Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
Female Reproductive system
Reproductive system
The Reproductive System consists of those organs whose function is to
produce a new individual.
Male And Female Sexual Reproductive Organs
The sex
organs in the male and female can be divided as:
Primary sex organs, i.e. those producing male and female gametes.
Secondary (or accessory) sex organs, i.e. those concerned with carriage
of gamete and other functions.
Primary Sex Organs in Male and Female
They are a
pair of testes producing spermatozoa (male gametes) while in females are a pair
of ovaries producing ovum (female gamete). These primary sex organs in addition
to producing male and female gametes secrete male and female sex hormones as
well.
Accessory Sex Organs in the Male
Epididymis
Vas deferens
Seminal vesicles
Prostate gland
Ejaculatory ducts
Urethra
Penis
Accessory Sex Organs in the Female
Fallopian tubes
Uterus
Vagina
Clitoris
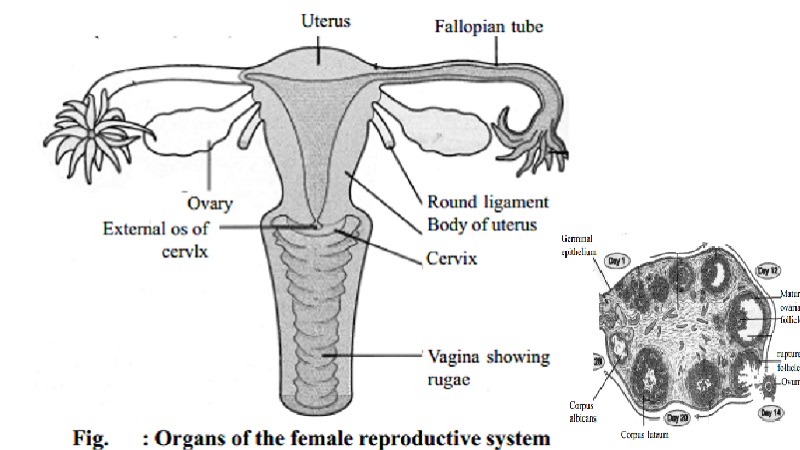
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Ovary
The gonads
of the female are called ovaries and the cells that they produce are known as
ova or egg-cells. Each female has a pair of oval-shaped structure, about the
size of an almond. Each ovary measures 3.5 x 2.5 x 11.5 cms and weighs about
8-10 gms. They are situated at the back of the abdominal cavity at the hip
level. An ovary consists of the following:
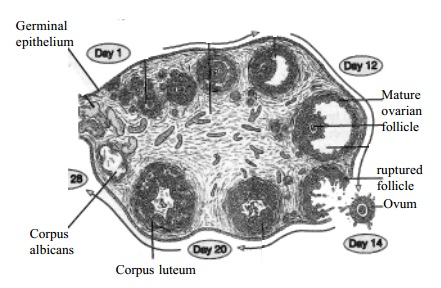
The Germinal
Epithelium: It is the outer part of the ovaries from which the primitive graafian
follicles develop. :
Tunica Albugina: This is made up of connective tissues found under the germinal epithelium.
Stroma: It is a connective tissue network continuous with Tunica albugina and containing involuntary muscle fibres. It supports
the ovarian tissues and carries blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves.
Graafian Follicles : These, are small islands of cells found at the peripheral part of the ovary. The female gametes called ova are
produced in the graafian follicles. When an ovum matures, the follicle in which
it develops bursts. The follicle usually takes 10-14 days. This process of
rupture of graafian follicle is called the 'ovulation'. Female gamete (ovum)
produced, during ovulation is secreted.
Corpus luteum: When the follicle ruptures Corpus luteum develops. In the absence of pregnancy, it persists upto 27th
day and degenerates on the 28th day. If pregnancy occurs it persists
to about 4 to 5 months. It secretes progesterone which is essential for the
maintenance of pregnancy.
Interstitial Cells: These are polyhedral cells found in between follicles. These cells secrete oestrogen.
Functions
Produce ova and expel one at approximately 28 days interval during the
reproductive life.
Secretes hormones (Oestrogen and progesterone). Oestrogen influences secondary sex characteristics and is
responsible for
the
changes in the accessory organs of reproduction. Progesterone prepares the uterus for the reception of the
fertilized ovum - implantation, the
development of the placenta, development of the mammary glands, and inducing
multiplication of the uterine muscle fibres.
Fallopian Tubes
Close to each ovary there is a narrow tube about 10 cm long with an open
end which looks like a fringe of petals. These tubes are called the fallopian
tubes. These are attached to the uterus at its upper outer angles.
Functions
These tubes act as ducts for the female gametes although they are not
connected to the ovaries. Fertilization of the male and female gametes normally
occurs in the tubes.
Uterus
Uterus is
a pear-shaped muscular organ the inside of which is hollow. It measures about
7.5 x 5 x 2.5 cms. consists of an upper portion called the body and a lower
portion called the cervix. The uterus is lined by a mucous membrane, known as endometrium.
Functions
The uterus
plays an important role in maintaining growth and development of the embryo.
The ovum is discharged from the ovary. It is then transported to the uterus
through the fallopian tubes. The fertilized ovum is embedded in the endometrium
of the uterus. Placenta is then formed from the embryonic and endometrium
tissues. This maintains the nutrition, respiration and excretion of embryo
until parturition.
Vagina
It is a muscular membranous tube situated between the rectum and the
urethra.
It is
estimated that, at birth, there are about 30000 ova or eggs in a female child.
No fresh ova are formed after birth but during the reproductive female life
that is commencing between 10 and 16 years of age and concluding between 45 and
55 years of age, these Ova develop within the follicles or sacs in which they
are embedded. They come progressively nearer to the surface of the ovary where
they mature and increase in size. About every 28 days one of these follicles
burst open from the ovum together with the fluid surrounding it, and is
expelled into the fallopian tubes; into uterus where it may or may not be
fertilized. If the ovum is fertilised by a male reproductive cell or
spermatozoa it then attaches itself to the uterine wall and develops there. If
the ovum does not become fertilised within a few days, it is cast off and the
process termed menstruation is initiated.
Related Topics