Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
Muscle Reflex action - conditioned and unconditioned reflex
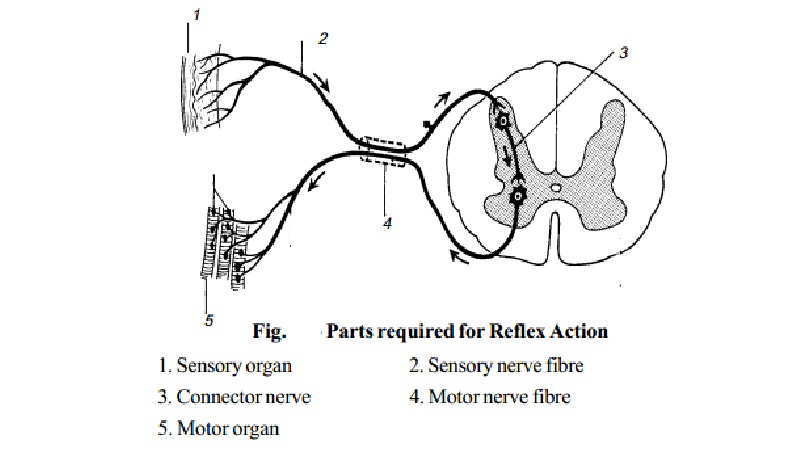
Reflex action
Brain is like a very fine electronic computer receiving information from various sources, collecting and analysing it and giving appropriate stimuli for action.
There are a large number of actions which do not require the intervention of the brain and can be executed at lower levels. Examples of this are heart beat, respiratory movements and gastric secretions which are carried out automatically. Autonomous nervous system controls the above said activities.
Apart from this there is a large group of activity, many of them voluntary in nature which are also done similarly. Examples are closing of the eyelids when light falls on it, removing the hand when it touches something hot, locking a knee joint to support the body when the other joint relaxes, coughing when the throat is irritated are all examples of related activity.
Most of the voluntary activities are reflex in nature and these are the most elementary type of nervous activity.
Example of Reflex Action
Knee jerk. When the patellar tendon is tapped by a knee hammer there is a sudden unconscious tensing of the thigh muscles resulting in an upward movement of the leg.
A reflex action requires the following structures :
A sensory organ which receives the stimuli, e.g. the skin.
A sensory nerve fibre which conducts this impulse to the cells of the spinal cord.
Spinal Cord - where connector nerves pass impulses on to the anterior horn of the cord.
A motor nerve cell which receives and transmits the impulse along the motor nerve fibres.
A motor organ e.g., a muscle, which performs the action, when stimulated by the motor nerve impulse.
1. Sensory organ
2. Sensory nerve fibre
3. Connector nerve
4. Motor nerve fibre
5. Motor organ
Reflex action can be divided into conditioned reflex and unconditioned reflex.
Conditioned Reflex
This type of reflex is developed only with experience. A new born child will not secrete saliva if food is shown or if it smells food. On the other hand, an adult will salivate on the sight or smell of food because of the association of the special senses with food. These types of reflexes are called Conditioned reflexes.
Conditioned reflexes were first demonstrated by Pavlov, a Russian Physiologist. He conducted his experiment with a dog which salivated at the sight of the food. Then the stimulus i.e., food was associated with the ringing of the bell. The animal was fed a number of times immediately after the ringing of the bell. Then the original stimulus (food) was withdrawn and mere ringing of the bell produced salivation. This is referred to as 'Conditioned Reflex'.
Unconditioned Reflex
These actions are carried out entirely through centres situated in the spinal cord or lower levels of the brain. Unconditioned reflexes are inborn and habitual. They are not dependant on past experience, education or training. For example, while walking, the flexors of the leg contract simultaneously and the extensors relax simultaneously. When the leg is stretched these two activities namely the contraction and relaxation occur vice versa.
Related Topics