Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
Types of muscle tissues
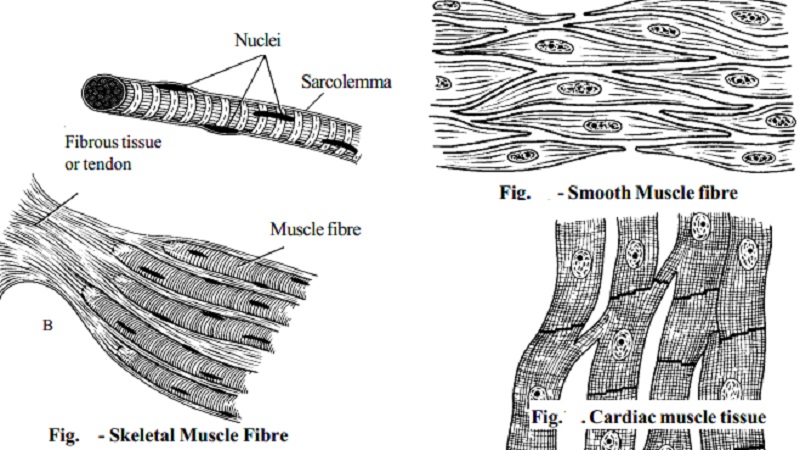
MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY
All physical functions of the body involve muscle activity. These functions include skeletal movements, contraction of the heart, contraction of blood vessels, peristalsis in the digestive tract and many more.
There are 3 different types of muscle tissues responsible for these activities.
Skeletal, Voluntary or striated muscle.
Visceral, involuntary or smooth muscle.
Cardiac muscle.
Skeletal muscle tissue
This may be described as skeletal, striated, striped or voluntary muscle. It is called voluntary because contraction is under the control of the will.
When voluntary muscle is examined microscopically the cells are found to be roughly cylindrical in shape and may be as long as 35 cm. Each cell, commonly called a fiber, has several nuclei situated just under the sarcolemma, or cell membrane of each muscle fiber.
The muscle fibers lie parallel to one another, and when viewed under the microscope, they show well-marked transverse dark and light bands, hence the name striated or striped muscle.
A muscle consists of a large number of muscle fibers. In addition to the sarcolemma mentioned previously, each fiber is enclosed in and attached to fine fibrous tissue called endomysium.
Small bundlesof fibers are enclosed in perimysium, and the whole muscle in epimysium.
The fibrous tissue enclosing the fibers, the bundles and the whole muscle extends beyond the muscle fibers to become the tendon which attaches the muscle to bone or skin.
Visceral muscle tissue
Visceral muscle may also be described as smooth or involuntary (figure 10). It is not under the control of the will. It is found in the walls of blood and lymph vessels, the alimentary tract, the respiratory tract, the urinary bladder, the biliary tract and the uterus.
When examined under a microscope, the cells are seen to be spindle-shaped with only one central nucleus. There is no distinct sarcolemma but a very fine membrane surrounds each fiber. Bundles of fibers form sheets of muscle, such as those found in the walls of the above structures.
Cardiac muscle
Related Topics