Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
Adrenal gland
Endocrines : The glands of the body may be divided into those with an external
secretion (exocrine glands) and those with an internal secretion (endocrine
glands). Example of exocrine glands are the sweat, Lachrymal and mammary glands
which pass their secretion along the ducts to the external surface of the body
and the glands of the mouth, stomach, and intestine which pass their secretions
along ducts into the alimentary tract. The endocrine or ductless gland on the
other hand have no ducts or openings to the exterior.
The secretions are passed directly into the blood stream and transmitted
to the tissues.
A hormone is a chemical substance produced by the endocrine
glands and their overall function is to regulate the activities of various body
organs and their functions. The first hormone was discovered by Bayliss in
1903.
The main endocrine glands in the body are :
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Islets of Langerhans
Adrenal gland
Pituitary and
Sex glands
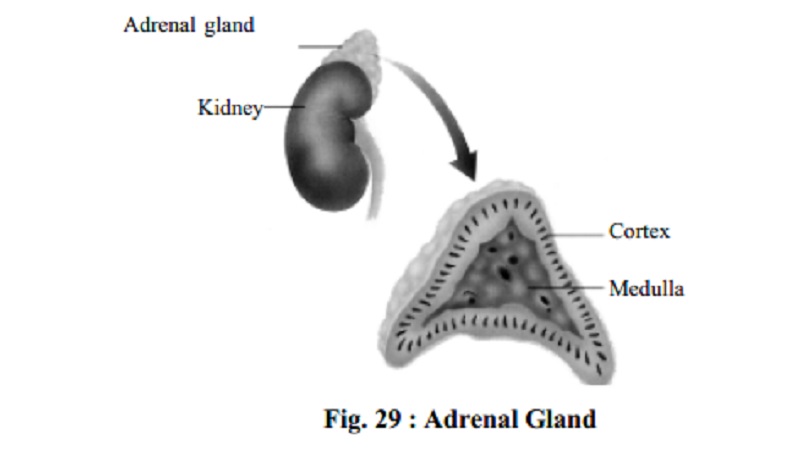
Adrenal Gland
The adrenal or supra renals are two small glands each one situated above
a kidney. Adrenal gland consists of two different parts each of which acts as a
separate gland. The inner area is called the medulla which is brown in colour while the outer area is called the
cortex which is lighter in colour.
Adrenal Cortex
It is composed
of three layers. They are (a) Zona glomerulosa (outer layer) (b) Zona
fasciculata (middle layer) and (c) Zona reticularis (inner layer).
The adrenal cortex secretes three hormones. They
are:
Glucocorticoids : Acts as antagonists to insulin and cause increase in blood sugar.
Mineralocorticoids: Acts on sodium and potassium and help in the conservation of sodium in the body.
Sexsteroids : Stimulates the development of the reproductive organs in childhood. It is responsible for development of secondary
sex characteristics and reproductive function.
Functional
insufficiency of the adrenal cortex and tuberculosis of the adrenal gland gives
rise to Addison's disease. Its early
signs are dark pigmentation of the skin, especially of the hands, neck and face,
anemia, loss of energy, weakness, decreased appetite, nausea, and vomiting.
Patients are very sensitive to cold and pain and susceptible to infections.
This can be treated by administering the hormone in combination with a diet
high in sodium and low in potassium.
Over
activity of adrenal cortex increases the secretion of this hormone, and
sexsteroids, this results in an acute change of secondary sex characteristics.
For example, female may develop male secondary characteristics like growth of
beard, low pitch of the voice, lack of menstruation and male may develop female
secondary sex characteristics.
Adrenal Medulla
Adrenal
medulla secretes two hormones. They are Adrenalin and Nor-adrenaline.
Functions of Medullary Hormones
Dilation of the pupils and improves visual acuity.
Increases both rate and amplitude of contraction of heart and raises the
cardiac output.
Increases both rate and amplitude of respiratory movements and causes
dilation of the bronchioles.
Raises the blood sugar level by means of glycogenolysis.
Increases the Basal Metabolic Rate and thus raises the body temperature.
Dilation of the walls of intestine and the urinary bladder.
The
functions of adrenalin are similar to that of Nor-adrenalin except in a few
instances. For example, adrenalin increases the heart rate whereas
Nor-adrenalin decreases heart rate.
Related Topics