein layers. The protein layer contributes to the structural strength of the membrane, also acts as carrier for transporting substances through the membrane.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
This is a network of tubular structures found in the cytoplasm. The endoplasmic reticulum is continuous with the nuclear membrane and with the inner chambers of the golgi complex. It connects directly through small openings with the exterior of the cell. The main function is transporting substances formed in different parts of the cell which enter the endoplasmic reticulum and are conducted to other parts of the cell. There are two types of ER:
a) Granular ER :This type of ER contains many small granular particles called ribosomes which are attached to the outer surface. The ribosomes contain ribonucleic acid (RNA) which is necessary for protein synthesis.
b) Agranular ER : This type of ER contains no ribosomes attached to it. This is otherwise known as smooth ER. This helps in synthesizing lipid substances.
Golgi complex
This is a specialized derivative of the endoplasmic reticulum. It is usually composed of 4 or more layers of thin vesicles. The golgi complex is very prominent in secretory cells. It's function is believed to be temporary storage and condensation of secretory substances and preparation of these substances for final secretion. It also synthesizes carbohydrates and combines it with protein to form glycoproteins. eg: mucopolysaccharide ground substance of both cartilage and bone. The golgi complex is also involved in formation of lysosomes which are important for digesting intracellular substances.
Mitochondria
The mitochondria are composed of a double - layered membrane, an outer membrane and an inner membrane. Many infoldings of the inner membrane form shelves onto which oxidative enzymes of the cell are attached. The inner cavity of the mitochondrion is filled with a gelatinous matrix containing enzymes. Mitochondria are the 'power-house' of the cell. They provide most of the energy needed for performing cellular functions.
Lysosomes
These are spherical organelles surrounded by a membrane. The lysosomes provide an intracellular digestive system that allows the cell to digest and remove unwanted substances and structures, especially foreign bodies such as bacteria.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the control center of the cell. The nucleus consists of a double walled nuclear membrane with pores, chromatin material throughout the nucleoplasm which becomes the chromosomes during cell division, and a protein structure called nucleolus. The nucleolus contains large amounts of RNA. The nucleus controls chemical reactions of the cell and cell reproduction. The nucleus contains large amounts of DNA which are important in cell division. The chromosomes consist of DNA and protein,
Related Topics