Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
Male Reproductive System
There is one pair of testes lying one in each scrotal sac. The scrotum is a bag of skin having two separate compartments, one for each testis lying at the root of the penis. Each testis is oval shaped, measures 5 x 3 x 2 cm and weighs about 15 gm.Reproductive system
The Reproductive System consists of those organs whose function is to
produce a new individual.
Male And Female Sexual Reproductive Organs
The sex
organs in the male and female can be divided as:
Primary sex organs, i.e. those producing male and female gametes.
Secondary (or accessory) sex organs, i.e. those concerned with carriage
of gamete and other functions.
Primary Sex Organs in Male and Female
They are a
pair of testes producing spermatozoa (male gametes) while in females are a pair
of ovaries producing ovum (female gamete). These primary sex organs in addition
to producing male and female gametes secrete male and female sex hormones as
well.
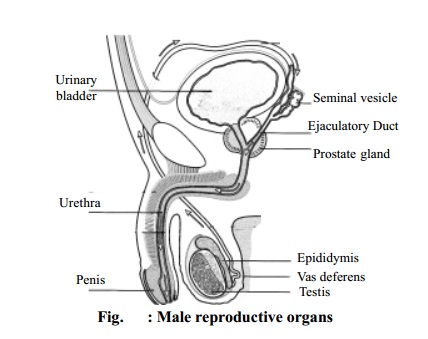
Accessory Sex Organs in the Male
Epididymis
Vas deferens
Seminal vesicles
Prostate gland
Ejaculatory ducts
Urethra
Penis
Accessory Sex Organs in the Female
Fallopian tubes
Uterus
Vagina
Clitoris
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
There is
one pair of testes lying one in each scrotal sac. The scrotum is a bag of skin
having two separate compartments, one for each testis lying at the root of the
penis. Each testis is oval shaped, measures 5 x 3 x 2 cm and weighs about 15
gm.
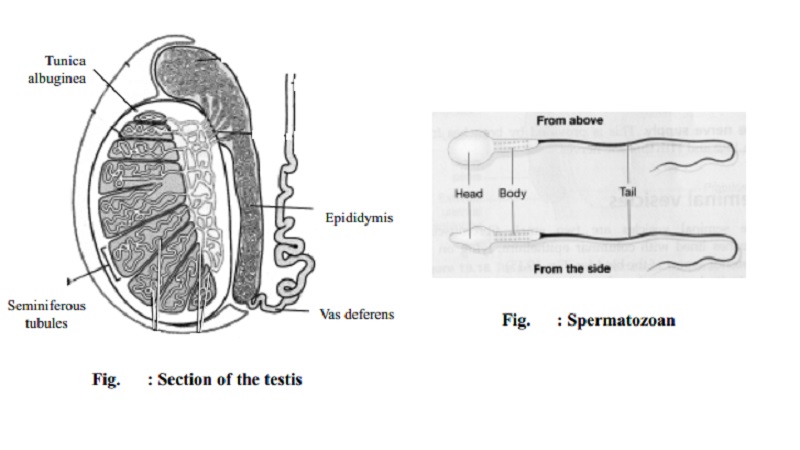
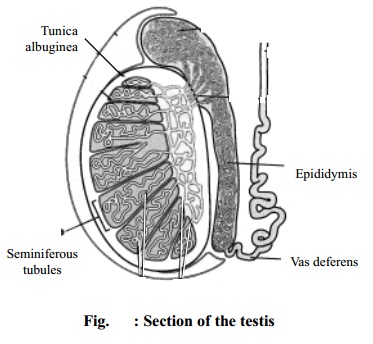
Each testis is covered with a
layer of fibrous tissue called tunica
albuginea. Many septa from this
layer divide the testes into pyramidal lobules
in which lie seminiferous tubules and the interstitial cells. The seminiferous
tubules are concerned with process of spermatogenesis.
The interstitial cells called leydig
cells lie between the tubules and secrete the testosterone (male sex
hormone). From the lining of these tubules spermatozoa are produced by the
process of cell division.
The epididymis is a very fine
convoluted tube, being 4-6 meters long and joins the posterior part of the
testes and vas deferens. It stores the spermatozoa. The spermatozoa remain
inactive in epididymis and are capable of surviving for months.
Vas deferens is a fibro-elastic duct 30-40 cm in length and extends from epididymis to end in ejaculatory duct
which is joined by seminal duct and opens in prostatic urethra.
The seminal vesicles are two
small pouches lying at the back of the urinary bladder. They secrete a fluid
called semen.
The prostate gland lies at the base of the
urinary bladder and is covered with fibrous capsule which by a number of septa
divides into many follicles. The ejaculatory ducts lead from the seminal
vesicle through the prostate gland to the urethra.
In males
the urethra is about 20-22 cm in length and serves the purpose of urination as
well as ejaculation of semen.
Functions of the Testes
They produce and mature the male reproductive cells called spermatozoa.
Secrete seminal fluid.
Secrete hormone testosterone directly into the blood.
The testes
normally do not begin to function till the onset of puberty, which is usually
at about 14 to 15 years. At this age they begin to secrete hormones and produce
the sperms. Before puberty, mature sperms are not formed. It ceases in old age.
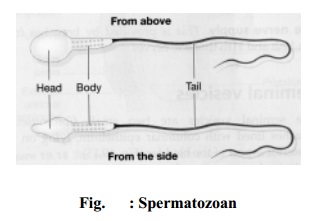
Each sperm is about 1 mm long consists of a head piece, middle piece and
a tail piece. The head is the nucleus. The nucleus is covered by a cap the 'acrosome'.
The neck piece contains 'centrioles' . The tail piece
consists of a spiral mitochondrial sheath surrounding a group of fibres. The
FSH secreted from the anterior pituitary gland controls spermatogenesis.
Functions of Hormone
Testosterone
Stimulates the development of the secondary sexual characteristics of
the male such as the growth of beard, the deepening of the voice, the growth
and the distribution of hair on the body, the growth and development of the
accessory sex organs.
Stimulates the production of sperms at puberty.
Related Topics