Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
Muscle contraction
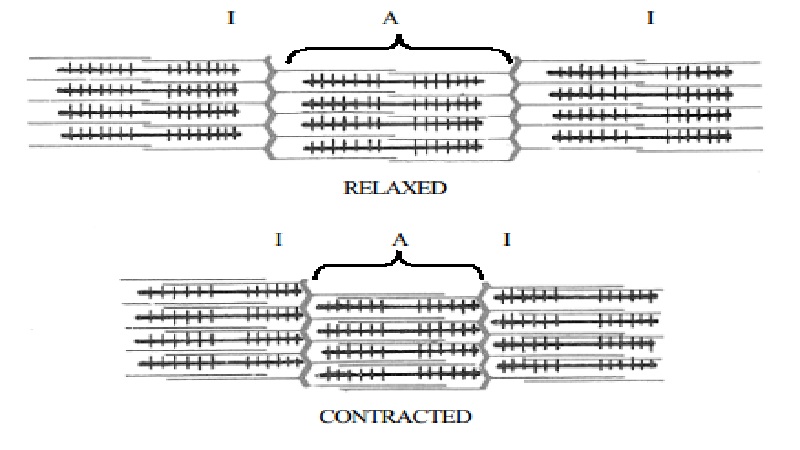
Muscle contraction
A single muscle is made up of thousands of individual muscle fibers. Every fiber extends the entire length of the muscle and is attached at each end to muscle tendons. When stimulated, muscle fibers contract, and the force of contraction is transmitted to the bones through the tendons.
Anatomy of skeletal muscle fiber
Each muscle fiber is between 10 and 100 microns in diameter and it varies from a few millimeters to 50 cm. in length, depending on the muscle. The longitudinal view shows dark and light bands along the fiber. This is characteristic of skeletal and cardiac muscle but not smooth muscle. The segment of fiber between each two successive bands is called a sarcomere.
Each muscle fiber contains several hundred to several thousand myofibrils. Each myofibril is composed of several filaments. There are two types of filaments - actin and myosin filaments which are responsible for muscle contraction. These can be seen in longitudinal view in an electron micrograph as shown below.
The actin filaments are thin filaments and form light bands called I-bands. The myosin filaments are thick filaments that form the dark bands called A-bands. The myosin filaments have small projections from the sides called cross-bridges. The actin and myosin filaments partially interdigitate and thus cause the myofibrils to have alternate light and dark bands.
The interaction between the cross-bridges and the actin filaments cause contraction of a muscle fiber. The actin filaments are attached to the Z-line. Numerous mitochondria are present which provide the energy for muscle contraction. Presence of Ca ++ ions is necessary for activating muscle contraction. Basic mechanism of contraction involves the actin filaments to slide over the myosin filaments. Thus muscle contraction occurs by a sliding filament mechanism.
Characteristics of whole muscle contraction
Motor Unit
Several hundreds to several thousands nerve fibers enter most muscles. On an average, a single motor nerve fiber can innervate about 180 muscle fibers. Thus, stimulating one nerve fiber, can cause contraction of 180 muscle fibers all at the same time. All the muscle fibers innervated by the same nerve fiber is called a motor unit because they are always excited simultaneously and contract together.
Isometric and Isotonic contraction
In the human body, muscle contraction is of both isometric and isotonic types.
When a person is simply standing, he tenses his leg muscles to maintain a fixed position of the joints. This is isometric contraction.Isometric means 'same length'. Here the muscle tightens but does not shorten. When a person is walking and moving his legs, or when he is lifting his arms, the contraction is isotonic contraction. Isotonic means 'same force'. Here the muscle shortens in length.
Related Topics