Chapter: Orthopaedics
Pelvic Fracture
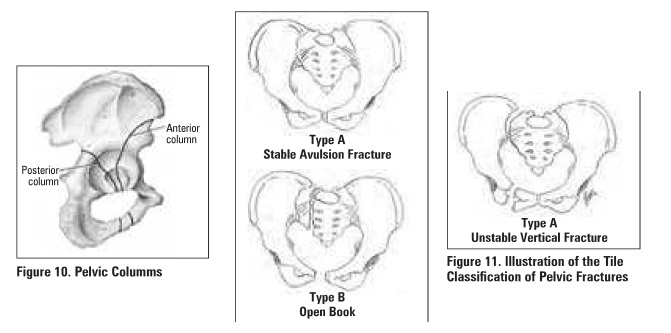
Pelvis
Pelvic Fracture
Mechanism
·
young: high energy trauma, either direct or by
force transmitted longitudinally through the femur
·
elderly: fall from standing height. low energy
trauma
Clinical Features
·
local swelling. tenderness
·
deformity oflower extremity
·
pelvic instability
Investigations
·
x-ray: AP pelvis, inlet and outlet for pelvic fracture
o
Judet films (obturator and iliac oblique) for
acetabular fracture
o
6 cardinal radiographic Unes of the acetabulum: ilioischial
line, iliopectlneal line, tear drop. roof, posterior rim. anterior rim
·
CT scan useful for evaluating posterior pelvic injury
and acetabular fracture
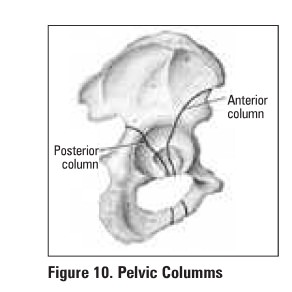
Table 4. Tile Classification of Pelvic
Fractures (see Figure 11)
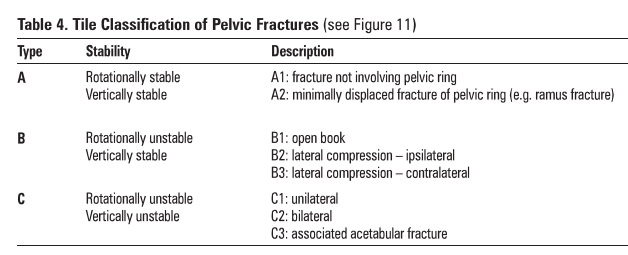
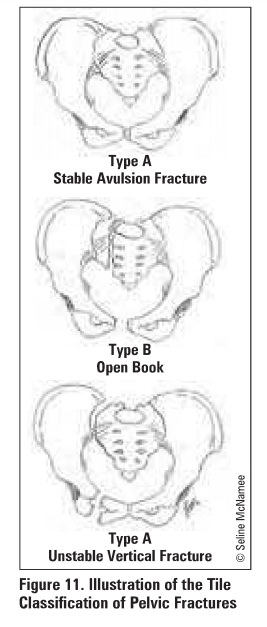
Type: Stability Description
A
Rotationally stable Vertically stable
A1:
fracture not involving pelvic ring
A2:
minimally displaced fracture of pelvic ring {e.g. ramus fracture)
B
Rotationally unstable Vertically stable
B1 : open
book
B2:
lateral compression- ipsilateral
B3:
lateral compression- contralateral
c
Rotationally unstable
C1:
unilateral Vertically unstable
C2:
bilateral
C3:
associated acetabular fracture
Treatment
·
ABCs
·
assess genitourinary injury (rectal exam, vaginal
exam, hematuria, blood at urethral meatus)
o
if involved, the fracture is considered an open
fracture
·
stable fractures - nonoperative treatment,
protected weight bearing
·
indications for operative treatment
o
unstable pelvic ring injury
o
disruption of anterior and posterior SI ligament
o
symphysis diastasis >2.5 cm
o
vertical instability of the posterior pelvis
Specific Complications (see
General Fracture Complications)
·
hemorrhage (life-threatening) - 1500-3000 ml blood
loss
·
injury to rectum or urogenital structures
·
obstetrical difficulties
·
persistent sacroiliac (SI) joint pain
·
post-traumatic arthritis of the hip with
acetabular fractures
·
high risk of DVT/PE
Related Topics